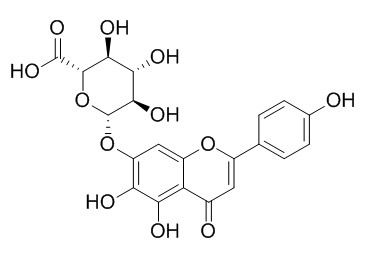
Scutellarin
Scutellarin has many pharmacological effects, such as antioxidant, antitumor, antiviral, neuroprotection and antiinflammatory activities. It down-regulates the STAT3/Girdin/Akt signaling in HCC cells, and inhibits RANKL-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway in osteoclasts.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Neurochem Res.2021, s11064-021-03449-0
bioRxiv-Pharm.&Toxi.2022, 2022.481203.
J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol.2016, 27(1):1-8
Korean Herb. Med. Inf.2020, 8(2):205-213
Oncology Letters2018, 4690-4696
Biochem Pharmacol.2017, 130:10-20
Nutrients2022, 14(14)2929
Food Chem X.2024, 21:101127.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(21):13406.
J Ethnopharmacol.2017, 196:75-83
Related and Featured Products
Life Sci. 2004 Apr 30;74(24):2959-73.
Protection against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells by scutellarin.[Pubmed:
15051420 ]
The present study investigated the protective actions of the antioxidant Scutellarin against the cytotoxicity produced by exposure to H2O2 in PC12 cells. This was done by assaying for MTT (3,(4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl)2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide) reduction and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and Ca2+ in cells were evaluated by fluorescent microplate reader using DCFH and Fura 2-AM, respectively, as probes. Lipid peroxidation was quantified using thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS). Mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) was assessed by the retention of rhodamine123 (Rh123), a specific fluorescent cationic dye that is readily sequestered by active mitochondria, depending on their transmembrane potential. The DNA content and percentage of apoptosis were monitored with flow cytometry. Vitamin E, a potent antioxidant, was employed as a comparative agent. Preincubation of PC12 cells with Scutellarin prevented cytotoxicity induced by H2O2. Intracellular accumulation of ROS, Ca2+ and products of lipid peroxidation, resulting from H2O2 were significantly reduced by Scutellarin. Incubation of cells with H2O2 caused a marked decrease in MMP, which was significantly inhibited by Scutellarin. PC12 cells treated with H2O2 underwent apoptotic death as determined by flow cytometric assay. The percentage of this H2O2-induced apoptosis in the cells was decreased in the presence of different concentrations of Scutellarin. Scutellarin exhibited significantly higher potency compared to the antioxidant vitamin E.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present findings showed that Scutellarin attenuated H2O2-induced cytotoxicity, intracellular accumulation of ROS and Ca2+, lipid peroxidation, and loss of MMP and DNA, which may represent the cellular mechanisms for its neuroprotective action.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun . 2017 Jan 29;483(1):509-515.
Scutellarin suppresses migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the STAT3/Girdin/Akt activity[Pubmed:
27998773]
Abstract
Scutellarin is an active flavone from Erigeron breviscapine (vant) Hand Mass. This study aimed to investigate the potential role of Scutellarin in migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and its possible mechanism. In comparison with the vehicle-treated controls, treatment with Scutellarin (50 mg/kg/day) for 35 days significantly mitigated the lung and intrahepatic metastasis of HCC tumors in vivo. Scutellarin treatment significantly reduced HepG2 cell viability in a dose-dependent manner, and inhibited migration and invasion of HCC cells in vitro. Scutellarin treatment significantly reduced STAT3 and Girders of actin filaments (Girdin) expression, STAT3 and Akt phosphorylation in HCC cells. Introduction of STAT3 overexpression restored the Scutellarin-downregulated Girdin expression, Akt activation, migration and invasion of HCC cells. Furthermore, induction of Girdin overexpression completely abrogated the inhibition of Scutellarin on the Akt phosphorylation, migration and invasion of HCC cells. Scutellarin can inhibit HCC cell metastasis in vivo, and migration and invasion in vitro by down-regulating the STAT3/Girdin/Akt signaling.
Keywords: Akt; Girdin; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Invasion; STAT3; Scutellarin.
Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;162(3):688-700.
Scutellarin alleviates interstitial fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction of infarct rats by inhibiting TGFβ1 expression and activation of p38-MAPK and ERK1/2.[Pubmed:
20942814]
Interstitial fibrosis plays a causal role in the development of heart failure after chronic myocardial infarction (MI), and anti-fibrotic therapy represents a promising strategy to mitigate this pathological process. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of long-term administration of Scutellarin (Scu) on cardiac interstitial fibrosis of myocardial infarct rats and the underlying mechanisms.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Scu was administered to rats that were subjected to coronary artery ligation. Eight weeks later, its effects on cardiac fibrosis were assessed by examining cardiac function and histology. The number and collagen content of cultured cardiac fibroblasts exposed to angiotensin II (Ang II) were determined after the administration of Scu in vitro. Protein expression was detected by Western blot technique, and mRNA levels by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR.
The echocardiographic and haemodynamic measurements showed that Scu improved the impaired cardiac function of infarct rats and decreased interstitial fibrosis. Scu inhibited the expression of FN1 and TGFβ1, but produced no effects on inflammatory cytokines (TNFα, IL-1β and IL-6) in the 8 week infarct hearts. Scu inhibited the proliferation and collagen production of cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) and the up-regulation of FN1 and TGFβ1 induced by Ang II. The enhanced phosphorylation of p38-MAPK and ERK1/2 in both infarct cardiac tissue and cultured CFs challenged by Ang II were suppressed by Scu.
CONCLUSIONS:
Long-term administration of Scu improved the cardiac function of MI rats by inhibiting interstitial fibrosis, and the mechanisms may involve the suppression of pro-fibrotic cytokine TGFβ1 expression and inhibition of p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 phosphorylation.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Mar 13;162:69-78.
Biological evaluation and molecular docking of baicalin and scutellarin as Helicobacter pylori urease inhibitors.[Pubmed:
25557028]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Baicalin and Scutellarin effectively suppressed Helicobacter pylori urease in dose-dependent and time-independent manner with IC50 of 0.82±0.07 mM and 0.47±0.04 mM, respectively, compared to AHA (IC50=0.14±0.05 mM). Structure-activity relationship disclosed 4'-hydroxyl gave flavones an advantage to binding with Helicobacter pylori urease. Kinetic analysis revealed that the types of inhibition were non-competitive and reversible with inhibition constant Ki of 0.14±0.01 mM and 0.18±0.02 mM for baicalin and Scutellarin, respectively. The mechanism of urease inhibition was considered to be blockage of the SH groups of Helicobacter pylori urease, since thiol reagents (L,D-dithiothreitol, L-cysteine and glutathione) abolished the inhibitory action and competitive active site Ni(2+) binding inhibitors (boric acid and sodium fluoride) carried invalid effect. Molecular docking study further supported the structure-activity analysis and indicated that baicalin and Scutellarin interacted with the key residues Cys321 located on the mobile flap through S-H·π interaction, but did not interact with active site Ni(2+). Moreover, Baicalin (at 0.59-1.05 mM concentrations) and Scutellarin (at 0.23-0.71 mM concentrations) did not exhibit significant cytotoxicity to GES-1.
CONCLUSIONS:
Baicalin and Scutellarin were non-competitive inhibitors targeting sulfhydryl groups especially Cys321 around the active site of Helicobacter pylori urease, representing potential to be good candidate for future research as urease inhibitor for treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Furthermore, our work gave additional scientific support to the use of Scutellaria baicalensis in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) to treat gastrointestinal disorders.
Pharmazie. 2014 Jul;69(7):537-41.
In vivo effects of scutellarin on the activities of CYP1A2, CYP2C11, CYP2D1, and CYP3A1/2 by cocktail probe drugs in rats.[Pubmed:
25073400]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Scutellarin and saline were intravenously administered to male Wistar rats via the caudal vein for 7 days consecutively. On the 8th day, the rats were treated with probe drugs of caffeine (10 mg/kg), tolbutamide (10 mg/kg), metoprolol (20 mg/kg), dapsone (10 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection, and the blood samples were collected at different times. The probe drugs in the blood samples were measured by ultra performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometer (UPLC-MS/MS) and the changes of the pharmacokinetics parameters of the drugs were observed to evaluate the effects of Scutellarin on the four CYP450 isoforms in rats.
The activity of CYP1A2 in rats was inhibited significantly after treatment with Scutellarin by increased caffeine t1/2 (21.76%, P < 0.05), T(max) (43.05%, P < 0.05), C(max) (43.92%, P < 0.01) and AUC(0-infinity) (50.88%, P < 0.01) in the Scutellarin-treated group compared with those of the blank control. The activity of CYP2C11 in rats was inhibited significantly after treatment with Scutellarin by increased tolbutamide t1/2 (16.74%, P < 0.01), T(max) (116.87%, P < 0.05), C(max) (63.78%, P < 0.01) and AUC(0-infinity) (70.61%, P < 0.01) in the Scutellarin-treated group compared with those of the blank control. The activity of CYP3A1/2 in rats was inhibited significantly after treatment with Scutellarin by increased dapsone t1/2 (45.28%, P < 0.05), T(max) (81.55%, P < 0.05), C(max) (155.58%, P < 0.01)and AUC(0-infinity) (176.35%, P < 0.01) in the Scutellarin-treated group compared with those of the blank control. The pharmacokinetic parameters of metoprolol were not significantly changed in the Scutellarin-treated group compared with those of the blank control.
CONCLUSIONS:
Scutellarin could significantly inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2C11 and CYP3A1/2 activities in rats in vivo, but had no effects on the activity of CYP2D1.
Pharmacol Res. 2005 Mar;51(3):205-10.
Effect of scutellarin on nitric oxide production in early stages of neuron damage induced by hydrogen peroxide.[Pubmed:
15661569 ]
The aims of the present study were to investigate the regulatory function of Scutellarin on production of nitric oxide (NO) as well as activities of constitutive NO synthase (cNOS) and inducible NO synthase (iNOS) in early stages of neuron damage induced by hydrogen peroxide.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Direct detection of NO production was performed on primary cultures of living rat neuronal cells with an electrochemical sensor. Hydrogen peroxide significantly increased culture supernatant levels of NO, the total integral value of the defined areas (500-6500 sxpA) reached 3.68 x 10(6). Pre-treatment with Scutellarin, caused the total integral value to decrease in a dose-dependent fashion (3.24 x 10(6), 2.15 x 10(6), 1.84 x 10(6) for groups 10, 50, and 100 uM Scutellarin, respectively). After exposure to 2.0mM hydrogen peroxide for 2h, malondialdehyde (MDA) level, a marker of lipid peroxidation, was remarkably increased. The elevation can be suppressed by Scutellarin. Hydrogen peroxide also caused significant loss of neuron viability. In comparison with the control group, Scutellarin significant attenuated the loss. Results also showed that hydrogen peroxide increased activity of cNOS, which was markedly inhibited by Scutellarin. However, exposure of neuronal cells to hydrogen peroxide did not lead to an increase in iNOS activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, our results suggest that NO production, which increased in early stages of neuron damage induced by hydrogen peroxide can be effectively inhibited by Scutellarin. Moreover, our results indicate that increase in NO production is mediated by cNOS.
Molecules. 2014 Sep 29;19(10):15611-23.
Anti-fibrosis effect of scutellarin via inhibition of endothelial-mesenchymal transition on isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis in rats.[Pubmed:
25268717]
Scutellarin (SCU) is the major active component of breviscapine and has been reported to be capable of decreasing myocardial fibrosis. The aim of the present study is to investigate whether SCU treatment attenuates isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis and the mechanisms of its action.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Rats were injected subcutaneously with isoprenaline (Iso) to induce myocardial fibrosis and rats in the SCU treatment groups were intraperitoneally infused with SCU (10 mg·kg-1·d-1 or 20 mg·kg-1·d-1, for 14 days). Post-treatment, cardiac functional measurements and the left and right ventricular weight indices (LVWI and RVWI, respectively) were analysed. Pathological alteration, expression of type I and III collagen, Von Willebrand factor, α-smooth muscle actin, cluster of differentiation-31 (CD31), and the Notch signalling proteins (Notch1, Jagged1 and Hes1) were examined. The administration of SCU resulted in a significant improvement in cardiac function and decrease in the cardiac weight indices; reduced fibrous tissue proliferation; reduced levels of type I and III collagen; increased microvascular density; and decreased expression of α-smooth muscle actin and increased expression of CD31, Notch1, Jagged1 and Hes1 in isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis in rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggest that SCU prevents isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis via inhibition of cardiac endothelial-mesenchymal transition potentially, which may be associated with the Notch pathway.