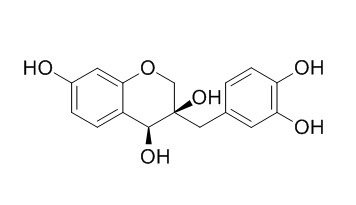
Sappanol
Sappanol inhibits lipid peroxidation in a concentration-dependent manner, can significantly attenuated H2O2-induced retinal death, can be potential antioxidant treatment for retinal diseases.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Plant Cell.2024, 158: 62.
Pharmacognosy Magazine2024, 20(2):632-645.
JEJU National University2022, 10478.
J Appl Biol Chem.2024, 67:33,238-244
Separations2021, 8(1), 1.
Vietnam Journal of Food Control2022, 5(3):pp.390-401.
Microorganisms.2021, 9(12):2514.
Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov.2022, 17(4):416-426.
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 978:176800.
Pharmaceutics.2022, 14(3):564.
Related and Featured Products
BMB Rep. 2015 May;48(5):289-94.
One-step isolation of sappanol and brazilin from Caesalpinia sappan and their effects on oxidative stress-induced retinal death.[Pubmed:
25248564 ]
Caesalpinia sappan is a well-distributed plant that is cultivated in Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Americas. C. sappan has been used in Asian folk medicine and its extract has been shown to have pharmacological effects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two homoisoflavonoids, Sappanol and brazilin, were isolated from C. sappan by using centrifugal partition chromatography (CPC), and tested for protective effects against retinal cell death. The isolated homoisoflavonoids produced approximately 20-fold inhibition of N-retinylidene-N-retinyl-ethanolamine (A2E) photooxidation in a dose-dependent manner. Of the 2 compounds, brazilin showed better inhibition (197.93 ± 1.59 μM of IC50). Cell viability tests and PI/Hoechst 33342 double staining method indicated that compared to the negative control, Sappanol significantly attenuated H2O2-induced retinal death.
CONCLUSIONS:
The compounds significantly blunted the up-regulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), and Sappanol inhibited lipid peroxidation in a concentration-dependent manner. Thus, both compounds represent potential antioxidant treatments for retinal diseases.