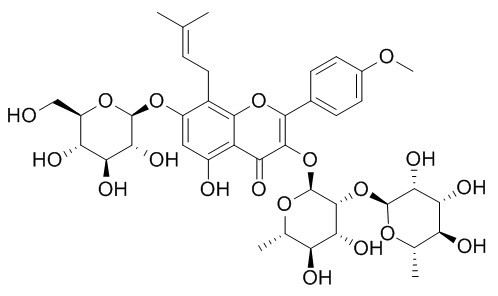
Epimedin C
Epimedin C and diphylloside A have antiinflammation effect, can reduce the swelling of the rats foot induced by egg. The accumulation of epimedinsA, B, C, and icariin in a traditional medicinal plant could be suppressed by light stress.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules 2021, 26(4),1092.
Pak J Pharm Sci.2019, 32(6):2879-2885
Foods.2022, 11(12):1708.
Food Chem.2024, 452:139555.
Food and Agriculture Org. Of the UN2019, 151-160
J Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis2022, 114631.
Rec. Nat. Prod.2024, 18:4,405-418.
Environ Toxicol.2021, 36(9):1848-1856.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2024, 17(3):341.
Front Pharmacol.2021, 12:690113.
Related and Featured Products
Acta Physiol Plant, 2013, 35(11):3271-5.
Light stress suppresses the accumulation of epimedins A, B, C, and icariin in Epimedium, a traditional medicinal plant.[Reference:
WebLink]
Epimedium is well-known in China and East Asia due to high content of flavonoid derivatives, including icariin, Epimedin A, epimedin B, and Epimedin C, hereafter designated as bioactive components, which have been extensively utilized to cure many diseases. So far, the molecular mechanism of the bioactive components biosynthesis remains unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the effect of light stress (24 h illumination) on the accumulation of bioactive components and the expression of flavonoid genes in Epimedium was investigated. Under light stress, the structural genes CHS1, CHI1, F3H, FLS, DFR1, DFR2, and ANS were remarkably up-regulated while CHS2 and F3′H were significantly down-regulated. For transcription factors, the expression of Epimedium MYB7 and TT8 were increased while Epimedium GL3, MYBF, and TTG1 expression were depressed. Additionally, the content of bioactive components was significantly decreased under light stress.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggested that the decrease of bioactive compounds may be attributed to transcripts of late genes (DFRs and ANS) increased to a higher level than that of early genes (FLS and CHS1).
Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2012(3):198-201.
Antiinflammatory Effect of Epimedin C and Diphylloside A of Epimedium Wushanense T.S.Ying.s.[Reference:
WebLink]
To study the antiinflammatory effect of Epimedin C and diphylloside A of Epimedium wushanense T.S.Ying.s on rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Effect of Epimedin C and diphylloside A on swelling foot of rats induced by egg was assayed,degree of swelling was calculated,and compared with distilled water or indomethacin. Swelling of the rats foot induced by egg was reduced by Epimedin C and diphylloside A,and there was significant difference,compared with distilled water;and there was significant difference of Epimedin C in high dosage,compared with indomethacin,but there was no significant difference of Epimedin C in low dosage.
CONCLUSIONS:
Epimedin C and diphylloside A have antiinflammation effect.
Biomed Chromatogr. 2014 Oct;28(10):1306-12.
Metabolite profiles of epimedin C in rat plasma and bile by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-TOF-MS.[Pubmed:
24853580]
Epimedin C is one of the major bioactive constituents of Herba Epimedii. In this study, the metabolite profiles of Epimedin C in rat plasma and bile were qualitatively investigated, and the possible metabolic pathways of Epimedin C were subsequently proposed.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After oral administration of Epimedin C at a single dose of 80 mg/kg, rat biological samples were collected and pretreated by protein precipitation. Then these pretreated samples were injected into an Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column and detected by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. In all, 12 metabolites were identified in the biosamples. Of these, eight, two from plasma and six from bile, are, to our knowledge, reported here for the first time.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicated that Epimedin C was metabolized via desugarization, dehydrogenation, hydrogenation, dehydroxylation, hydroxylation, demethylation and glucuronidation pathways in vivo. Thus, this study revealed the possible metabolite profiles of Epimedin C in rat plasma and bile.