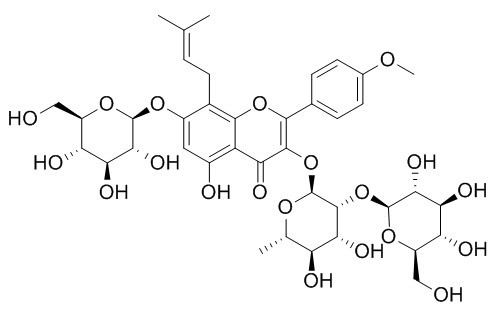
Epimedin A
Epimedin A,epimendin B, epimendin C, icariin and baohuoside are flavonoids, main active ingredient in Epimedium, have clear anti-osteoporosis effect, the accumulation of epimedins A, B, C, and icariin in a traditional medicinal plant could be suppressed by light stress.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Cell Death Discov.2023, 9(1):350.
Molecules.2021, 26(9):2765.
Biochem Pharmacol.2023, 211:115502.
South African J of Botany2020, 135:50-57
Life Sci.2021, 270:119074.
Biomed Pharmacother.2022, 146:112497.
FASEB J.2019, 33(2):2026-2036
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 181:117647.
J Pharm Pharmacol.2023, 75(9):1225-1236.
Hortic Res.2023, 10(9):uhad154.
Related and Featured Products
Acta Physiol Plant, 2013, 35(11):3271-5.
Light stress suppresses the accumulation of epimedins A, B, C, and icariin in Epimedium, a traditional medicinal plant.[Reference:
WebLink]
Epimedium is well-known in China and East Asia due to high content of flavonoid derivatives, including icariin, Epimedin A, Epimedin B, and epimedin C, hereafter designated as bioactive components, which have been extensively utilized to cure many diseases. So far, the molecular mechanism of the bioactive components biosynthesis remains unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the effect of light stress (24 h illumination) on the accumulation of bioactive components and the expression of flavonoid genes in Epimedium was investigated. Under light stress, the structural genes CHS1, CHI1, F3H, FLS, DFR1, DFR2, and ANS were remarkably up-regulated while CHS2 and F3′H were significantly down-regulated. For transcription factors, the expression of Epimedium MYB7 and TT8 were increased while Epimedium GL3, MYBF, and TTG1 expression were depressed. Additionally, the content of bioactive components was significantly decreased under light stress.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggested that the decrease of bioactive compounds may be attributed to transcripts of late genes (DFRs and ANS) increased to a higher level than that of early genes (FLS and CHS1).
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2014 Jun;49(6):932-7.
[Two-dimensional zebrafish model combined with hyphenated chromatographic techniques for evaluation anti-osteoporosis activity of epimendin A and its metabolite baohuoside I].[Pubmed:
25212043]
This article firstly established a new efficient method for screening anti-osteoporosis ingredients, which used two-dimensional zebrafish model combined with hyphenated chromatographic techniques to evaluate anti-osteoporosis activities of Epimedin A and its metabolite baohuoside I.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Adult zebrafish was used for metabolism of Epimedin A in 0.5% DMSO, and LC-MS was used for analysis of the metabolite, which was captured by HPLC, and prednisolone-induced osteoporosis model of zebrafish was used to evaluate the anti-osteoporotic activities of trace amounts of Epimedin A and baohuoside I. The results indicated that Epimedin A and baohuoside I can prevent prednisolone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish. The developed method in this paper enables the separation, enrichment and analysis of micro-amount metabolite of Epimedin A, and anti-osteoporosis activities in vivo of Epimedin A and baohuoside I was simple and efficient screening resorting to zebrafish osteoporosis mode.
CONCLUSIONS:
This paper would provide new ideas and methods for a rapid and early discovery of anti-osteoporosis activities of micro-ingredients and its metabolite of traditional Chinese medicine.
National Symposium on Chinese medicine and natural medicine. 2014.
Study on Different Factors Affecting the Bionic Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Icariin,Epimedin A,Epimendin B,Epimendin C and Eplmedium Flavonolds[Reference:
WebLink]
Flavonoids were the main active ingredient in Epimedium and mainly included icariin,Epimedin A,epimendin B,epimendin C and baohuoside.Modern pharmacological studies have shown that Epimedium flavone had clear anti-osteoporosis effect.
In order to obtain an improved absorption,transformation to secondary glycosides by intestinal enzymes and intestinal bacteria is necessary after the oral administration[1].However,intestinal enzymes and intestinal bacteria were unstable and could be affected by race,age,diet and medication[2].To screen effective and safe hydrolase in vitro and add it to epimedium flavone preparation could promote oral absorption of epimedium flavonoids,increase its bioavailability and improve its efficacy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study aims to screen effective and safe hydrolase,investgate different factors which affect the bionic enzymatic hydrolysis of epimedium flavonoids and optimize the reaction conditions for building a novel bionic enzymolysis drug delivery system.To simulate the environment in vivo,37 °C was set as the temperature and artificial intestinal juice and gastric juice was selected as the buffer solutions.Taking the conversion of epimedium flavonoids as index,the effects of the kinds of enzyme,the ratio of enzyme and substrate,substrate concentration,reaction time,pancreatin were investigated.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results show the conversion of epimedium flavonoids was highest and their enzymolysis products was accordant with the intestinal metabolites by using snailase in artificial intestinal juice.Moreover,the main flavonoids could be completely transformed into the secondary glycoside or aglycone during 2~6 h.
Chromatographia, 2014, 77(17-18):1223-34.
Identification of Metabolites of Epimedin A in Rats Using UPLC/Q–TOF–MS.[Reference:
WebLink]
Herba Epimedii ( Epimedium ) is a kind of tonic herb, widely used in China. Epimedin A is a major component of Herba Epimedii with bioactivities. Analysis of the metabolic profile in vivo plays a pivotal role in understanding how traditional Chinese medicine works. And the metabolites of Epimedin A might influence the effects of Herba Epimedii. Moreover, the metabolic routes of Epimedin A provide an important basis for safety evaluation. Until now, little has been known about the metabolism of Epimedin A.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The current study was designed to characterize the metabolic pathways of Epimedin A in vivo. The metabolites in rat plasma, bile, feces, and urine were identified by UPLC/Q–TOF–MS analysis. A total of 27 metabolites from Epimedin A were detected or tentatively identified. The major metabolic processes were hydrolysis, hydrogenation, hydroxylation, dehydrogenation, demethylation, and conjugation with glucuronic acid and different sugars. The present study revealed the metabolic pathways of Epimedin A in rat for the first time, and Epimedin A could undergo extensive phase I and phase II metabolism in rat.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings would provide an important basis for the further study and clinical application of Epimedin A. In addition, the results of this work have shown the feasibility of the UPLC/Q–TOF–MS approach for rapid and reliable characterization of metabolites.