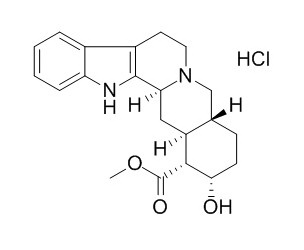
Yohimbine Hydrochloride
Yohimbine hydrochloride is an alpha 2-adrenoreceptor antagonist, blocking the pre- and postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenoreceptors and causing an increased release of noradrenaline and dopamine.It is an antagonist to xylazine hydrochloride-ketamine hydrochloride immobilization of white-tailed deer. Yohimbine has been used as a mydriatic and in the treatment of impotence. It is also alleged to be an aphrodisiac.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Brain Res Bull.2024, 218:111103.
LWT2024, v208:116677
ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci.2024, 7(2):395-405.
Processes2023, 11(2), 385¡£
Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2018, 505(4):1148-1153
Planta Med.2018, 84(6-07):465-474
Heliyon2022, 8(2):e08866.
Dental Journal2024, 57(4): 254-258
Herbal Formula Science2024, 32(3):203-221
BMC Complement Med Ther.2023, 23(1):264.
Related and Featured Products
Am. J.Vet. Res., 1986, 47(4):949-52.
Effect of yohimbine hydrochloride on serum prolactin concentration in the rat: possible antagonist for fescue toxicosis.[Pubmed:
3963600]
Yohimbine Hydrochloride is an indole alkaloid which blocks alpha 2-adrenergic and dopamine receptors and stimulates serotonergic receptors. Yohimbine was selected for testing as a possible antagonist in fescue toxicosis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Reduced body weight gains in cattle with chronic fescue toxicosis may be due to ergot alkaloids produced by fungi which infect the fescue grass. Ergot alkaloids stimulate dopamine receptors, antagonize serotonin, and lower serum prolactin concentrations. It was hypothesized that yohimbine may reverse or counteract the effects of the toxic fescue. Investigation was made of the treatment effects of multiple doses of yohimbine given in rats by intraperitoneal and oral routes. Given intraperitoneally once a day for 8 days, Yohimbine Hydrochloride increased serum prolactin concentrations. When given orally in feed for 7 days, the drug decreased the serum prolactin concentration. The effects of yohimbine on prolactin concentrations were dependent on the dosages and routes of administration.
CONCLUSIONS:
The inability of yohimbine, when given orally, to increase serum prolactin levels decreased its potential usefulness for prolonged treatment of fescue toxicosis.
Psychother Psychosom. 2012;81(1):29-37.
Does yohimbine hydrochloride facilitate fear extinction in virtual reality treatment of fear of flying? A randomized placebo-controlled trial.[Pubmed:
22116378]
Research suggests that Yohimbine Hydrochloride (YOH), a noradrenaline agonist, can facilitate fear extinction. It is thought that the mechanism of enhanced emotional memory is stimulated through elevated noradrenaline levels. This randomized placebo-controlled trial examined the potential exposure-enhancing effects of YOH in a clinical sample of participants meeting DSM-IV criteria for a specific phobia (fear of flying).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Sixty-seven participants with fear of flying were randomized to 4 sessions of virtual reality exposure therapy (VRET) combined with YOH (10 mg), or 4 sessions of VRET combined with a placebo. Treatment consisted of 4 weekly 1-hour exposure sessions consisting of two 25-minute virtual flights. At pre- and post- treatment, fear of flying was assessed. The YOH or placebo capsules were administered 1 h prior to exposures. The manipulation of the noradrenaline activity was confirmed by salivary α-amylase (sAA) samples taken pre-, during and post-exposure.
Forty-eight participants completed treatment. Manipulation of noradrenaline levels with YOH was successful, with significantly higher levels of sAA in the YOH group when entering exposure. Results showed that both groups improved significantly from pre- to post-treatment with respect to anxiety reduction. However, although the manipulation of noradrenaline activity was successful, there was no evidence that YOH enhanced outcome.
CONCLUSIONS:
Participants improved significantly on anxiety measures independently of drug condition, after 4 sessions of VRET. These data do not support the initial findings of exposure-enhancing effects of YOH in this dosage in clinical populations.
J Wildl Dis. 1986 Jul;22(3):403-6.
Effect of caffeine sodium benzoate, ketamine hydrochloride, and yohimbine hydrochloride on xylazine hydrochloride-induced anorexia in white-tailed deer.[Pubmed:
3735587]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Fifteen male white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) were administered xylazine hydrochloride (1 mg/kg BW i.m.), xylazine hydrochloride (1 mg/kg i.m.) followed by caffeine sodium benzoate (10 mg/kg i.m.), xylazine hydrochloride (0.5 mg/kg i.m.) and ketamine hydrochloride (4.5 mg/kg i.m.), and xylazine hydrochloride (1 mg/kg i.m.) followed by Yohimbine Hydrochloride (0.125 mg/kg i.m.), in a Latin Square design. Mean dry matter intake (DMI) for 4 days pre-treatment was compared to each of 4 days post-treatment. A significant (P less than 0.01) decrease in DMI was found only on the first day following treatment for each of the four drug combinations. The percent decreases in DMI on the first 24-hr period after immobilization were: xylazine hydrochloride 47%, xylazine hydrochloride/caffeine sodium benzoate 36%, xylazine hydrochloride/Yohimbine Hydrochloride 36%, and xylazine hydrochloride/ketamine hydrochloride 31%. The xylazine hydrochloride/ketamine hydrochloride combination was found to be insufficient to adequately sedate the deer.
CONCLUSIONS:
The use of caffeine or Yohimbine Hydrochloride is recommended to reduce recumbency time, but offers no improvement in xylazine hydrochloride-induced anorexia.
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2011 Nov;82(1):270-8.
Molecular structure, vibrational spectra and HOMO, LUMO analysis of yohimbine hydrochloride by density functional theory and ab initio Hartree-Fock calculations.[Pubmed:
21856216]
Yohimbine Hydrochloride (YHCl) is an aphrodisiac and promoted for erectile dysfunction, weight loss and depression. The optimized geometry, total energy, potential energy surface and vibrational wavenumbers of Yohimbine Hydrochloride have been determined using ab initio, Hartree-Fock (HF) and density functional theory (DFT/B3LYP) method with 6-311++G(d,p) basis set. A complete vibrational assignment is provided for the observed Raman and IR spectra of Yohimbine Hydrochloride. The UV absorption spectrum was examined in ethanol solvent and compared with the calculated one in gas phase as well as in solvent environment (polarizable continuum model, PCM) using TD-DFT/6-31G basis set. These methods are proposed as a tool to be applied in the structural characterization of Yohimbine Hydrochloride. The calculated highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) with frontier orbital gap are presented.