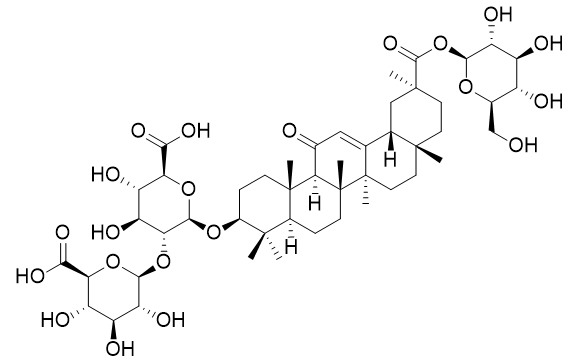
Licoricesaponin A3
Licoricesaponin A3 shows the cytotoxic activity against the human cancer cell lines MGC-803, SW620, and SMMC-7721 with IC50 > 100 μmol/L.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2023, 210:115463.
Agriculture2024, 14(12), 2301
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.2019, 1113:1-13
Auburn University2015, 1-58
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal2023, 31(12):101829
Int Immunopharmacol.2022, 106:108603.
VNU Journal of Science2023, No. 20.
Foods.2024, 13(19):3092.
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy.2015, 46(4):352-364
Environ Toxicol.2020, doi: 10.1002
Related and Featured Products
Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs, 2013, 44(12):1552-1557.
Chemical constituents of triterpenoid saponins from Glycyrrhiza uralensis.[Reference:
WebLink]
To study the chemical constituents from the roots and rhizomes of Glycyrrhiza uralensis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The compounds were separated and purified by solvent and chromatographic methods. Their structures were identified by spectroscopic techniques. Fourteen triterpenoid saponins isolated from 50% ethanol extract of the roots and rhizomes of G. uralensis were identified as uralsaponin C (1), uralsaponin D (2), Licoricesaponin A3 (3), uralsaponin F (4), 22β-acetoxyl-glycyrrizin (5), 24-hydroxyl-licorice-saponin E2 (6), licorice-saponin E2 (7), licorice-saponin G2 (8), 22β-acetoxyl-glyrrhaldehyde (9), 3β-O-[β-D-glucuronopyranosyl-(1→2) - β-D-glucuronopyranosyl]-glycyrretol (10), araboglycyrrhizin (11), licorice-saponin J2 (12), glycyrrhizin (13), and glycyrrhetic acid monoglucuronide (14). Compounds 1-14 showed the cytotoxic activity against the human cancer cell lines MGC-803, SW620, and SMMC-7721 with IC50 > 100 μmol/L. The aglycones of compounds 2, 6-8, and 13 displayed the inhibition on the growth of cancer cells with IC50 at 18.3-41.6 μmol/L.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compound 14 is a new natural product, and compound 11 is isolated from the plant for the first time; Compounds 1-14 show no cytotoxic activity against the human cancer cell lines MGC-803, SW620, and SMMC-7721, and the aglycones of compounds 2, 6-8, and 13 could significantly increase the cytotoxic activity after hydrolysis.
Arch Pharm Res. 2012 Nov;35(11):1945-52.
Comparative study of bioactive constituents in crude and processed Glycyrrhizae radix and their respective metabolic profiles in gastrointestinal tract in vitro by HPLC-DAD and HPLC-ESI/MS analyses.[Pubmed:
23212636]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two HPLC methods with diode array detection (HPLC-DAD) and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI/MS), respectively, were developed to investigate the differences of chemical constituents and their metabolism in gastrointestinal tract in vitro between two decoctions of crude and processed Glycyrrhizae radix. Total of eleven constituents (liquiritin apioside, liquiritin, licuraside, isoliquiritin, ononin, glycyrrhizin, liquiritigenin-7,4'-diglucoside, Licoricesaponin A3, 22β-acetoxylglycyrrhizic acid, licorice saponin G2, and yunganoside E2) were identified in the two decoctions, whereas lower contents of these constituents were usually found in the decoction of processed Glycyrrhizae Radix. [corrected] Furthermore, these constituents were metabolized into their respective aglycons in human intestinal bacteria juice, and the metabolism ratios were all higher in processed Glycyrrhizae Radix [corrected] decoction. No change was found in artificial gastric or intestinal juice.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study revealed that the processing can alter the contents of main constituents in crude G. radix and their metabolism in gastrointestinal tract, in which intestinal bacteria play an important role in the metabolism of licorice constituents.