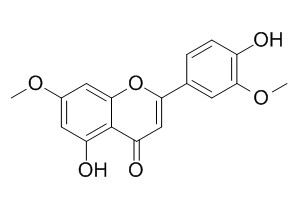
Velutin
Velutin has strong anti-inflammatory activity, it can effectively inhibit the expression of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 in low micromole levels by inhibiting NF-κB activation and p38 and JNK phosphorylation. Velutin controls HIF-1α activity during PgLPS-activated osteoclastogenesis probably through modulation of the NF-κB pathway, perhaps it could be used therapeutically to prevent bone loss seen in periodontitis.Velutin can induce apoptosis in tumor cells.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Oxid Med Cell Longev2019, 9056845:13
Eur J Pharmacol.2023, 960:176121.
Metabolites.2023, 13(6):689.
Plants (Basel).2023, 12(22):3877.
Front Pharmacol.2019, 10:1355
J Agric Food Chem.2016, 64(35):6783-90
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2019, 172:268-277
J Ethnopharmacol.2023, 313:116534.
J Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis2022, 114631.
Appl. Sci.2024, 14(12), 5280.
Related and Featured Products
J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Sep;23(9):1184-91.
The açaí flavonoid velutin is a potent anti-inflammatory agent: blockade of LPS-mediated TNF-α and IL-6 production through inhibiting NF-κB activation and MAPK pathway.[Pubmed:
22137267]
Recent studies have shown that some flavonoids are modulators of proinflammatory cytokine production.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, Velutin, a unique flavone isolated from the pulp of açaí fruit (Euterpe oleracea Mart.), was examined for its effects in reducing lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6 production in RAW 264.7 peripheral macrophages and mice peritoneal macrophages. Three other structurally similar and well-studied flavones, luteolin, apigenin and chrysoeriol, were included as controls and for comparative purposes. Velutin exhibited the greatest potency among all flavones in reducing TNF-α and IL-6 production. Velutin also showed the strongest inhibitory effect in nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation (as assessed by secreted alkaline phosphatase reporter assay) and exhibited the greatest effects in blocking the degradation of inhibitor of NF-κB as well as in inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 and JNK phosphorylation; all of these are important signaling pathways involved in production of TNF-α and IL-6.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present study led to the discovery of a strong anti-inflammatory flavone, Velutin. This compound effectively inhibited the expression of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 in low micromole levels by inhibiting NF-κB activation and p38 and JNK phosphorylation.
Toxicol In Vitro. 2010 Jun;24(4):1250-7.
Differential abilities of the mushroom ribosome-inactivating proteins hypsin and velutin to perturb normal development of cultured mouse embryos.[Pubmed:
20149862]
The teratogenicity of two fungal ribosome-inactivating proteins, hypsin from Hypsizigus mamoreus and Velutin from Flammulina velutipes, was examined in this investigation using microinjection and postimplantation whole-embryo culture.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The results demonstrated that hypsin induced abnormal embryonic development at 2.5 microM during the organogenesis period from E8.5 to E9.5. As its dosage increased, there was an increase in the total number of abnormal embryos, a drop in the final somite number, and a rise of abnormal structures. Structural abnormalities were detected: open cranial neural tube, abnormal branchial arches, absence of forelimb buds and twisted body axis. The otic and optic placodes were, however, less affected.
CONCLUSIONS:
Histological study of the abnormal embryos revealed a correlation of increased cell death with abnormal structures, suggesting that induction of cell death by hypsin may account for its teratogenicity. In contrast, Velutin did not exert any adverse influence on mouse development.
Yoo Y C, Lee K B. Korea Society of Laboratory Animals, 2003,6: 101-101.
Velutin and betulinic acid isolated from Korean mistletoe induce apoptosis in tumor cells[Reference:
WebLink]
Velutin and betulinic acid isolated from Korean mistletoe induce apoptosis in tumor cells.
Faseb Journal, 2011, 25(1):772.
Velutin reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine TNFα and IL-6 production by inhibiting NF-κB activation.[Reference:
WebLink]
Five flavonoids, (2S,3S)-dihyrokaempferol 3-O-b-D-glucoside (1) and its isomer (2R,3R)-dihydrokaempferol 3-O-b-D-glucoside (2) , isovitexin (3), Velutin (4) and 5,40-dihydroxy-7,30,50-trimethoxyflavone (5), were isolated from acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) pulp.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structures of these compounds were elucidated based upon spectroscopic and chemical analyses. To our knowledge, compounds 1, 2, 4 and 5 were identified from acai pulp for the first time. The in vitro antioxidant activities of these compounds were evaluated by the oxygen radial absorbance capacity (ORAC) assay. The ORAC values varied distinctly (4458.0–22404.5 lmol Trolox equivalent (TE)/g) from 5,40-dihydroxy-7,30,50-trimethoxyflavone (5) to isovitexin (3) and were affected by the numbers/positions of hydroxyl groups, substitute groups, as well as stereo configuration. The anti-inflammatory effects of these compounds were screened by the secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter assay, which is designed to measure NF-jB activation. Velutin (4) was found to dose-dependently inhibit SEAP secretion in RAW-blue cells induced by LPS, with an IC50 value of 2.0 lM. Velutin (4) also inhibited SEAP secretion induced by oxidised LDL, indicating potential athero-protective effects.
Aadr Meeting & Exhibition. 2014.
Velutin Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis by Suppressing HIF-1α and NF-κB pathways.[Reference:
WebLink]
Periodontitis is a biofilm-related inflammatory disease that involves progressive loss of alveolar bone around the teeth caused by osteoclasts. While nuclear factor-kappa beta (NF-κB) is involved in periodontal inflammation, another biomolecule, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) regulates local tissue hypoxia. Both are likely involved in osteoclastogenesis. Velutin is an anti-inflammatory polyphenol that modulates the NF-κB pathway. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of Velutin on osteoclastogenesis in vitrothrough the modulation HIF-1αand NF-κB signaling pathways.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Osteoclastogenesis was induced in RAW 264.7 osteoclast precursor cells with 30 ng/mL of RankL for 5 days at 37oC / 5%CO2. Cells were co-stimulated with 1 08g/mL of Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide (PgLPS) and treated with various concentrations of Velutin (0.25 – 1 08M). Alamar blue assays and TRAP assays were used to verify osteoclast viability and formation, respectively. Immunoblotting assays assessed the expression of HIF-1α and p-IκBαin all experimental groups. Alpha was set at 5%. Velutin was not toxic to RAW cells in all used concentrations (p>0.05) but reduced osteoclast formation dose-dependently when compared to control (p<0.05). Velutin also decreased HIF-1α and p-IκBαexpression during osteoclastogenesis (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:
Within the limitations of the study design it was concluded that Velutin controls HIF-1α activity during PgLPS-activated osteoclastogenesis probably through modulation of the NF-κB pathway. Perhaps Velutin could be used therapeutically to prevent bone loss seen in periodontitis.