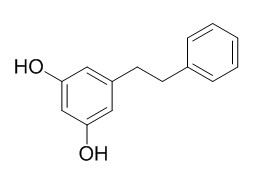
Dihydropinosylvin
Dihydropinosylvinin is an phytoalexin, it shows antifungal activity against Cladosporium cladosporioides, Botryodiplodia theobromae, Aspergillus niger and Penicillium schlerotgenum, it also exhibits strong antibacterial activity against Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli.Dihydropinosylvin and batatasin IV can inhibit the germination of seeds of and root elongation in young seedlings of Sorghum bicolor.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Oncol Rep.2016, 35(3):1356-64
Int J Vitam Nutr Res.2022, doi: 10.1024.
Separations2021, 8(1), 1.
Molecules. 2013, 18(11):14105-21
Acta Edulis Fungi2020, 27(02):63-76.
J.Korean Soci. Food Sci. Nutri.2024, 53(11):1166-1177
Chung Shan Medical University2020, US20200323790A1
Plant Foods Hum Nutr.2021, 76(4):472-477.
J Food Biochem.2019, 43(9):e12970
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC)2024, 158:54
Related and Featured Products
Phytochemistry, 1989, 28(10):2621-5.
Induction of pal activity and dihydrostilbene phytoalexins in Dioscorea alata and their plant growth inhibitory properties[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Dihydropinosylvin, batatasin IV, demethylbatatasin IV and batatasin III were found in the water yam ( Dioscorea alata ) which had been inoculated with Botryodiplodia theobromae or treated with mercuric chloride.
Following induction, transient increases were observed in the first three compounds and this was preceded by a transient increase in the activity of phenylalanine ammonia lyase but not tyrosine ammonia lyase activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
In mercuric chloride treated tubers an increase in polyphenol oxidase was also observed.
The dormancy inducing compounds Dihydropinosylvin and batatasin IV were also found to inhibit the germination of seeds of and root elongation in young seedlings of Sorghum bicolor . By comparison, demethylbatatasin IV was not inhibitory.
Phytochemistry, 1987, 26(12): 3187-9.
Dihydrostilbene phytoalexins from Dioscorea rotundata.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
2′,3-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybibenzyl (Batatasin IV), its demethyl derivative and 3,5-dihydroxybibenzyl (Dihydropinosylvin) were isolated only from flesh of Dioscorea rotundata infected with Botryodiplodia theobromae and may therefore be considered phytoalexins. These compounds were found to be antifungal using bioassays with Cladosporium cladosporioides, Botryodiplodia theobromae, Aspergillus niger and Penicillium schlerotgenum .
CONCLUSIONS:
Dihydro-pinosylvinin also exhibited strong antibacterial activity against Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli .
Phytochemistry. 2004 Jan;65(1):99-106.
Dihydrophenanthrenes and other antifungal stilbenoids from Stemona cf. pierrei.[Pubmed:
14697275]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three new dihydrophenanthrenes, stemanthrenes A-C, along with the new dihydrostilbene stilbostemin G were isolated and identified from the underground parts of Stemona cf. pierrei together with the known pinosylvin, 4'-methylpinosylvin, Dihydropinosylvin, stilbostemins B, D, and E as well as the pyrrolo[1,2-a]azepine alkaloids protostemonine and stemonine.
The structures of all new stilbenoids, elucidated by NMR analyses, showed a common substitution pattern for aromatic ring A and characteristic C-methylations for ring B. The trivial name racemosol, previously reported for S. collinsae, was renamed to stemanthrene D due to its priority for another compound. Bioautographic tests on TLC plates with Cladosporium herbarum displayed high antifungal activity for compounds with an unsubstituted aromatic ring A, e.g. pinosylvin, but only weak effects for the higher substituted stilbostemin G and stemanthrenes A-C.
CONCLUSIONS:
Similar results were obtained by germ tube inhibition of five microfungi using 2-fold serial broth dilutions determined by a microplate reader. Because of weak inhibition and chemical instability of stemanthrenes, no EC(50) and EC(90) values could be calculated.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Jan;38(2):204-7.
[Chemical constitunents of seeds of Oroxylum indicum].[Pubmed:
23672042]
To study the chemical constituents in the seeds of Oroxylum indicum.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Twenty compounds were isolated and purified by silica gel, and Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography, and their structures were determined by spectroscopic analysis including NMR and MS. Twenty compounds were isolated and identified as oroxin A (1), oroxin B (2), chrysin (3), baicalein (4), quercetin (5), apigenin (6), kaempferol (7), quercetin-3-O-ara-binopyranoside (8), lupeol C9), lup-20 (29)-ene-2alpha,3beta-diol (10), pinosylvin (11), Dihydropinosylvin (12), cholest-5-ene-3, 7-diol (13), rengyol (14), isorengyol (15), zarzissine (16), (E) -pinosylvin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (17), adenosine (18), sitosterol (19) and daucosterol (20).
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 11-13 and 15-18 were obtained from the genus Oroxylum for the first time, and except compound 18, the remaining 6 compounds were obtained from the family Bignoniaceae for the first time.