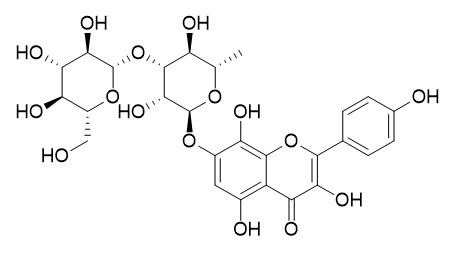
Rhodiosin
Rhodiosin exhibits potent, dose-dependent inhibitory effects on acetylcholinesterase (AChE), it also can inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 non-competitively with the IC50 value of 0.761 microM.
Rhodiosin has hepatoprotective effects, it shows a protective effect on D-galactosamine-induced cytotoxicity in primary cultured mouse hepatocytes. Rhodiosin shows noncompetitive inhibition against Flavobacterium prolyl endopeptidase, with an IC50 of 41 microM, the enzyme that plays a role in the metabolism of proline-containing neuropeptidase which is recognized to be involved in learning and memory. Rhodiosin exhibits antioxidant activity, it could used as the treatment of lifestyle-related diseases such as hyperlipidemia and exogeneous obesity and as health foods.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Chemistry of Plant Materials.2019, 215-222
Talanta.2022, 249:123645.
Planta Med.2022, a-1876-3009.
Nutraceuticals2022, 2(3),150-161
Trop J Nat Prod Res, February2023, 7(2):2371-2381
Preprints2021, doi:10.20944
J.Food Pharm.Sci.2024, 12(2), 116-124.
ACS Nano.2023, 17(11):9972-9986.
Cell Death Discov.2023, 9(1):350.
J Plant Biotechnol.2023, 50:070-075.
Related and Featured Products
Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Nov;104(Pt A):527-532.
Molecular interaction studies of acetylcholinesterase with potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from the root of Rhodiola crenulata using molecular docking and isothermal titration calorimetry methods.[Pubmed:
28625836]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
(-)-Epicatechin gallate ((-)-ECG), 1,2,3,4,6-O-pentagalloylglucose (PGG), rhodionin, herbacetin and Rhodiosin isolated from the root of Rhodiola crenulata exhibited potent, dose-dependent inhibitory effects on acetylcholinesterase (AChE) with IC50 ranged from 57.50±5.83 to 2.43±0.34μg/mL. With the aim of explaining the differences in activity of these active ingredients and clarifying how they inhibit AChE, the AChE-inhibitor interactions were further explored using molecular docking and isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) methods in the present study. Molecular docking studies revealed that all compounds except PGG showed binding energy values ranging from -10.30 to -8.00kcal/mol while the binding energy of galantamine, a known AChE inhibitor, was -9.53kcal/mol; they inhibited the AChE by binding into the ligand pocket with the similar binding pattern to that of galantamine by interacting with Glu199 of AChE. Inhibition constant of these active ingredients had a positive correlation with binding energy. The interaction between AChE and PGG was further evaluated with the ITC method and the results indicated that the PGG-AChE interaction was relevant to AChE concentration.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results revealed a possible mechanism for the AChE inhibition activity of these bioactive ingredients, which may provide some help in lead compounds optimization in the future.
Molecules. 2012 Sep 27;17(10):11484-94.
The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds isolated from the root of Rhodiola sachalinensis A. BOR.[Pubmed:
23018923 ]
Isolation of compounds from the root of Rhodiola sachalinensis (RRS) yielded tyrosol (1), salidroside (2), multiflorin B (3), kaempferol-3,4'-di-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (4), afzelin (5), kaempferol (6), rhodionin (7), and Rhodiosin (8).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Quantification of these compounds was performed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). To investigate the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of the compounds, DPPH radical scavenging, NBT superoxide scavenging and nitric oxide production inhibitory activities were examined in LPS-stimulated Raw 264.7 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
We suggest that the major active components of RRS are herbacetin glycosides, exhibiting antioxidant activity, and kaempferol, exhibiting anti-inflammatory activity.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2007 Oct;55(10):1505-11.
Bioactive constituents from Chinese natural medicines. XXVI. Chemical structures and hepatoprotective effects of constituents from roots of Rhodiola sachalinensis.[Pubmed:
17917296]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The methanolic extract from the roots of Rhodiola sachalinensis was found to show a protective effect on D-galactosamine-induced cytotoxicity in primary cultured mouse hepatocytes. From the methanolic extract, five new glycosides, two monoterpene glycosides, two flavonol bisdesmosides, and a cyanogenic glycoside, were isolated together with 34 known compounds.
CONCLUSIONS:
The structures of new constituents were elucidated on the basis of chemical and physicochemical evidence. In addition, the principal constituents, sachalosides III and IV, Rhodiosin, and trans-caffeic acid, displayed hepatoprotective effects.
Planta Med. 2008 Nov;74(14):1716-9.
Constituents of Rhodiola rosea showing inhibitory effect on lipase activity in mouse plasma and alimentary canal.[Pubmed:
18982538 ]
As a methanol extract of the rhizome of Rhodiola rosea inhibits the activity of lipase in isolated mouse plasma in vitro and in the mouse gastrointestinal tube in vivo, the active components in this plant were investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After fractionation and separation processes, rhodionin and Rhodiosin were isolated as active ingredients. Their IC50 values were 0.093 mM and 0.133 mM in vitro, respectively. Both compounds significantly suppressed the elevation of the postprandial blood triglyceride level, e.g., by 45.6 % (150 mg/kg, 60 min after oral administration) and 57.6 % (200 mg/kg, 180 min after oral administration), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Consequently, we anticipate the application of this plant and its constituents to the treatment of lifestyle-related diseases such as hyperlipidemia and exogeneous obesity and to health foods.
Pharmazie. 2013 Dec;68(12):974-6.
Two potent cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibitors found in Rhodiola rosea.[Pubmed:
24400445]
Throughout the world, in particular in Russia, Northern Europe and China, Rhodiola species are used as herb supplements. Previously, we found that the extract of Rhodiola rosea, one of the most widely used Rhodiola species, had an inhibitory effect on the catalytic activity of cytochrome P450 2D6. Here, its inhibitory components were identified.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A human liver microsomal in vitro system was used with dextromethorphan as substrate. The production rate of destrorphan, a metabolite of dextromethorphan, was used to measure enzyme activity. The concentration of destrorphan in the samples was measured using LC-MS/MS. Inhibitory activity of eight main components from Rhodiola rosea was evaluated.Rhodiosin and rhodionin showed inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 0.761 microM and 0.420 microM, respectively. The other components showed no obvious inhibition (with a residual enzyme activity of more than 90%). Both Rhodiosin and rhodionin were determined to be non-competitive inhibitors with Ki values of 0.769 microM and 0.535 microM.
CONCLUSIONS:
Two of the main Rhodiola rosea compounds, Rhodiosin and rhodionin, can inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 non-competitively with high specificity which could have implications for interactions with co-administered drugs.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2001 Apr;49(4):396-401.
Prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors from the underground part of Rhodiola sachalinensis.[Pubmed:
11310664]
The methanolic extract of the underground part of Rhodiola sachalinensis was found to show inhibitory activity on prolyl endopeptidase (PEP, EC. 3.4.21.26), an enzyme that plays a role in the metabolism of proline-containing neuropeptidase which is recognized to be involved in learning and memory.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
From the MeOH extract, five new monoterpenoids named sachalinols A (24), B (25) and C (26) and sachalinosides A (23) and B (27) were isolated, together with twenty-two known compounds, gallic acid (1), trans-p-hydroxycinnamic acid (2), p-tyrosol (3), salidroside (4), 6n-O-galloylsalidroside (5), benzyl beta-D-glucopyranoside (6), 2-phenylethyl beta-D-glucopyranoside (7), trans-cinnamyl beta-D-glucopyranoside (8), rosarin (9), rhodiocyanoside A (10), lotaustralin (11), octyl beta-D-glucopyranoside (12), 1,2,3,6-tetra-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose (13), 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose (14), kaempferol (15), kaempferol 3-O-beta-D-xylofuranosyl(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (16), kaempferol 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (17), rhodionin (18), Rhodiosin (19), (-)-epigallocatechin (20), 3-O-galloylepigallocatechin-(4-->8)-epigallocatechin 3-O-gallate (21) and rosiridin (22).
CONCLUSIONS:
Among these, nineteen compounds other than 3, 4 and 9 have been isolated for the first time from R. sachalinensis, and six (6, 8, 13, 16, 17, 20) are isolated from Rhodiola plants for the first time. Among them, six compounds (13, 14, 18, 19, 21, 22) showed noncompetitive inhibition against Flavobacterium PEP, with an IC50 of 0.025, 0.17, 22, 41, 0.44 and 84 microM, respectively.