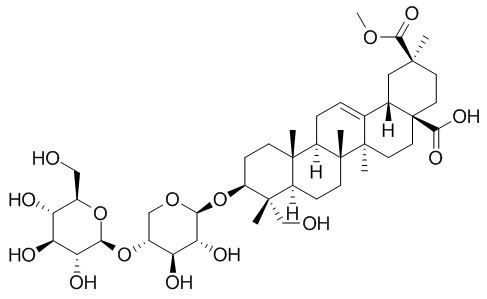
Esculentoside C
Esculentoside C exerts proinflammatory effects synergistically, it can induce inflammatory stimulation.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
JPC-Journal of Planar Chromatography2023, 36:179-190
Separations2021, 8(6),80.
Nutrients.2024, 16(20):3521.
Front Pharmacol.2022, 13:919230.
J Adv Res.2021, 35:245-257.
Plants (Basel).2020, 9(11):1422.
Acta Edulis Fungi2020, 27(02):63-76.
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal2023, 31(12):101829
Industrial Crops and Products2024, 219:119123
Oxid Med Cell Longev.2021, 2021:4883398.
Related and Featured Products
Pharm. Biol.,2016;54(1):98-104.
Rabbit conjunctivae edema and release of NO, TNF-α, and IL-1β from macrophages induced by fractions and esculentosides isolated from Phytolacca americana.[Pubmed:
25894210 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Petroleum ether (PE), CH2Cl2, n-BuOH, and water fractions were isolated from 70% ethanol extract of P. americana. The n-BuOH fraction was dissolved in 50% ethanol and precipitated by adding ethyl ether. The resultant supernatants and precipitates were referred to as SUPs and SEDs fractions, respectively. SUPs fraction was separated by column chromatography into four main stimulating esculentosides that were identified by HR-ESI/MS and NMR as Esculentoside A(EsA), Esculentoside B(EsB), Esculentoside C(EsC), and Esculentoside F(EsF. The irritating effects of esculentosides on rabbit conjunctivae (500 μg/eye) was observed by pathological examination and those on macrophages (5, 25, 50 and 100 μg/mL) were evaluated by detecting changes of NO, TNF-α, and IL-1β levels.n-BuOH, SUP fractions, and EsC induced severe conjunctival edema. The four esculentosides induced dose-dependent releases of proinflammatory mediators NO, TNF-α, and IL-1β from macrophages, and releasing amounts peaked after 2 h of treatment. EsC and EsF induced macrophages to release mediators most significantly. EsC (50 μg/mL) functioned more effectively than EsF did, and similarly n-BuOH and SUPs fractions functioned more effectively than the esculentoside mixture.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, the four esculentosides exerted proinflammatory effects synergistically.All extracted esculentosides, especially EsC, induced inflammatory stimulation. Phytolacca americana-induced irritation of the gastrointestinal tract may be associated with esculentosides such as EsC.
Isonemerosin
Catalog No: CFN95008
CAS No: 181524-79-8
Price: $268/20mg
3''-Galloylquercitrin
Catalog No: CFN95048
CAS No: 503446-90-0
Price: $368/5mg
5,7,2',4'-Tetrahydroxy-8,3'-di(gamma,gamma-dimethylallyl)-isoflavanone
Catalog No: CFN95084
CAS No: 141846-47-1
Price: $413/5mg
Cistantubuloside C1
Catalog No: CFN95121
CAS No: 620632-36-2
Price: $298/10mg
Pueroside B
Catalog No: CFN95141
CAS No: 100692-54-4
Price: $288/10mg
Isoeuphorbetin
Catalog No: CFN95207
CAS No: 50677-55-9
Price: $318/5mg
Andrographidine A
Catalog No: CFN95210
CAS No: 113963-37-4
Price: $318/10mg
2-Phenylethyl-beta-glucopyranoside
Catalog No: CFN95429
CAS No: 18997-54-1
Price: $318/10mg
Kidjolanin
Catalog No: CFN95503
CAS No: 38395-01-6
Price: $318/5mg
12beta-Acetoxy-3,7,11,15,23-pentaoxo-lanost-8,20-dien-26-oic acid
Catalog No: CFN95505
CAS No: 1309931-91-6
Price: $318/5mg