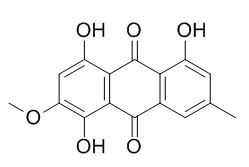
Xanthorin
Xanthorin has anticomplementary activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Chem.2019, 279:80-87
Applied Biological Chemistry 2021, 64(75)
Pak J Pharm Sci.2019, 32(6):2879-2885
Molecules.2023, 28(19):6767.
Chem Biodivers.2023, 20(10):e202300741.
Bioorg Chem.2024, 152:107720.
J Liq Chromatogr R T2025, 2505536.
J Pharmaceut Biomed2020, 178:112894
Kor. J. Herbol.2019, 34(2):59-66
Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia2024, 34:1276-1286.
Related and Featured Products
Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2013, 44(18): 2502-7.
Anti-complementary anthraquinones from Polygonum cuspidatum and their action targets.[Reference:
WebLink]
To study the anti-complementary anthraquinones from Polygonum cuspidatum and their action targets.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The anti-complementary activity-directed isolation was carried out with the hemolysis test as guide. All isolates were evaluated for their in vitro anti-complementary activities. The action targets of the main bioactive constituents were also examined using complement-depleted sera. Ten anthraquinones and three other compounds were isolated from the EtOAc fraction of P.cuspidatum extract, including physcion(1), chrysophanol(2), questin(3), emodin-8-O-β-D-glucoside(4), emodin(5), rhein(6),fallacinol(7), citreorosein(8), Xanthorin(9), isorhodoptilometrin(10), 2, 5-dimethyl-7-hydroxychromone(11), 7-hydroxy-4-methoxy-5-methylcoumarin(12), and 5, 7-dihydroxy-1-isobenzofuranone(13). Compounds 9 and 10 were isolated from the the plants of Polygonaceae for the first time, and compound 9 was the alizarin-type anthraquinone first obtained from P. cuspidatum. Compounds3—9 showed the anti-complementary activity in different degrees, and compound 7 exhibited the most significant activity against the classical and alternative pathway [CH50=(6 ± 2) μg/mL, AP50=(50 ± 5) μg/mL]. The study on the preliminary mechanism revealed that compound 4 interacted with C1q, C2, and C9 in complement activation cascade, while compound 7 acted on C1q, C2, C4, and C9.
CONCLUSIONS:
The anthraquinones are main anti-complementary constituents in P. cuspidatum; and fallacinol(7) is a potential complement inhibitor with strong activity and definite targets, which should be further studied in future.
J Nat Prod. 1999 Sep;62(9):1298-300.
New xanthorin glycosides from a Dermocybe species.[Pubmed:
10514318]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A mixture of the 8-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside of omega-hydroxyXanthorin 1-O-methyl ether (3) and the 8-O-beta-D-gentiobioside of Xanthorin 1-O-methyl ether (4) was isolated from the water-soluble extractives of the Australian toadstool Dermocybe sp. WAT 22963.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 3 and 4 were identified by characterization of their respective peracetyl derivatives 5 and 6.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2008 Sep;56(9):1248-52.
Anthraquinone-benzisochromanquinone dimers from the roots of Berchemia floribunda.[Pubmed:
18758095]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Four novel anthraquinone-benzisochromanquinone dimers, named floribundiquinones A, B, C, and D (1-4), along with six known anthraquinones, 10-(chrysophanol-7'-yl)-10-hydroxychrysophanol-9-anthrane (5), physcion (6), chrysophanol (7), 1,5,8-trihydroxy-3-methyl-anthraquinone (8), aloe-emodin (9), and Xanthorin (10), were isolated from the roots of Berchemia floribunda. Their structures including the absolute axial stereochemistry were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic methods. Floribundiquinones represent a novel carbon skeleton with an anthraquinone-benzisochromanquinone unit.
CONCLUSIONS:
Hepatoprotective activities were evaluated against D-galactosamine-induced toxicity in WB-F344 rat hepatic epithelial stem-like cells.