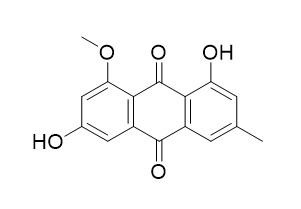
Questin
Questin has promising inhibitory potential against AChE, BChE, and BACE1, it may be used in the development of therapeutic or preventive agents for Alzheimer's disease. Questin is a Cdc25B phosphatase inhibitor, it inhibited the enzymatic activity of Cdc25B phosphatase with the IC(50) value of 34 microg/mL, it also strongly inhibited the growth of human colon cancer cells, SW620 with the GI(50) value of 0.9 microg/mL. Questin shows considerably high immunosuppressive activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Archives of Biological sciences2022, 00:21-21
Phytomedicine.2019, 58:152893
Applied Biological Chemistry 2021, 64(75)
Research J. Pharm. and Tech.2020, 13(7):3059-3064.
Tumour Biol.2015, 36(12):9385-93
J Ethnopharmacol.2016, 192:370-381
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC)2024, 158:54
J Nat Prod.2022, 85(5):1351-1362.
Natural Product Communications2020, doi: 10.1177.
Appl. Sci.2020, 10(23), 8729
Related and Featured Products
PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e29906.
Trypacidin, a spore-borne toxin from Aspergillus fumigatus, is cytotoxic to lung cells.[Pubmed:
22319557 ]
Inhalation of Aspergillus fumigatus conidia can cause severe aspergillosis in immunosuppressed people. A. fumigatus produces a large number of secondary metabolites, some of which are airborne by conidia and whose toxicity to the respiratory tract has not been investigated. We found that spores of A. fumigatus contain five main compounds, tryptoquivaline F, fumiquinazoline C, Questin, monomethylsulochrin and trypacidin.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Fractionation of culture extracts using RP-HPLC and LC-MS showed that samples containing Questin, monomethylsulochrin and trypacidin were toxic to the human A549 lung cell line. These compounds were purified and their structure verified using NMR in order to compare their toxicity against A549 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Trypacidin was the most toxic, decreasing cell viability and triggering cell lysis, both effects occurring at an IC₅₀ close to 7 μM. Trypacidin toxicity was also observed in the same concentration range on human bronchial epithelial cells.
In the first hour of exposure, trypacidin initiates the intracellular formation of nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂).
This oxidative stress triggers necrotic cell death in the following 24 h. The apoptosis pathway, moreover, was not involved in the cell death process as trypacidin did not induce apoptotic bodies or a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential. This is the first time that the toxicity of trypacidin to lung cells has been reported.
Nat Prod Res. 2007 May 20;21(6):487-93.
Anthraquinones, Cdc25B phosphatase inhibitors, isolated from the roots of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb.[Pubmed:
17497420]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three anthraquinones, Cdc25B phosphatase inhibitors, were isolated from the methanolic extract of the roots of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. (Polygonaceae).
CONCLUSIONS:
Anthraquinones, physcion (1), emodin (2), and Questin (3), inhibited the enzymatic activity of Cdc25B phosphatase with IC(50) values of 62.5, 30, and 34 microg mL(-1), respectively. Emodin (2) and Questin (3) strongly inhibited the growth of human colon cancer cells, SW620 with GI(50) values of 6.1 and 0.9 microg mL(-1), respectively.
Commercially available anthraquinones, chrysophanol (4), and rhein (5) also inhibited Cdc25B phosphatase with IC(50) values of 10.7 and 22.1 microg mL(-1), respectively.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1999 Oct;47(10):1426-32.
Immunomodulatory constituents from an ascomycete, Microascus tardifaciens.[Pubmed:
10553639]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Fractionation guided by the immunosuppressive activity of the defatted AcOEt extract of an Ascomycete, Microascus tardifaciens, afforded eight constituents, Questin (emodin 8-O-methylether) (1), rubrocristin (2), 5,7-dihydroxy-4-methylphthalide (3), cladosporin (asperentin) (4), cladosporin 8-O-methylether (5), tradioxopiperazine A [cyclo-L-alanyl-5-isopentenyl-2-(1',1'-dimethylallyl)-L-tryptophan] (6), tradioxopiperazine B [cyclo-L-alanyl-7-isopentenyl-2-(1',1'-dimethylallyl)-L-tryptophan] (7), and asperflavin (8), among which 6 and 7 were new compounds.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1 and 2 showed considerably high immunosuppressive activity, 6 was moderate and, 3, 4, 5, 7 and 8 showed low activity.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;191:152-160.
Inhibitory activities of major anthraquinones and other constituents from Cassia obtusifolia against β-secretase and cholinesterases.[Pubmed:
27321278 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In vitro enzyme assays demonstrated that C. obtusifolia and its major constituents have promising inhibitory potential against AChE, BChE, and BACE1. All Cassiae semen constituents exhibited potent inhibitory activities against AChE and BACE1 with IC50 values of 6.29-109μg/mL and 0.94-190μg/mL, whereas alaternin, Questin, and toralactone gentiobioside exhibited significant inhibitory activities against BChE with IC50 values of 113.10-137.74μg/mL. Kinetic study revealed that alaternin noncompetitively inhibited, whereas cassiaside and emodin showed mixed-type inhibition against BACE1. Furthermore, molecular docking simulation results demonstrated that hydroxyl group of alaternin and emodin tightly interacted with the active site residues of BACE1 and their relevant binding energies (-6.62 and -6.89kcal/mol), indicating a higher affinity and tighter binding capacity of these compounds for the active site of BACE1.
CONCLUSIONS:
The findings of the present study suggest the potential of C. obtusifolia and its major constituents for use in the development of therapeutic or preventive agents for AD, especially through inhibition of AChE, BChE and BACE1 activities.
1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2-methylanthraquinone 3-O-alpha-L-rhamnosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No: CFN95096
CAS No: 87686-88-2
Price: $318/10mg
3,7,25-Trihydroxycucurbita-5,23-dien-19-al
Catalog No: CFN95150
CAS No: 85372-65-2
Price: $318/5mg
Specioside B
Catalog No: CFN95165
CAS No: 126589-95-5
Price: $368/5mg
Deoxy euphorbia factor L1
Catalog No: CFN95340
CAS No: 247099-01-0
Price: $318/10mg
10-O-trans-p-Feruloylscandoside
Catalog No: CFN95392
CAS No: 1428268-72-7
Price: $318/10mg
4'-Hydroxy-3',5,5',6,7,8-hexamethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN95407
CAS No: 85644-03-7
Price: $318/5mg
3'-Hydroxy-2,4,5-trimethoxydalbergiquinol
Catalog No: CFN95410
CAS No: N/A
Price: $413/5mg
5-O-Coumaroylquinic acid
Catalog No: CFN95507
CAS No: 32451-86-8
Price: $318/5mg
Methyl ganoderate A
Catalog No: CFN95550
CAS No: 105742-78-7
Price: $413/5mg
4-Keto-laurifoline
Catalog No: CFN95594
CAS No: N/A
Price: $318/10mg