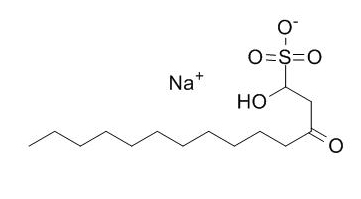
Sodium houttuyfonate
Sodium houttuyfonate is anti-pseudomonas agents, inhibits virulence related motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.It also inhibits biofilm formation and alginate biosynthesis-associated gene expression in a clinical strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro. Sodium houttuyfonate has anti-inflammatory activity, inhibits inflammation by blocking the MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathways in bovine endometrial epithelial cells.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Pharm Biol.2016, 54(7):1255-62
Sci Rep.2024, 14(1):23786.
J Immunol.2023, ji2200727.
Microb Pathog.2019, 131:128-134
Semyung University2017, 149407
J Sci Food Agric.2018, 98(3):1153-1161
J Nat Prod.2015, 78(6):1339-4
iScience.2024, 4790628.
J of Advanced Scientific R.2020, 11(3), p109-120.
Food and Fermentation Industries2019, 45(7):45-51
Related and Featured Products
Exp Ther Med. 2015 Aug;10(2):753-758.
Sodium houttuyfonate inhibits biofilm formation and alginate biosynthesis-associated gene expression in a clinical strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro.[Pubmed:
26622388]
The increasing multidrug resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa has become a serious public-health problem.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the inhibitory activities of Sodium houttuyfonate (SH) against biofilm formation and alginate production in a clinical strain of P.aeruginosa (AH16) were investigated in vitro using crystal violet dying and standard curve methods, respectively. The cellular morphology of P. aeruginosa treated with SH was observed using a scanning electron microscope. Furthermore, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to identify differences in the expression levels of genes associated with alginate biosynthesis as a result of the SH treatment. The results indicated that SH significantly inhibited biofilm formation, and decreased the levels of the primary biofilm constituent, alginate, in P. aeruginosa AH16 at various stages of biofilm development. In addition, scanning electron microscopy observations demonstrated that SH markedly altered the cellular morphology and biofilm structure of P. aeruginosa. Furthermore, the results from the reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis indicated that SH inhibited biofilm formation by mitigating the expression of the algD and algR genes, which are associated with alginate biosynthesis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, the present study has provided novel insights into the potent effects and underlying mechanisms of SH-induced inhibition of biofilm formation in a clinical strain of P. aeruginosa.
Res Vet Sci. 2015 Jun;100:245-51.
Sodium houttuyfonate inhibits inflammation by blocking the MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathways in bovine endometrial epithelial cells.[Pubmed:
25935757]
Sodium houttuyfonate (SH) has traditionally been used for the therapy of inflammatory diseases. In this research, we tried to assess the anti-inflammatory effects of Sodium houttuyfonate on LPS-induced bovine endometrial epithelial cell (bEEC) inflammation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Sodium houttuyfonate cell toxicity was measured using the MTT and LDH assays, and inflammatory cytokine expression was assessed by ELISA, qRT-PCR and Western blotting. We demonstrated that Sodium houttuyfonate was not cytotoxic to bEECs, and that it significantly decreased the LPS-induced mRNA and protein expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and IL-8. Furthermore, in LPS-induced bEECs, SH inhibited IκBα degradation and NF-κB p65 phosphorylation, and suppressed the phosphorylation of the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK).
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, we found that Sodium houttuyfonate could effectively block the NF-κB-mediated signaling pathway and reduce the inflammatory process, thereby exerting a protective effect on bEECs.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015 Apr;40(8):1585-8.
Sodium houttuyfonate inhibits virulence related motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa[Pubmed:
26281603]
Sodium houttuyfonate (SH) is a derivative of effective component of a Chinese material medica, Houttuynia cordata, which is applied in anti-infection of microorganism. But, the antimicrobial mechanisms of SH still remain unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we firstly discovered that SH effectively inhibits the three types of virulence related motility of.Pseudomonas aeruginosa, i.e., swimming, twitching and swarming. The plate assay results showed that the inhibitory action of SH against swimming and twitching in 24 h and swarming in 48 h is dose-dependent; and bacteria nearly lost all of the motile activities under the concentration of 1 x minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) (512 mg x L(-1) same as azithromycin positive group (1 x MIC, 16 mg x L(-1)). Furthermore, we found that the expression of structural gene flgB and pilG is down-regulated by SH, which implies that inhibitory mechanism of SH against motility of P. aeruginosa may be due to the inhibition of flagella and pili bioformation of P. aeruginosa by SR.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, our presented results firstly demonstrate that SH effectively inhibits the motility activities of P. aeruginosa, and suggest that SH could be a promising antipseudomonas agents in clinic.