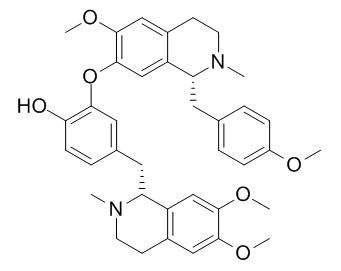
Neferine
Neferine, a autophagy inducer, which has anti-amnesic, sedative, anti-anxiety, antidepressant, cardioprotective, anti- pulmonary fibrosis,anti-cancer, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities. It inhibited ChEs, BACE1, NF-kappaB, PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, Neferine has effects similar to rosiglitazone in decreasing fasting blood glucose, insulin, TG, TNF-alpha and enhancing insulin sensitivity in insulin resistant rats.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Toxins (Basel).2021, 13(12):898.
Korean Herb. Med. Inf.2020, 8(2):205-213
J Insect Sci.2020, 20(5):18.
Food Research International2016, 106-113
Sci Rep.2025, 15(1):29590.
Phytomedicine.2021, 83:153483.
Environ Toxicol.2019, 34(12):1354-1362
Biomed Chromatogr.2022, 36(11):e5462.
J Pain Res.2022, 15:3469-3478.
NanoBioScience2024, v13:3:115.
Related and Featured Products
Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb 29;677(1-3):47-54.
Neferine, an alkaloid ingredient in lotus seed embryo, inhibits proliferation of human osteosarcoma cells by promoting p38 MAPK-mediated p21 stabilization.[Pubmed:
22227330 ]
Identification of natural products that have antitumor activity is invaluable to the chemoprevention and therapy of cancer. The embryos of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seeds are consumed in beverage in some parts of the world for their presumed health-benefiting effects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this report we studied the effects of Neferine, a major alkaloid component in lotus embryos, on human osteosarcoma cells and the underlying mechanisms. We found that Neferine possessed a potent growth-inhibitory effect on human osteosarcoma cells, but not on non-neoplastic human osteoblast cells. The inhibitory effect of Neferine on human osteosarcoma cells was largely attributed to cell cycle arrest at G1. The induction of G1 arrest was p21(WAF1/CIP1)-dependent, but was independent of p53 or RB (retinoblastoma-associated protein). The up-regulation of p21 by Neferine was due to an increase in the half-life of p21 protein. We examined four kinases that are known to affect the stabilization of p21, and found that p38 MAPK and JNK were activated by Neferine. However, only SB203580 (an inhibitor of p38), but not SP600125 (the inhibitor of JNK), can attenuate the up-regulation of p21 in response to Neferine. Furthermore, the p21-stabilizing effect of Neferine was abolished when p38 was silenced by RNA interference. Finally, we showed that Neferine treatment led to an increased phosphorylation of p21 at Ser130 that was dependent on p38.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results for the first time showed a direct antitumor effect of Neferine, suggesting that consumption of Neferine may have cancer-preventive and cancer-therapeutic benefit.
Biofactors . 2016 Jul 8;42(4):407-17.
Neferine prevents NF-κB translocation and protects muscle cells from oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by hypoxia[Pubmed:
27041079]
Abstract
Neferine (Nef), a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid from lotus seed embryo has a wide range of pharmacological activities. Possible molecular mechanism for the cytoprotective action of Nef during hypoxic stress has not been explored till now. Hence, this is an attempt to elucidate the molecular mechanism involved in the Nef mediated cytoprotection on hypoxia-induced cell injury. Cytoprotective dose of Nef in muscle cells (Human rhabdomyosarcoma cells) exposed to hypoxia was determined by MTT assay. Nef at 500 nM offered better cytoprotection and was used for all the experiments. ROS, intracellular calcium accumulation and mitochondrial membrane (ΔψM) potential were measured using fluorescent probes. Further, we evaluated the effect Nef on hypoxia induced inflammatory and apoptotic responses by FACS and analyzing the expression patterns of NF-κB, COX-2, HIF-1α, caspase-3, caspase-9, Bcl2, and Bax. The results of this study revealed that pretreatment of the cells with Nef significantly decreased the ΔψM and ROS in the cells subjected to hypoxia. Further, Nef inhibited NF-κB there by inhibiting the expression of its downstream regulator COX-2, while it induced the functional HIF-1α expression. The results also indicate that Nef significantly inhibited the ROS dependent mitochondrial mediated apoptosis induced during hypoxia. The cytoprotection elicited by Nef in a model of hypoxia induced cell death involves both anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic response. These results suggest that Nef may be used as prophylactic agent against the hypoxic challenge. © 2016 BioFactors, 42(4):407-417, 2016.
Keywords: HIF-1α; apoptosis; hypoxia; Neferine; reactive oxygen species.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Jul 6;124(1):98-102.
Neferine enhances insulin sensitivity in insulin resistant rats.[Pubmed:
19527823 ]
Neferine was isolated from green seed embryo of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn which has been used as an anti-obesity agent in traditional Chinese herbal medicine.
This study was conducted to investigate the effects of Neferine on enhancing insulin sensitivity in insulin resistant rats compared with rosiglitazone and to potentially reveal its role in mediating the anti-obesity properties of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Fasting blood glucose (FBG), fasting blood insulin (FINS), triglycerides (TG) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) were measured, and the oral glucose tolerance test for 2-h plasma glucose level (2-h PG) was carried out. The glucose infusion rate (GIR) was used to measure the insulin sensitivity by hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp technique.
The levels of FBG, FINS, TG, TNF-alpha and 2-h PG all decreased significantly in the rosiglitazone and Neferine groups compared with the insulin resistance (IR) model group. Neferine diminished the 2-h PG more than did rosiglitazone treatment. Compared to the IR model group, the treatments of Neferine and rosiglitazone remarkably increased GIRs but no difference between these two treatments themselves was evident.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data demonstrate that Neferine has effects similar to rosiglitazone in decreasing fasting blood glucose, insulin, TG, TNF-alpha and enhancing insulin sensitivity in insulin resistant rats.
Phytomedicine. 2008 Dec;15(12):1117-24.
Effects of extracts and neferine from the embryo of Nelumbo nucifera seeds on the central nervous system.[Pubmed:
19010651 ]
The effects of embryos of the seeds of Nelumbo nucifera on the central nervous system were studied in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
MeOH extracts of embryos of Nelumbo nucifera seeds significantly inhibited locomotor activity in mice. The MeOH extract was successively partitioned between H(2)O and n-hexane, between H(2)O and CHCl(3), and between H(2)O and n-BuOH. CHCl(3) extracts strongly inhibited locomotor activity in mice, although other extracts had no effect on locomotor activity. The main alkaloid of CHCl(3) extracts, Neferine, dose-dependently inhibited locomotor activity in mice. Neferine induced hypothermia in mice and apparently potentiated thiopental-induced sleeping time. An anxiolytic, diazepam, decreased locomotor activity, rectal temperature and enhanced sleep elicited by thiopental, similar to Neferine. In addition, Neferine and diazepam showed anti-anxiety effects in the elevated plus maze test. Neferine did not affect muscle coordination by the rota-rod test. Neferine did not affect strychnine- nor picrotoxin-induced seizure. In contrast, diazepam had apparent muscle relaxant and anti-convulsant effects.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Neferine has several central effects and that Neferine may participate in the efficacy of the sedative effects of embryos of the seeds of Nelumbo nucifera. The mechanisms of the sedative effects of Neferine are not similar to those of diazepam.
Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2013 Jun;13(2):168-79.
Protective effect of neferine against isoproterenol-induced cardiac toxicity.[Pubmed:
23274852 ]
The present study was designed to investigate the cardioprotective effect of Neferine against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Neferine was given orally for 30 days, and isoproterenol was injected subcutaneously for 2 days. Histopathological examination of heart tissue of isoproterenol-treated rats showed myocardial necrosis. Biochemical analysis of isoproterenol-treated rats showed significant increase in the serum marker enzymes--creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, and aspartate transaminase and increased serum glycoprotein components with a concomitant decrease in the heart tissue homogenate when compared to control. Increased lipid peroxidation and decreased antioxidants reduced glutathione, superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione-S-transferase, glutathione peroxidase and altered lipid profile in serum and tissue was also recorded in the isoproterenol-treated rats, whereas the rats which received Neferine pre-treatment followed by isoproterenol injection showed minimal histological changes, absence of inflammation, and a significant decrease in the serum marker enzymes and serum glycoprotein components with a concomitant increase in the heart tissue homogenate when compared to isoproterenol group. Neferine pre-treatment restored the altered biochemical parameters and lipid profile to near normal.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results of the present study showed that Neferine exerts strong antioxidant property against isoproterenol-induced oxidative stress and can be used as a potent cardioprotective agent against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction.
Oncotarget . 2016 Sep 20;7(38):61703-61715.
Neferine inhibits proliferation and collagen synthesis induced by high glucose in cardiac fibroblasts and reduces cardiac fibrosis in diabetic mice[Pubmed:
27533252]
Abstract
Cardiac fibrosis is a common pathological process accompanying diabetes mellitus. In this report, we studied the effects of Neferine (a major bisbenzylisoquinline alkaloid derived from lotus embryos) on cardiac fibrosis induced by diabetes mellitus, as well as the underlying molecular pathways. In vivo, type 1 diabetes mellitus was induced in mice by administering streptozotocin. Diabetic mice were treated with Neferine through oral gavage, and cardiac function was assessed using echocardiography. Total collagen deposition was assessed by Masson's trichrome and Picrosirius staining. In vitro, cardiac fibroblasts were cultured in normal or high-glucose medium with or without Neferine. Neferine attenuated left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling and reduced collagen deposition in diabetic mice. In vitro, Neferine inhibited cardiac fibroblast proliferation, migration, and differentiation into myofibroblasts. In addition, Neferine reduced high-glucose-induced collagen production and inhibited TGF-β1-Smad, ERK and p38 MAPK signaling activation in cardiac fibroblasts. These results suggest that Neferine may have antifibrogenic effects in diabetes-related cardiac fibrosis.
Food Chem. 2013 Dec 15;141(4):3598-605.
Neferine from Nelumbo nucifera induces autophagy through the inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and ROS hyper generation in A549 cells.[Pubmed:
23993526 ]
Previously we have reported that Neferine from the medicinal plant Nelumbo nucifera, inhibited cancer cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis. The present study was focused on the action mechanism of Neferine in inducing autophagy in lung cancer cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Neferine markedly inhibited A549 cell proliferation in a dose dependent manner. Acidic vesicular accumulation was observed in Neferine treated cells as an indication of autophagy. Neferine could induce the conversion of LC3B-I to LC3B-II without affecting the expression levels of PI3KCIII and Beclin1. It has been observed that Neferine mediated autophagy is dependent on inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling by Neferine. Neferine treatment could also lead to the ROS hypergeneration and depletion of cellular antioxidant, GSH. The results demonstrate that Neferine-induced autophagy is mediated through ROS hypergeneration and mTOR inhibition.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the present study unveils a novel mechanism of action of Neferine on lung cancer cells in the induction of autophagy.
J Cell Biochem. 2017 Sep;118(9):2865-2876
Neferine Potentiates the Antitumor Effect of Cisplatin in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells Via a Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis Pathway.[Pubmed:
28214344]
Cell lines: A549 cells
Concentrations: 1-30μM
Incubation Time: 12h, 24h, 48h and 72h
Method:
The cells are seeded at a density of 1x104 cells/well, and were allowed to attach for overnight in a CO2 incubator. Cells are then treated with different concentrations of cisplatin/Neferine and incubated for different time periods (12h, 24h, 48h and 72h). After the treatment period, 20 μl of MTT reagent (5mg/ml) in 100 μl medium is added and incubated at 37°C for 4 h after aspirating the medium with Neferine and cisplatin. Then the media with MTT is flicked off, the purple formazan crystals are dissolved in 200 μl of DMSO and the absorbance is recorded with a microquant plate reader at 570 nm.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Feb 10;627(1-3):304-12.
Neferine, a bisbenzylisoquinline alkaloid attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.[Pubmed:
19909737 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we evaluated the potential anti-fibrotic property of Neferine, a bisbenzylisoquinline alkaloid extracted from the seed embryo of Nelumbo mucifera Gaertn. Intratracheal bleomycin administration resulted in pulmonary fibrosis 14 and 21 days posttreatment, as evidenced by increased hydroxyproline content in bleomycin group (255.77+/-97.17 microg/lung and 269.74+/-40.92 microg/lung) compared to sham group (170.78+/-76.46 microg/lung and 191.24+/-60.45 microg/lung), and the hydroxyproline was significantly suppressed (193.07+/-39.55 microg/lung and 201.08+/-71.74 microg/lung) by Neferine administration (20mg/kg, b.i.d). The attenuated-fibrosis condition was also validated by histological observations. Biochemical measurements revealed that bleomycin caused a significant decrease in lung superoxidae dismutase (SOD) activity, which was accompanied with a significant increase in malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity on the 7th and 14th days. However, Neferine reversed the decrease in SOD activity as well as the increase in MDA and MPO activity. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and radio-immunity assay showed that treatment with Neferine alleviated bleomycin-induced increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-6 and endothelin-1 in plasma or in tissue. Additionally, Neferine blocked bleomycin-induced increases of NF-kappaB in nuclear extracts and TGF-beta(1) in total protein extracts of murine RAW264.7 macrophages.
CONCLUSIONS:
In summary, Neferine attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in vitro and in vivo. The beneficial effect of Neferine might be associated with its activities of anti-inflammation, antioxidation, cytokine and NF-kappaB inhibition.
Life Sci. 2010 Sep 25;87(13-14):420-30.
Anti-amnesic activity of neferine with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities, as well as inhibition of ChEs and BACE1.[Pubmed:
20736023 ]
the multifunctional potential of Neferine derived from the embryo of Nelumbo nucifera seeds for the age-related neurodegenerative disorders, in vivo anti-amnesic activities and in vitro cholinesterases (ChEs)- and β-site APP cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1)-inhibitory activities, as well as anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities were investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
in vivo anti-amnesic activities were performed via the passive avoidance, Y-maze, and Morris water maze tasks in a scopolamine-induced amnesia model. The cell-free antioxidant capacities were evaluated by in vitro scavenging activities against 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS) radicals, and peroxynitrite (ONOO(-)), as well as inhibitory activities against nitric oxide (NO), superoxide anion (O(2)(-)), lipid peroxidation, and ONOO(-)-mediated tyrosine nitration. The intracellular antioxidant capacities were also determined via inhibitory activities of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced NO generation and NF-κB activation in RAW 264.7 cells.
Neferine showed significant improvement in cognitive impairment in scopolamine-induced amnesia animal models and moderate inhibitory activities in ChEs and BACE1 assays. In addition, it exhibited notable scavenging activities against DPPH, ABTS, NO, and O(2)(-) radicals, as well as ONOO(-). Neferine also demonstrated remarkable inhibitory activity against lipid peroxidation and protein nitration in cell-free antioxidant assays and moderate inhibitory activity of NO generation with exceptional suppression of NF-κB activation in cell-based assays.
CONCLUSIONS:
the results demonstrate that the anti-amnesic effect of Neferine may be mediated via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities, as well as inhibition of ChEs and BACE1.