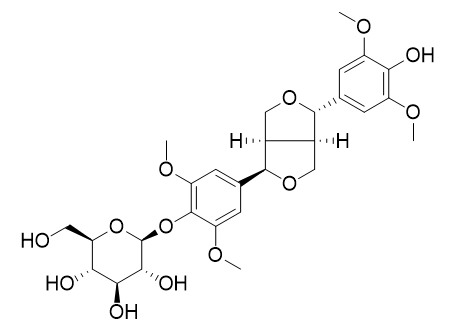
Tortoside A
Tortoside A inhibit NFAT transcription factor.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Sci Rep.2021, 11(1):21038.
Phytomedicine.2019, 62:152962
Eur J Pharmacol.2021, 899:174010.
Front Pharmacol.2022, 13:906763.
Virus Res.2023, 335:199199.
Molecules.2019, 24(21):E3834
J.Food Pharm.Sci.2024, 12(2), 116-124.
J Ethnopharmacol.2020, 249:112381
Natural Product Communications2020, doi: 10.1177.
Front Microbiol.2019, 10:2806
Related and Featured Products
Arch Pharm Res . 2004 Jul;27(7):738-41
Inhibitory lignans against NFAT transcription factor from Acanthopanax koreanum[Pubmed:
15357001]
Three lignans isolated from the roots of A. koreanum (Araliaceae), namely eleutheroside E (1), Tortoside A (2), and hemiariensin (4), were evaluated for their ability to inhibit NFAT transcription factor. Of these compounds, compound 4, possessing a diarylbutane skeleton, exhibited potent inhibitory activity against NFAT transcription factor (IC50: 36.3 +/- 2.5 microM). However, the activities of 1 (IC50: > 500 microM) and 2 (IC50: 136.1 +/- 9.4 microM), which possess bisaryldioxabicyclooctane skeletons, were lower. As the lignan derivatives of the same skeletons, hinokinin (5) and (-)-yatein (6) with diarylbutane skeletons and (+)-syringaresinol (3) with a bisaryldioxabicyclooctane skeleton were also studied for their inhibitory effects on NFAT transcription factor.
Toxicol Res . 2013 Dec 31;29(4):279-83
Evaluation of the Mutagenic Properties of Two Lignans from Acanthopanax koreanum Nakai[Pubmed:
24578798]
Acanthopanax koreanum Nakai, a well known traditional herb grown in Jeju Island, South of Korea, has been used as a tonic and sedative agent, as well as in the treatment of diabetes and immune diseases. Mutagenicity of two lignans, syringaresinol and Tortoside A isolated from A. koreanum, was assessed using Salmonella/microsome (Ames) test. Tester strains used were Salmonella typhimurium TA98, TA100, TA1535, and Escherichia coli WP2uvrA. The mutagenic activity was determined both in the absence or presence of S9 mixture. As a result, Tortoside A did not cause any increase in the number of his(+) revertants in S. typhimurium and E. coli WP2uvrA strains in the presence or absence of S9 mix, compared to the controls. Similarly, low concentrations of syringaresinol (750 and 1,500 μg/plate) did not show any mutagenic properties in all bacterial strains, in the presence or absence of S9 mixture. However, in the high concentration of syringaresinol (3,000 μg/plate), the number of revertants were increased in TA1535 strains, in the absence of S9 metabolic activation. Therefore, in vivo experiments such as comet assay are needed to further determine the genotoxic/carciogenic potential of syringaresinol isolated from A. koreanum.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett . 2016 Aug 15;26(16):3913-7.
New naphthalene derivatives and isoquinoline alkaloids from Ancistrocladus cochinchinensis with their anti-proliferative activity on human cancer cells[Pubmed:
27423477]
Five new compounds, named ancistronaphtosides A and B (1 and 2), anciscochine (3), anciscochine 6-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (4), and 4'-methoxy-5-epi-ancistecrorine A1 (5), together with Tortoside A (6) and 4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenyl-6-O-syringoyl-β-d-glucopyranoside (7) were isolated from the methanolic extract of Ancistrocladus cochinchinensis. Their chemical structures were established using HR-ESI-MS, NMR spectroscopic, and chiroptical methods. Compound 5 significantly exhibited anti-proliferation against HL-60, LU-1, and SK-MEL-2 cells with IC50 values of 5.0±1.2, 6.5±1.6, and 6.8±2.0μg/mL, respectively.
J Asian Nat Prod Res . 2006 Sep;8(6):505-10
Studies on chemical constituents from Ilex pubescens[Pubmed:
16931425]
Two new phenolic glycosides, ilexpubsides A and B, along with four known lignan glycosides were isolated from the roots of Ilex pubescens. By spectral evidence, the structures of the new compounds were elucidated as 4-O-beta-D-[6'-O-(4''-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylvanilloyl)glucopyranosyl] vanillic acid (1) and syringinic 6'-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside (2). The known compounds were identified to be liriodendrin (3), (-)-olivil (4), Tortoside A (5) and (+)-cyclo-olivil (6). All compounds were first isolated from Ilex pubescens.