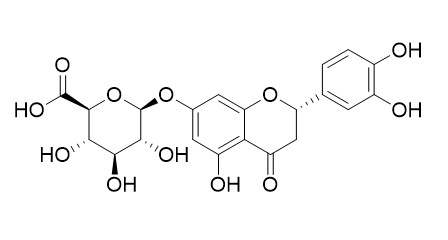
Eriodictyol 7-O-glucuronide
Eriodictyol 7-O-glucuronide can be considered as potent inhibitors for DENV NS2B/NS3pro for the development of anti-dengue drugs.
Antioxidants.Cytotoxic.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol.2019, 66:109-115
Front Pharmacol.2022, 13:919230.
Applied Biological Chemistry2022, 65(77).
J Pharm Pharmacol.2022, rgac033.
Food Chem Toxicol.2023, 176:113785.
Virus Res.2023, 335:199199.
Mediators Inflamm. 2016, 2016:6189590
Int Immunopharmacol.2020, 90:107268.
J Nat Prod.2017, 80(4):854-863
Molecules.2016, 21(10)
Related and Featured Products
Virusdisease . 2016 Sep;27(3):220-225
Identification of new potent inhibitors of dengue virus NS3 protease from traditional Chinese medicine database[Pubmed:
28466032]
Dengue virus (DENV) has emerged as an increasing fitness problem in the world for which no specialized drug is available. The non-structural protein NS3 protease of DENV has already been recognized as a potential therapeutic target for the discovery and development of novel antiviral agents against DENV infections. In this study, we employed the virtual screening technique to explore the potent inhibitors of DENV NS2B/NS3pro from Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) database. Total 200 inhibitors from TCM against DENV NS3pro were screened and only five TCM compounds like Eriodictyol 7-O-glucuronide, luteolin 8-C-beta-glucopyranoside, (-)-epicatechin-3-O-gallate, 6-O-trans-p-coumaroylgeniposide and luteolin-7-O-glucoside were selected for further analysis which showed binding energies, -7.000, -7.380, -7.380, -7.440 and -7.440 kcal/mol, respectively. The findings of this study suggest that these five TCM compounds can be considered as potent inhibitors for DENV NS2B/NS3pro for the development of anti-dengue drugs.
Int J Mol Sci . 2020 Mar 6;21(5):1828
JA-Ile-macrolactone 5b Induces Tea Plant ( Camellia sinensis) Resistance to Both Herbivore Ectropis obliqua and Pathogen Colletotrichum camelliae[Pubmed:
32155845]
Jasmonates (JAs), the group of lipid-derived hormones, were found to control the defense responses in a myriad of plants. Meaningfully, the macrolactones of 12-hydroxy jasmonate isoleucine (12OH-JA-Ile) were reported to induce the defensive response of wild tobacco. However, little to nothing has been known about the elicitation effect of JA-Ile-macrolactones on woody plants to harmful organisms, let alone its underlying mechanisms. Here, we first optimized the synthetic routine using mild toxic reagent isobutyl chloroformate instead of ethyl chloroformate for conjugation, and we used acetonitrile (MeCN) instead of ethyl alcohol for the better dissolution of p-toluenesulfonic acid (p-TsOH) to gain JA-Ile-macrolactones. JA-Ile-macrolactone 5b-treated tea plants significantly inhibited the larvae weight gain of Ectropis obliqua larvae and the lesions caused by Colletotrichum camelliae. Furthermore, the expression level of CsOPR3 was significantly upregulated in 5b-treated leaves. Meanwhile, 5b reduced the accumulation of Eriodictyol 7-O-glucuronide (EDG) in tea plants, which was confirmed to promote the growth rate of E. obliqua larvae by artificial diet assay. In conclusion, our study proved that the exogenous application of 5b could induce the tea plant resistance both to herbivore E. obliqua and pathogen C. camelliae, and EDG was identified as one of the secondary metabolites that could influence the growth rate of E. obliqua, but it did not directly influence the infection of C. camelliae in vitro. Further research should be carried out to clarify the mechanism through which 5b induces tea plant resistance to C. camelliae.
Molecules . 2019 Dec 5;24(24):4457.
Phytochemical Fingerprinting and In Vitro Bioassays of the Ethnomedicinal Fern Tectaria coadunata (J. Smith) C. Christensen from Central Nepal[Pubmed:
31817382]
Tectaria coadunata, an ethnomedicinal fern used in Nepal to treat a large number of diseases, has been poorly studied with regard to its phytochemical composition and possible bioactivity. This study was performed with the aim of supporting traditional medicine as a new source of bioactive constituents. Phytochemical compositions of methanol extracts were determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), liquid chromatography-diode array detector-mass spectrophotometry (LC-DAD-MS), and liquid chromatography-fluorescence-mass spectrometry. Quali-quantitative data revealed large amount of procyanidins, mainly of the A-type, as well as eriodictyol-7-O-glucuronide and luteolin-7-O-glucoronide as main constituents. The antioxidant, cytotoxic, and inhibitory activity of five enzymes that are implicated in human diseases was evaluated for the extract and fractions. High free-radical scavenging activity in 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) (ABTS) assays and inhibitory activities against cholinesterases and tyrosinase were observed. Furthermore, a moderate cytotoxic effect was observed on the 2008 and BxPC3 cell lines. Overall results showed potential usefulness of this fern as a source of phytochemicals for pharmaceutical uses.
Nat Prod Commun . 2015 Jun;10(6):937-40.
Water Extract of Mentha x villosa: Phenolic Fingerprint and Effect on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury[Pubmed:
26197521]
Qualitative analysis of the water extract of Mentha x villosa Huds. leaves was performed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and quantitative analysis was made by reverse-phase liquid chromatography coupled with photodiode array detection (LC-DAD). Sixteen phenolic compounds were identified and quantified consisting of 8 phenolic acids/derivatives and 8 flavonoid glycosides (quinic acid, chlorogenic acid, coumaroyl-hexoside, caffeic acid, coumaroylquinic acid, lithospermic acid, rosmarinic acid, salvianolic acid A, luteolin-7-O-glucuronide, luteolin-7-O-glucoside, luteolin-7-O-rutinoside, eriodictyol-7-O-rutinoside, apigenin-7-O-glucuronide, kaempferol-3-O-glucuronide, chrysoeriol-7-O-rutinoside, and hesperetin-7-O-rutinoside). Luteolin-7- O-rutinoside (25.6 ± 0.7 mg/g dry extract) and rosmarinic acid (17.9 ± 0.4 mg/g dry extract) were the most abundant. High antioxidant activity of this phenolic-rich water extract was confirmed in vitro by DPPH and ABTS tests and ex vivo in the ischemia-reperfusion injured rat superior mesenteric artery. Thus, the water extract of M. x villosa leaves seems to be a promising agent in prevention of tissue injury caused by oxidative stress.
Chem Biodivers . 2007 Feb;4(2):154-62.
Chemosystematic value of flavonoids from Crataegus x macrocarpa (Rosaceae) with special emphasis on (R)- and (S)-eriodictyol-7-O-glucuronide and luteolin-7-O-glucuronide[Pubmed:
17311228]
The chemotaxonomic investigation of Crataegus x macrocarpa, a hybrid of C. laevigata and C. rhipidophylla, presents the qualitative and quantitative composition of its flavonoid pattern in relationship to its parent species for the first time. Six flavonoids were identified as vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside (1), vitexin (2), isovitexin (3), rutin (4), hyperoside (5), and isoquercitrin (6). Furthermore, two flavonoids were isolated from C. x macrocarpa and identified as a diastereoisomeric mixture of (R)- and (S)-eriodictyol-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide (7) and luteolin-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide (8) by means of 1D- and 2D-NMR, MS, and UV experiments. Compounds 7 and 8 were isolated for the first time from Crataegus species. While missing in C. laevigata, their occurrence in C. rhipidophylla additionally emphasizes its chemotaxonomic relationship to C. x macrocarpa.