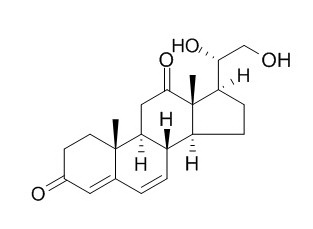
Neridienone B
Neridienone B has significant effects on calcein accumulation. Neridienone exhibits significant leishmanicidal activity against amastigotes of L. mexicana.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2022, 2022:1307173.
Korean Journal of Plant Resources2021, 34(1):52-58.
Sci Rep. 2018, 10590
Plants (Basel).2021, 10(4):702.
Phytother Res.2015, 29(7):1088-96
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(21):13112.
Neurochem Res.2021, s11064-021-03449-0
Planta Med.2016, 82(13):1208-16
Molecules2022, 27(14),4462
Int J Vet Sci Med.2024, 12(1):134-147.
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 2007 Jan;70(1):14-8.
Bioactive pregnanes from Nerium oleander.[Pubmed:
17253842]
A new cholesterol derivative, pentalinonsterol (cholest-4,20,24-trien-3-one, 1), and a new polyoxygenated pregnane sterol glycoside, pentalinonside (2), together with 18 known compounds, including 14 sterols (3-16), three coumarins (17-19), and a triterpene (20), were isolated from a n-hexane partition of a methanol extract of the roots of the Mexican medicinal plant Pentalinon andrieuxii.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Structure elucidation of compounds 1 and 2 was accomplished by spectroscopic data interpretation. All isolates were evaluated in vitro for their antileishmanial activity. Among these compounds, 6,7-dihydroneridienone (15) was found to be the most potent principle against promastigotes of Leishmania mexicana (L. mexicana). The cholesterol analogue, pentalinonsterol (1), together with two known sterols, 24-methylcholest-4,24(28)-dien-3-one (3) and neridienone (16), also exhibited significant leishmanicidal activity in this same bioassay. Compounds 1, 3, 15, 16, cholest-4-en-3-one (4), and cholest-5,20,24-trien-3β-ol (7), showed strong antileishmanial activity against amastigotes of L. mexicana, and 4 was found to be the most potent agent with an IC(50) value of 0.03μM. All the isolates were also evaluated for their cytotoxicity in non-infected bone marrow-derived macrophages, but none of these compounds was found active towards this cell line.
CONCLUSIONS:
The intracellular parasites treated with compounds 1, 3, 4, 15, and 16 were further studied by electron microscopy; morphological abnormalities and destruction of the amastigotes were observed, as a result of treatment with these compounds.
Phytochemistry. 2012 Oct;82:128-35.
Sterols with antileishmanial activity isolated from the roots of Pentalinon andrieuxii.[Pubmed:
22840389]
A new cholesterol derivative, pentalinonsterol (cholest-4,20,24-trien-3-one, 1), and a new polyoxygenated pregnane sterol glycoside, pentalinonside (2), together with 18 known compounds, including 14 sterols (3-16), three coumarins (17-19), and a triterpene (20), were isolated from a n-hexane partition of a methanol extract of the roots of the Mexican medicinal plant Pentalinon andrieuxii.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Structure elucidation of compounds 1 and 2 was accomplished by spectroscopic data interpretation. All isolates were evaluated in vitro for their antileishmanial activity. Among these compounds, 6,7-dihydroneridienone (15) was found to be the most potent principle against promastigotes of Leishmania mexicana (L. mexicana). The cholesterol analogue, pentalinonsterol (1), together with two known sterols, 24-methylcholest-4,24(28)-dien-3-one (3) and neridienone (16), also exhibited significant leishmanicidal activity in this same bioassay. Compounds 1, 3, 15, 16, cholest-4-en-3-one (4), and cholest-5,20,24-trien-3β-ol (7), showed strong antileishmanial activity against amastigotes of L. mexicana, and 4 was found to be the most potent agent with an IC(50) value of 0.03μM. All the isolates were also evaluated for their cytotoxicity in non-infected bone marrow-derived macrophages, but none of these compounds was found active towards this cell line.
CONCLUSIONS:
The intracellular parasites treated with compounds 1, 3, 4, 15, and 16 were further studied by electron microscopy; morphological abnormalities and destruction of the amastigotes were observed, as a result of treatment with these compounds.