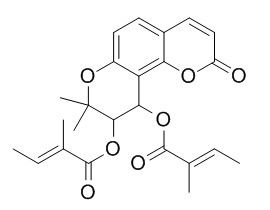
Praeruptorin B
Praeruptorin B has significant important phase II drug-metabolizing enzymes uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase (UGTs) isoforms inhibition activity. Praeruptorin B and praeruptorin A have LC 50 values of 34.5 and121.2 ug/ml, respectively, in Artemia salina test .
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Horticulturae2024, 10(5), 486.
Heliyon.2023, 9(6):e16138.
Biol Pharm Bull.2017, 40(6):797-806
Antioxidants (Basel).2020, 9(2): E119
Antioxidants (Basel).2023, 13(1):12.
Microorganisms.2021, 9(12):2514.
Nat Commun.2023, 14(1):8142.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2017, 482(4):1095-1101
Oncol Rep.2019, 41(4):2453-2463
Mediators Inflamm.2016, 2016:7216912
Related and Featured Products
Phytother Res. 2016 Nov;30(11):1872-1878.
The Inhibition of UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) Isoforms by Praeruptorin A and B.[Pubmed:
27534594 ]
Praeruptorin A (PA) and Praeruptorin B (PB) are two important compounds isolated from Bai-hua Qian-hu and have been reported to exert multiple biochemical and pharmacological activities. The present study aims to determine the inhibition of PA and PB on the activity of important phase II drug-metabolizing enzymes uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase (UGTs) isoforms.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In vitro UGT incubation system was used to determine the inhibition potential of PA and PB on the activity of various UGT isoforms. In silico docking was performed to explain the inhibition difference between PA and PB towards the activity of UGT1A6. Inhibition behaviour was determined, and in vitro-in vivo extrapolation was performed by using the combination of in vitro inhibition kinetic parameter (Ki ) and in vivo exposure level of PA. Praeruptorin A (100 μM) exhibited the strongest inhibition on the activity of UGT1A6 and UGT2B7, with 97.8% and 90.1% activity inhibited by 100 μM of PA, respectively. In silico docking study indicates the significant contribution of hydrogen bond interaction towards the stronger inhibition of PA than PB towards UGT1A6. Praeruptorin A noncompetitively inhibited the activity of UGT1A6 and competitively inhibited the activity of UGT2B7. The inhibition kinetic parameter (Ki ) of PA towards UGT1A6 and UGT2B7 was calculated to be 1.2 and 3.3 μM, respectively. The [I]/Ki value was calculated to be 15.8 and 5.8 for the inhibition of PA on UGT1A6 and UGT2B7, indicating high inhibition potential of PA towards these two UGT isoforms in vivo.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, closely monitoring the interaction between PA and drugs mainly undergoing UGT1A6 or UGT2B7-catalyzed metabolism is very necessary.
Phytother Res . 2016 Nov;30(11):1872-1878.
The Inhibition of UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) Isoforms by Praeruptorin A and B[Pubmed:
27534594]
Abstract
Praeruptorin A (PA) and B (PB) are two important compounds isolated from Bai-hua Qian-hu and have been reported to exert multiple biochemical and pharmacological activities. The present study aims to determine the inhibition of PA and PB on the activity of important phase II drug-metabolizing enzymes uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase (UGTs) isoforms. In vitro UGT incubation system was used to determine the inhibition potential of PA and PB on the activity of various UGT isoforms. In silico docking was performed to explain the inhibition difference between PA and PB towards the activity of UGT1A6. Inhibition behaviour was determined, and in vitro-in vivo extrapolation was performed by using the combination of in vitro inhibition kinetic parameter (Ki ) and in vivo exposure level of PA. Praeruptorin A (100 μM) exhibited the strongest inhibition on the activity of UGT1A6 and UGT2B7, with 97.8% and 90.1% activity inhibited by 100 μM of PA, respectively. In silico docking study indicates the significant contribution of hydrogen bond interaction towards the stronger inhibition of PA than PB towards UGT1A6. Praeruptorin A noncompetitively inhibited the activity of UGT1A6 and competitively inhibited the activity of UGT2B7. The inhibition kinetic parameter (Ki ) of PA towards UGT1A6 and UGT2B7 was calculated to be 1.2 and 3.3 μM, respectively. The [I]/Ki value was calculated to be 15.8 and 5.8 for the inhibition of PA on UGT1A6 and UGT2B7, indicating high inhibition potential of PA towards these two UGT isoforms in vivo. Therefore, closely monitoring the interaction between PA and drugs mainly undergoing UGT1A6 or UGT2B7-catalyzed metabolism is very necessary. Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Keywords: Praeruptorin A; Praeruptorin B; UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs); drug-drug interaction (DDI).
Farmaco. 2001 May-Jul;56(5-7):417-20.
Isolation of praeruptorins A and B from Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn. and their general pharmacological evaluation in comparison with extracts of the drug.[Pubmed:
11482769]
The root of Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn. was extracted with solvents at different polarity obtaining three chemical fractions: aqueous (H2O), n-butanol (BuOH) and ethyl acetate (AcOEt).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
From AcOEt praeruptorin A and Praeruptorin B were isolated by column chromatography on silica gel, using toluene/ethyl acetate as eluent, and identified by 1H and 13C NMR analysis. The extracts and the praeruptorins were tested for gross behavioural effects and acute toxicity in mice; the cytotoxicity on Artemia salina Leach and the antimicrobial activity were also evaluated. None of the tested substances evoked behavioural effects or acute toxicity after oral administration in mice; delayed mortality was observed with AcOEt and praeruptorin A only after intraperitoneal administration of high doses (1 g/kg). In Artemia salina test AcOEt, and praeruptorins
A and Praeruptorin B had LC50 values of 40.2, 121.2 and 34.5 microg/ml, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
AcOEt and praeruptorin A showed antimicrobial activity on Streptococcus agalactiae; their MIC values were 250 and 100 microg/ml, respectively.
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 May;93:86-94.
1H nuclear magnetic resonance based-metabolomic characterization of Peucedani Radix and simultaneous determination of praeruptorin A and praeruptorin B.[Pubmed:
24041522]
As a widely used traditional herbal medicine, it is crucial to characterize the holistic metabolic profile of Peucedani Radix (Chinese name: Qian-hu). However, it is quite arduous to obtain the whole picture of chemical constituents appropriately with the existing analytical techniques that were based on HPLC-UV or LC-MS/MS system.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In present investigation, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy coupled with principal components analysis (PCA) was introduced to metabolomic characterization of Qian-hu crude extracts without any chromatographic separation. In addition, the contents of praeruptorin A (PA) and proaeruptorin B (PB) in Qian-hu were simultaneously determined using quantitative (1)H NMR (q(1)H NMR) spectroscopy. Eighteen reference compounds (1-18), which were purified from this herbal drug extract previously, were recruited for the assignment of the protonic signals in the (1)H NMR spectra. Following PCA, 15 batches of Peucedani Radix were divided into two groups (I and II), and angular-type pyranocoumarins, in particular PA and PB, as well as 5-methoxycoumarin were demonstrated as the predominant markers being responsible for the distinguishment of Qian-hu from different districts. The contents of the two analytes (PA & PB) were calculated by the relative ratio of the integral values of the target peak for each compound to the known amount of the internal standard, formononetin (IS). The lower limits of quantitation were determined as 19.5μg/mL for both PA and PB.
CONCLUSIONS:
The quantitative results indicated that the contents of PA and PB showed quite variable qualities among different extract samples. Above all, (1)H NMR spectroscopy, that could not only provide comprehensive profiles of the metabolites but also achieve convenient determination of praeruptorin A and Praeruptorin B, is a promising means for evaluating the medicinal samples of Peucedani Radix.