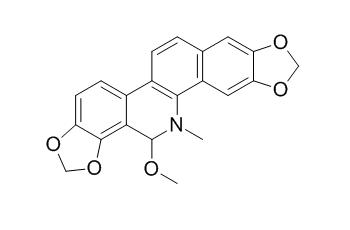
6-Methoxydihydrosanguinarine
6-Methoxydihydrosanguinarine may have anti-inflammatory effects via the inhibition of NO and IL-6 expression through the down-regulation of MAP kinase (ERK1/2, p38) phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 cells. It has antibacterial activity against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) ranging from1.9 to 3.9 microg/ml. 6-Methoxydihydrosanguinarine shows a dose-dependent effect at 1-10 microM on causing apoptotic cell death in HT29 colon carcinoma cells (IC50 = 5.0+/-0.2 microM). It also shows strong nematocidal activities, however, it is highly cytotoxic; thus, the prospect of its direct application is low.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Pharmacia2022, 69(3): 883-890.
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 978:176800.
J Lipid Res.2024, 65(10):100640.
Org Biomol Chem.2017, 15(31):6483-6492
Pharmacol Rep.2019, 71(2):289-298
Journal of Molecular Liquids2021, 334:116014.
Journal of Functional Foods2022, 96: 105216.
American Association for Anatomy2020, doi: 10.1002.
Journal of Food Composition and Analysis2021, 100:103905.
J Nat Med.2020, 74(3):550-560.
Related and Featured Products
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012 Jul;16 Suppl 3:121-5.
Anti-inflammatory effects of Hylomecon hylomeconoides in RAW 264.7 cells.[Pubmed:
22957426]
Papaveraceae serve as a rich source of various alkaloids which have anti-inflammatory effect.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we investigated the effect of Hylomecon hylomeconoides ethanol extract (HHE) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced NO and interleukin-6 (IL-6) production in RAW 264.7 cells.
HHE inhibited LPS-induced NO and IL-6 production. Moreover, HHE suppressed the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, major constituents, dihydrosanguinarine and 6-Methoxydihydrosanguinarine, of the chloroform-soluble extract were analyzed.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the results of this study indicate that the anti-inflammatory effects of HHE may occur via the inhibition of NO and IL-6 expression through the down-regulation of MAP kinase (ERK1/2, p38) phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 cells.
Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2010 Apr;160(8):2467-74.
Antibacterial activity of Hylomecon hylomeconoides against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.[Pubmed:
19578993 ]
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is serious clinical urgent problems worldwide.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the antibacterial activity of Hylomecon hylomeconoides was investigated. The EtOH extract and its fraction (n-hexane, CH(2)Cl(2), EtOAc, and H(2)O) were investigated against MRSA. The most active extract (CH(2)Cl(2)) led to the isolation of 6-Methoxydihydrosanguinarine (6-MS), 6-acetonylhydrosanguinarine, and dihydrosanguinarine.
These compounds were very active against MRSA strains with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) ranging from 1.95 to 250 microg/ml. Our study did however focus on 6-MS as it appeared to be the most active with MICs in the range of 1.9 to 3.9 microg/ml.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results encourage us to think that 6-MS can be used as a natural antibacterial agent.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2002 Dec;25(12):1651-4.
Inhibitory effect of isoquinoline alkaloids on movement of second-stage larvae of Toxocara canis.[Pubmed:
12499659]
To find new anthelmintics against parasites living in host tissues, we used an in vitro assay to screen isoquinoline alkaloids for nematocidal activity on the larva of dog roundworm, Toxocara canis. To evaluate the efficacy of anthelmintics in vitro, Tsuda et al. previously introduced the concept of Relative Mobility (RM) of Toxocara larvae.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After improvement of the assay system using image data processing, we generated a new index, RM(50), the concentration at which RM=50%. However, except for pyrantel, the RM(50) of most existing anthelmintics could not be calculated because of low activity. Of the isoquinoline alkaloids tested, emetine, sanguinarine, 6-Methoxydihydrosanguinarine (6-MS), chelerythrine and berberine showed strong nematocidal activities. However, these compounds were highly cytotoxic; thus, the prospect of their direct application is low. We then tested the cytotoxicity (IC(50)) of other isoquinoline alkaloids in HL60 tissue-culture cells.
We continued our search for new anthelmintics by examining in detail the relationship between RM(50) and IC(50).
CONCLUSIONS:
We determined that an ideal target compound would exhibit a low RM(50)/IC(50) ratio. Allocryptopine, dehydrocorydaline and papaverine were identified as potentially effective anthelmintics.
Arch Pharm Res. 2004 Dec;27(12):1253-7.
Apoptosis inducing effects of 6-methoxydihydrosanguinarine in HT29 colon carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:
15646800]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
6-Methoxydihydrosanguinarine (6ME), a benzophenanthridine alkaloid derived from the methanol extracts of Hylomecon hylomeconoides, showed a dose-dependent effect at 1-10 microM on causing apoptotic cell death in HT29 colon carcinoma cells (IC50 = 5.0+/-0.2 microM). Treatment of HT-29 cells with 6ME resulted in the formation of internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Treatment of the cells with 6ME caused activation of caspase-3, -8 and 9 protease and subsequent proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase. 6ME increased the expression of p53 and Bax and decreased the expression of Bid.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that p53 and proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins might participate in the antiproliferative activity of 6ME in HT29 cells.