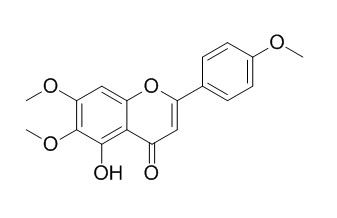
Salvigenin
Salvigenin, a potent hMAO-A [monoamine oxidases (MAOs)]inhibitor,
has neuroprotective, antitumor and immunomodulatory effects, it has potential to ameliorate Streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus and heart complications in rats. Salvigenin has dose-dependent analgesic effect so that it can be useful in controlling of inflammations, acute and chronic pain.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy2014, 113-120
Life Sci.2023, 317:121458.
Molecules.2019, 24(6):E1177
Green Chem.2023, 25:5222-5232
J Mass Spectrom.2022, 57(2):e4810.
Nat Commun.2023, 14(1):4540.
Plants (Basel).2024, 13(6):868.
Kyung Hee University2024, 4789969.
Pharmacol Rep.2019, 71(2):289-298
Food Res Int.2024, 197(Pt 1):115244.
Related and Featured Products
Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Dec;371(1-2):9-22.
Increase of autophagy and attenuation of apoptosis by Salvigenin promote survival of SH-SY5Y cells following treatment with H₂O₂.[Pubmed:
22899171]
Oxidative stress is a major component of harmful cascades activated in neurodegenerative disorders.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we tried to elucidate the possible neuroprotective effect of Salvigenin, a natural polyphenolic compound, on oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. We measured cell viability by MTT test and found that 25 μM is the best protective concentration of Salvigenin. GSH and SOD assays suggested that Salvigenin activates antioxidant factors. At the same time, measurement of ER stress-associated proteins including calpain and caspase-12 showed the ability of Salvigenin to decrease ER stress. We found that Salvigenin could decrease the apoptotic factors. Salvigenin inhibited H(2)O(2)-induced caspase-3 which is a hallmark of apoptosis in addition to reducing Bax\Bcl-2 ratio by 1.45 fold. Additionally, Salvigenin increased the levels of autophagic factors.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results showed an increase in LC3-II/LC3-I ratio, Atg7, and Atg12 in the presence of 25 μM of Salvigenin by about 1.28, 1.25, and 1.54 folds, respectively, compared to H(2)O(2)-treated cells. So it seems that H(2)O(2) cytotoxicity mainly results from apoptosis. Besides, Salvigenin helps cells to survive by inhibiting apoptosis and enhancing autophagy that opens a new horizon for the future experiments.
Cell Immunol. 2013 Nov-Dec;286(1-2):16-21.
Antitumor and immunomodulatory effects of salvigenin on tumor bearing mice.[Pubmed:
24270218]
Development of agents that specifically kill cancer cells and simultaneously elicit antitumor immune response is a step forward in cancer therapy. Immunostimulation can result in eliminating of the cancer cells; immunotherapy is a promising approach in balancing the immune response by Treg.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we investigated whether the administration of Salvigenin contributes to the augmentation of antitumor immunity and the regression of tumor tissues in a mouse model of breast cancer. Salvigenin was purified from Tanacetum canescens, and its effect on the tumor volume was investigated. The splenocyte proliferation, shifting of cytokine profile, and the presence of naturally-occurring CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg cells were assessed to describe the anti-tumor immune response.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results demonstrated that a significant decrease in the level of IL-4 and increase in the IFN-γ in the animals treated with Salvigenin and significant decreased in the level of splenic CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. The cytotoxic and immunomodulatory properties of Salvigenin were acknowledged in vivo.
Advaced Herbal Medicine , 2015, 1(3):31-41.
Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Properties of Salvigenin, Salvia officinalis Flavonoid Extracted.[Reference:
WebLink]
Salvigenin is one of the active flavonoids existing in this plant. The aim of this study was to evaluate the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect of Salvigenin, Salvia officinalis flavonoid extracted.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this laboratory experimental study, plant was extracted and the column chromatography was used to purify prepared extracts. 100 male albino mice and 48 male wistar rats were selected. In the hot plate test and in the writhing test, animals were divided randomly into 5 groups. Group 1 (received 10 mg/kg normal saline), groups 2, 3 and 4 (received Salvigenin 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg intraperitoneally, espectively), group 5 (received 10 mg/kg morphine in hot plate test and 10 mg/kg indomethacin in writhing test). In the inflammatory test, animals were divided into 6 groups. Group 1 was assigned as a control group which received 0.05 ml of carrageenin. Groups 2, 3 and 4 (received Salvigenin, at doses of 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg). Group 5 (received 10 mg/kg indomethacin) and then changes of the volume of all groups were measured. Data were analyzed using ANOVA and Tukey test and P. In writhing test, Salvigenin reduced the number of abdominal contractions at doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg. Increasing dose of Salvigenin, with reduction in abdominal cramps resulted in the increasing of pain inhibition, and the percentage of this inhibition was statistically significant (P<0.001). In hot plate test, also 30, 45 and 60 minutes after injection of Salvigenin and morphine showed significant difference compared to the control group (P<0.001). Also, Salvigenin increased the maximum percentage of analgesic compared to the control group (P<0.001). Salvigenin could reduce inflammation and in the group that received Salvigenin at 100 mg/kg, the inflammation was significantly lower than the control group (P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings showed that Salvigenin has dose-dependent analgesic effect so that it can be useful in controlling of inflammations, acute and chronic pain.
Molecules. 2015 Apr 23;20(5):7454-73.
Flavonoids from Sideritis Species: Human Monoamine Oxidase (hMAO) Inhibitory Activities, Molecular Docking Studies and Crystal Structure of Xanthomicrol.[Pubmed:
25915461]
The inhibitory effects of flavonoids on monoamine oxidases (MAOs) have attracted great interest since alterations in monoaminergic transmission are reported to be related to neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases and psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety, thus MAOs may be considered as targets for the treatment of these multi-factorial diseases.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, four Sideritis flavonoids, xanthomicrol (1), isoscutellarein 7-O-[6'''-O-acetyl-β-D-allopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside (2), isoscutellarein 7-O-[6'''-O-acetyl-β-D-allopyranosyl-(1→2)]-6''-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (3) and Salvigenin (4) were docked computationally into the active site of the human monoamine oxidase isoforms (hMAO-A and hMAO-B) and were also investigated for their hMAO inhibitory potencies using recombinant hMAO isoenzymes. The flavonoids inhibited hMAO-A selectively and reversibly in a competitive mode. Salvigenin (4) was found to be the most potent hMAO-A inhibitor, while xanthomicrol (1) appeared as the most selective hMAO-A inhibitor. The computationally obtained results were in good agreement with the corresponding experimental values. In addition, the x-ray structure of xanthomicrol (1) has been shown.
CONCLUSIONS:
The current work warrants further preclinical studies to assess the potential of xanthomicrol (1) and Salvigenin (4) as new selective and reversible hMAO-A inhibitors for the treatment of depression and anxiety.
British Journal of Medicine Medical Research., 2016, 15(2):1-12.
Salvigenin has Potential to Ameliorate Streptozotocin-induced Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Complications in Rats.[Reference:
WebLink]
Flavonoids are the active ingredients, found in herbal remedies for amelioration the variety of disorders. Salvigenin is a plant flavenoid, which is found in Salvia officinalis. Salvigenin has an antioxidant, anti-inflamatory, anti-tumor and vascular relaxant activities. This study was conducted to evaluate the possible antidiabetic and cardioprotective effects of Salvigenin.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
32 wistar rats were made diabetic using streptozotocin (60 mg/kg, i.p.). Rats were divided into four groups that treated with Salvigenin at doses of 5, 10 or 25 mg/kg. All the treatments were administered orally for 4 weeks. At the end of the experiment, the blood samples were collected for determining the FBS, HbA1C, insulin, triglyceride, cholesterol and HDL. After 72 hrs, animals were anesthetized; hearts were removed quickly and mounted on Langendorff apparatus. The max pressure, heart rate, max dP/dt, contractility index and coronary flow were measured. Administration of Salvigenin exhibited a significant reduction in fasting serum glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol, HbA1c and increased level of plasma insulin and HDL in diabetic rats (P<0/05). Salvigenin could significantly increased hemodynamic indices such as max pressure, max dP/dt, contractility and coronary flow (P<0/05).
CONCLUSIONS:
Salvigenin improved diabetes through decreasing blood glucose, lipid profile, HbA1c. Increased insulin secretion can be a mechanism for antidiabetic effect of Salvigenin. Regarding the antidiabetic and cardioprotective effects of Salvigenin, it can be concluded that this flavonoid compound can be potentially used to reduce diabetes and it’s cardiovascular complications.