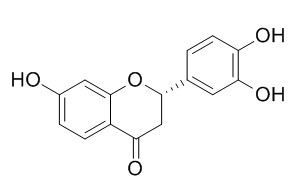
Butin
Butin has antioxidant activity, can protect cells against H2O2-induced apoptosis, oxidative DNA damage and oxidative mitochondrial dysfunction; it attenuates oxidative stress by activating Nrf2-mediated Mn SOD induction via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Butin against H2O2-induced apoptosis were exerted via blockade of membrane potential depolarization, inhibition of the JNK pathway and mitochondria-involved caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway, enhancing the expression of phosphorylated Akt (active form of Akt), a regulator of OGG1.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Metabolites.2020, 11(1):E11.
Nutraceutical Research . 2021, 19(1),p90-105.
Food Funct.2024, 15(4):1852-1866.
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 24(3):2102.
Molecules.2019, 24(20):3755
J Nat Med.2018, 72(3):734-744
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 24(22):16465.
Pest Manag Sci.2019, 75(9):2530-2541
Indian J. of Experimental Bio.2020, 9(58).
FARMACIA2023, Vol.71,3.
Related and Featured Products
J Cell Biochem. 2012 Jun;113(6):1987-97.
The cytoprotective effect of butin against oxidative stress is mediated by the up-regulation of manganese superoxide dismutase expression through a PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent pathway.[Pubmed:
22253095]
Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone), a flavonoid with antioxidant activity, was recently reported to protect cells against H2O2-induced apoptosis, oxidative DNA damage and oxidative mitochondrial dysfunction. The objective of the present study was to elucidate the mechanism by which Butin protects mitochondria.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antioxidant function of manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn SOD) is important in preventing oxidative stress. While exposure to H2O2 reduced the expression of Mn SOD in Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79-4), the addition of Butin restored Mn SOD expression at both the mRNA and protein levels, resulting in increased Mn SOD activity. The transcription factor NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) regulates Mn SOD gene expression by binding to the antioxidant responsive element (ARE). Butin enhanced the nuclear translocation and ARE-binding activity of Nrf2, which was decreased by H2O2. The siRNA-mediated knockdown of Nrf2 attenuated Butin-induced Mn SOD expression and activity. Further, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB, Akt) contributed to the ARE-driven Mn SOD expression. Butin activated PI3K/Akt and exposure to either LY294002 (a PI3K inhibitor), Akt inhibitor IV (an Akt-specific inhibitor), or Akt siRNA suppressed the Butin-induced activation of Nrf2, resulting in decreased Mn SOD expression and activity. Finally, the cytoprotective effect of Butin against H2O2-induced cell damage was suppressed by the siRNA-mediated knockdown of Mn SOD.
CONCLUSIONS:
These studies demonstrate that Butin attenuates oxidative stress by activating Nrf2-mediated Mn SOD induction via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2010 Mar;48(3):922-7.
Butin reduces oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction via scavenging of reactive oxygen species.[Pubmed:
20060874]
This study investigated the cytoprotective effect of Butin, a flavonoid, on hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2))-induced mitochondrial dysfunction.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Electron spin resonance (ESR) spectrometry revealed Butin's significant scavenging effects on superoxide radicals and hydroxyl radicals. When H(2)O(2) was used to induce an increase in mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) in Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79-4) cells, Butin treatment decreased high level of ROS. Butin also attenuated intracellular Ca(2+) levels that have been induced by H(2)O(2). Furthermore, Butin recovered ATP levels and succinate dehydrogenase activity that had been decreased by H(2)O(2) treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
We conclude these results suggest Butin decreased mitochondrial ROS accumulation, balanced intracellular Ca(2+) levels, and improved mitochondrial energy production, thus recovering mitochondrial function.
Chem Biol Interact. 2009 Oct 30;181(3):338-42.
Butin decreases oxidative stress-induced 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine levels via activation of oxoguanine glycosylase 1.[Pubmed:
19631197]
In response to oxidative DNA base damage, oxoguanine glycosylase 1 (OGG1), in a base-excision repair (BER) pathway in mammals, plays a vital role in the repair of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), which is a reliable marker of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced DNA base modification and contributes to the pathologic process of cancer.Recently, we have shown that Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone) protects cells against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced damage of cellular components including DNA.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we examined the possible protective effect of Butin on oxidative stress-induced DNA base modification, especially 8-OHdG. Hydrogen peroxide significantly increased the level of 8-OHdG, which was detected by 8-OHdG ELISA and confocal microscopy, but Butin decreased this level. Suppression of 8-OHdG formation by Butin was related to the enhanced mRNA and protein expression of OGG1, which was detected by RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. Butin also increased the transcriptional activity of OGG1, which was suppressed by H2O2 treatment; this transcriptional activity was detected by OGG1 promoter luciferase assay.
Butin enhanced the expression of phosphorylated Akt (active form of Akt), a regulator of OGG1, which was decreased by H2O2 treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
A PI3K-specific inhibitor, LY294002, abolished the phosphorylated Akt and OGG1 expressions induced by Butin, suggesting that OGG1 induction by Butin involves the PI3K/Akt pathway.
Sci Rep . 2017 Jan 27;7:41491.
Protective effect of butin against ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury in diabetic mice: involvement of the AMPK/GSK-3β/Nrf2 signaling pathway[Pubmed:
28128361]
Abstract
Hyperglycemia-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation contributes to development of diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM). This study was designed to determine the effect of an antioxidant Butin (BUT) on ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury in diabetic mice. Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (MI/R) was induced in C57/BL6J diabetes mice. Infarct size and cardiac function were detected. For in vitro study, H9c2 cells were used. To clarify the mechanisms, proteases inhibitors or siRNA were used. Proteins levels were investigated by Western blotting. In diabetes MI/R model, BUT significantly alleviated myocardial infarction and improved heart function, together with prevented diabetes-induced cardiac oxidative damage. The expression of Nrf2, AMPK, AKT and GSK-3β were significantly increased by BUT. Furthermore, in cultured H9c2 cardiac cells silencing Nrf2 gene with its siRNA abolished the BUT's prevention of I/R-induced myocardial injury. Inhibition of AMPK and AKT signaling by relative inhibitor or specific siRNA decreased the level of BUT-induced Nrf2 expression, and diminished the protective effects of BUT. The interplay relationship between GSK-3β and Nrf2 was also verified with relative overexpression and inhibitors. Our findings indicated that BUT protected against I/R-induced ROS-mediated apoptosis by upregulating the AMPK/Akt/GSK-3β pathway, which further activated Nrf2-regulated antioxidant enzymes in diabetic cardiomyocytes exposed to I/R.
Transl Neurosci . 2018 May 8;9:7-12.
Butin Attenuates Brain Edema in a Rat Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage by Anti Inflammatory Pathway[Pubmed:
29755784]
Abstract
Background: This study evaluates the effect of Butin against brain edema in intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH).
Methodology: ICH was induced by injecting bacterial collagenase in the brain and all the animals were separated into four groups such as control group, ICH group treated with vehicle, Butin 25 and 50 mg/kg group receives Butin (25 and 50 mg/kg, i.p.)60 min after the induction of ICH in all animals. One day after neurological score, hemorrhagic injury and expressions of protein responsible for apoptosis and inflammatory cytokines were assessed in the brain tissue of ICH rats.
Result: Neurological scoring significantly increased and hemorrhagic lesion volume decreased in Butin treated group of rats compared to ICH group. However, treatment with Butin significantly decreases the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 and protein expression of Cleaved caspase-3 than ICH group in dose dependent manner. Level of inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interlukin-6 (IL-6) in the brain tissues were significantly decreased in the Butin treated group than ICH group. In addition Butin attenuates the altered signaling pathway of NF-κB in the brain tissues of ICH rats.
Conclusion: Our study concludes that Butin attenuates the altered behavior and neuronal condition in ICH rats by reducing apoptosis and inflammatory response.
Keywords: Brain edema; Butin; Cytokines; Inflammation; Intracerebral hemorrhage.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Apr 1;24(7):1730-3.
Inhibitory effect of Rhus verniciflua Stokes extract on human aromatase activity; butin is its major bioactive component.[Pubmed:
24630560]
Rhus verniciflua Stokes has been used as a traditional herbal medicine in Asia. In this study, the effect of R. verniciflua extract on human aromatase (cytochrome P450 19, CYP19) activity was investigated to elucidate the mechanism for the effect of R. verniciflua extract on androgen hormone levels.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Androstenedione was used as a substrate and incubated with R. verniciflua extract in cDNA-expressed CYP19 supersomes in the presence of NADPH, and estrone formation was measured using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. R. verniciflua extract was assessed at concentrations of 10-1000 μg/mL. The resulting data showed that R. verniciflua extract inhibited CYP19-mediated estrone formation in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 136 μg/mL. Subsequently, polyphenolic compounds from R. verniciflua extract were tested to identify the ingredients responsible for the aromatase inhibitory effects by R. verniciflua extract. As a result, Butin showed aromatase inhibitory effect in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 9.6 μM, whereas the inhibition by other compounds was negligible.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that R. verniciflua extract could modulate androgen hormone levels via the inhibition of CYP19 activity and Butin is a major ingredient responsible for this activity.
Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(6):3871-87.
Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone) reduces oxidative stress-induced cell death via inhibition of the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway.[Pubmed:
21747713]
Recently, we demonstrated that Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone) protected cells against hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2))-induced apoptosis by: (1) scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), activating antioxidant enzymes such superoxide dismutase and catalase; (2) decreasing oxidative stress-induced 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine levels via activation of oxoguanine glycosylase 1, and (3), reducing oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. The objective of this study was to determine the cytoprotective effects of Butin on oxidative stress-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis, and possible mechanisms involved.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Butin significantly reduced H(2)O(2)-induced loss of mitochondrial membrane potential as determined by confocal image analysis and flow cytometry, alterations in Bcl-2 family proteins such as decrease in Bcl-2 expression and increase in Bax and phospho Bcl-2 expression, release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into the cytosol and activation of caspases 9 and 3. Furthermore, the anti-apoptotic effect of Butin was exerted via inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-4, c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) and activator protein-1 cascades induced by H(2)O(2) treatment. Finally, Butin exhibited protective effects against H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis, as demonstrated by decreased apoptotic bodies, sub-G(1) hypodiploid cells and DNA fragmentation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the protective effects of Butin against H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis were exerted via blockade of membrane potential depolarization, inhibition of the JNK pathway and mitochondria-involved caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway.