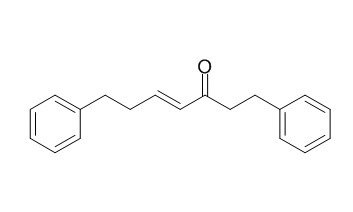
1,7-Diphenyl-4-hepten-3-one
1,7-Diphenyl-4-hepten-3-one has feeding deterrent activities against Tribolium castaneum.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
National Academy Science Letters2023, s40009.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021, 14(10):986.
Molecules.2021, 26(16):4722.
Biomol Ther (Seoul).2020, 28(6):542-548.
Pharmacol Res.2022, 182:106346.
Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci.2024, 12(5):986-993.
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 24(8):7442.
Cell Prolif.2021, 54(8):e13083.
Curr Res Virol Sci.2022, 3:100019.
Int J Mol Med.2016, 37(2):501-8
Related and Featured Products
Molecules. 2017 Apr 18;22(4).
Chemical Constituents of Supercritical Extracts from Alpinia officinarum and the Feeding Deterrent Activity against Tribolium castaneum.[Pubmed:
28420198 ]
Alpinia officinarum has been confirmed to possess bioactivities against some pests.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, a sample was obtained from A. officinarum rhizomes by supercritical fluid CO₂ extraction (SFE). According to GC-MS analysis, the main chemical components for SFE-sample included benzylacetone (26.77%), 1,7-diphenyl-5-hydroxy-3-heptanone (17.78%), guaiacylacetone (10.03%) and benzenepropanal (7.42%). The essential oil of A. officinarum rhizomes (LD50 = 20.71 μg/adult) exhibited more contact toxicity than SFE extract (LD50 = 82.72 μg/adult) against Tribolium castaneum. From SFE extracts, one new compound, 1-phenyl-4-(16,17-dimethyl-9,13-octadiene)-5-isopentenyl-7-(4"-methoxyl-3"-hydroxyl-phenyl)-3-heptanone (3), together with five known compounds identified as 5-hydroxy-1,7-diphenyl-3-heptanone (1), 1,7-Diphenyl-4-hepten-3-one (2), galangin (4), galangin-3-methyl ether (5) and pinocembrin (6), were isolated and their feeding deterrent activities against T. castaneum adults were assessed. It was found that compounds 1-6 had feeding deterrent activities against T. castaneum with feeding deterrent indices of 18.21%, 18.94%, 19.79%, 26.99%, 20.34%, and 35.81%, respectively, at the concentration of 1500 ppm.
CONCLUSIONS:
Hence, the essential oil and SFE extracts/compounds of A. officinarum rhizomes represent promising alternatives in the control of T. castaneum adults.