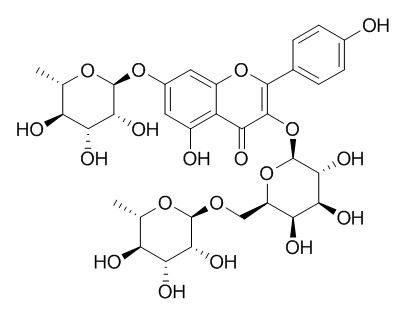
Robinin
Robinin has cardioprotective effect on doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity by modulating TGF-β1 signaling pathway in Sprague Dawley rats. Robinin has protective effect against the ox-LDL induced inflammation stress in hPBMCs by inhibiting TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Br J Pharmacol.2018, 175(6):902-923
Antioxidants (Basel).2023, 12(5):1111.
Research Square2021, 10.21203.
Fitoterapia.2021, 153:104995.
RSC Advances2017, 86
Molecules.2018, 23(3):E615
Horticulture Research2023, uhad259
Phytomedicine2022, 104:154318
Molecules.2016, 21(6)
Chem Biol Interact.2019, 315:108910
Related and Featured Products
Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Jan;18(1):191-7.
Robinin modulates TLR/NF-κB signaling pathway in oxidized LDL induced human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.[Pubmed:
24295649]
This study was designed to investigate whether Robinin administration modulates toll-like receptor (TLR) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway in oxidized LDL induced human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (hPBMCs).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The hPBMCs were isolated from healthy human volunteers and the cells were cultured in collagen coated plates at 37°C with 5% CO2 and RPMI as culture medium and were grouped as follows: Group I - control, group II - OxLDL treated and group III - OxLDL+Robinin (6μg/ml). We measured mRNA expression of TLR2 and TLR4 by reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and NF-κB transcription factor assay (ELISA), and western blotting studies were done for knowing expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP 1), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) interleukin-6 (IL-6) and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1). The result indicates that OxLDL that induces hPBMCs showed an upregulated expression of TLR2, TLR4, NF-κB, pro-inflammatory cytokines and VCAM-1.
CONCLUSIONS:
Robinin inhibited the ox-LDL induced TLR2 and TLR4 expression at mRNA level and inhibited the translocation of NF-κB p65 by modulating the TLR-NF-κB signaling pathway thereby inhibiting cytokine production and down regulated inflammatory enzymes like cyclooxygenase (COX), lipoxygenase (LOX), nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), thus having protective effect against the ox-LDL induced inflammation stress in hPBMCs by inhibiting TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 2014 Oct;68(8):989-98.
Robinin modulates doxorubicin-induced cardiac apoptosis by TGF-β1 signaling pathway in Sprague Dawley rats.[Pubmed:
25443416]
The study focussed on the cardioprotective effect of Robinin on doxorubicin-induced cardio-toxicity in Sprague Dawley rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After the experimental period, animals were sacrificed and the various parameters such as cardiac markers, toxicity parameters, antioxidant status, ROS generation, lipid peroxidation status and inflammatory parameters were assessed. Gene expression study by RT-PCR analysis and proteins expression study by western blotting were done. Doxorubicin causes significant increase in the levels of cardiac marker enzymes, namely lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine phospokinase (CPK), toxicity parameters like serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (SGOT) and serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase (SGPT). Antioxidant enzyme levels were decreased; lipid peroxidation products in heart tissue and inflammatory markers, namely cyclooxygenase (COX2) and lipooxygenase (LOX15) were significantly increased. Gene expression study by RT-PCR analysis of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), Smad2, murine double minute (Mdm2), Smad3, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A), Smad4 and Smad7 were significantly altered. The western blotting study of p53, Bcl-2 and Bax also showed altered expression. The supplementation of the Robinin along with DOX caused normalised level of all the above parameters and cardio-toxicity.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study revealed the cardioprotective nature of Robinin on doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity by modulating TGF-β1 signaling pathway in Sprague Dawley rats.
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011 Apr 28;55(1):109-13.
Simultaneous determination of the flavonoids robinin and kaempferol in human breast cancer cells by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:
21232900]
An accurate, precise and sensitive method was developed and validated for the simultaneous quantification of the flavonoid glycoside Robinin, and its algycone kaempferol in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The application of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) with a TurboIonspray interface in negative mode under multiple reactions monitoring was investigated. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a C(18) column using a mobile phase consisting of (A) water with 0.025% formic acid and 1mM ammonium formate and (B) acetonitrile with 0.025% formic acid. Rutin was used as the internal standard for Robinin and fisetin as the internal standard for kaempferol. The assay had a limit of detection of 0.1ng/ml for both compounds when present in cell lysate. The calibration curves were linear from 1 to 250ng/ml (r>0.999) for each compound. The intra- and inter-day coefficients of variation were less than 10% and intra- and inter-day accuracies were within 11%.
CONCLUSIONS:
This assay was successfully applied in a Robinin cellular uptake study to determine the intracellular concentrations of Robinin in MCF-7 cells.