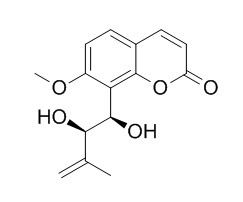
Murrangatin
Murrangatin may be a valuable anti-tumor-promoting agent, it
can significantly inhibit Epstein–Barr virus early antigen (EBV–EA) activation, and preserve the high viability of Raji cells, it also exhibits cytotoxicity against cholangiocarcinoma cell line, KKU-100. Murrangatin exhibits antibacterial activity against P. gingivalis (ATCC 33277). Murrangatin also shows soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity with IC50 values 13.9±6.5uM. Murrangatin and murracarpin may be a new backbone for developing inhibitors of cyclooxygenase 2, they show chondroprotective activity by downregulation of interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factorα, prostaglandins E2,and matrix metalloproteinases -13, and both of them may be a new backbone for developing inhibitors of cyclooxygenase 2.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
EXCLI J.2023, 22:482-498.
Molecules.2022, 27(7):2116.
Foods.2022, 11(12):1773.
Enzyme Microb Technol.2022, 161:110111.
FUTURE VIROLOGYVOL.2023, 18(5).
Lab Chip.2018, 18(6):971-978
Nutrients.2022, 14(16):3393.
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(8):4211.
J Ethnopharmacol.2017, 206:73-77
The Korea Journal of Herbology2016, 29-35
Related and Featured Products
J.Intercult.Ethnopharmacol.,2013; 2(2):91-8.
Chondroprotective evaluation of two natural coumarins: murrangatin and murracarpin.[Reference:
WebLink]
To evaluate the chondroprotective activity of Murrangatin and murracarpin from the leaves of Murraya exotica.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Column chromatography was employed to separate the compounds; interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor α, prostaglandins E2, and matrix metalloproteinases-13 were determined by ELISA; the docking with cyclooxygenase 2 was investigated by AutoDock 4.2 software. Murrangatin and murracarpin both significantly down-regulated the concentrations of interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor α, prostaglandins E2 in the rat osteoarthritis serum and prostaglandins E2 and matrix metalloproteinases-13 in the osteoarthritis chandrocytes cultured solution. The docking results showed that they shared a similar binding conformation with that of Indomethacin. Murrangatin and murracarpin both had lower affinity with cyclooxygenase 2, probably due to lack of carboxyl group coordinating to Arg120.
CONCLUSIONS:
Both Murrangatin and murracarpin show chondroprotective activity by downregulation of interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor α, prostaglandins E2, and matrix metalloproteinases-13, and both of them might be a new backbone for developing inhibitors of cyclooxygenase 2.
Cancer Lett. 1999 Apr 26;138(1-2):87-92.
Anti-tumor-promoting effects of 8-substituted 7-methoxycoumarins on Epstein-Barr virus activation assay.[Pubmed:
10378778]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In a search for anti-tumor-promoting agents, we carried out a primary screening of twenty-nine 8-substituted and four 6-substituted derivatives of 7-methoxycoumarins isolated from plants of the Murraya and/or Citrus species (Rutaceae), examining their possible inhibitory effects on Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) activation induced by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) in Raji cells. This investigation indicated that the prenyl (3-methyl-2-butenyl) or 2-hydroxy-3-methylbutyl (or butenyl) unit as an isoprenoid moiety at C-8 on the 7-methoxycoumarin nucleus plays an important role in the anti-tumor-promoting activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Some of the 8-substituted 7-methoxycoumarins isolated from Murraya species, Murrangatin (7), minumicrolin (10) and chloticol (18), were found to significantly inhibit EBV-EA activation, and preserved the high viability of Raji cells, suggesting that 7, 10 and 18 might be valuable anti-tumor-promoting agents.
Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015 Nov;28(6):1947-51.
Coumarins and flavonoid from Murraya paniculata (L.) Jack: Antibacterial and anti-inflammation activity.[Pubmed:
26639491]
The ethyl acetate extract of leaves of Murraya paniculata (L.) Jack was described in the previous in vitro study on the inhibition effect on the growth of periodontopathic bacteria and the reduction of cytokines from LPS-stimulated macrophages.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, four coumarins including Murrangatin (1), Murrangatin acetate (2), murranganonesenecionate (3), micropubescin (4) and one flavonoid, 3', 4', 5', 7-tetramethoxyflavone (5) were isolated from the leaves of ethyl acetate extract of M. paniculata. MTT assay was used to test cytotoxicity on human gingival fibroblast and monocytes. The isolated compounds were evaluated for their antibacterial effect against Porphyromonas gingivalis (ATCC33277) and anti-inflammation on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammation using monocyte cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
All isolated compounds exhibited antibacterial activity against P. gingivalis (ATCC 33277). Murranganonesenecionate (3) was highly potent anti-inflammation properties. The coumarin constituents from M. paniculata leaves might be potential lead molecules for the development of antimicrobial drugs for treating periodontal disease.
Pmio, 2016, 3(03):e68-e71.
Coumarins Isolated from Murraya paniculata in Vietnam and Their Inhibitory Effects against Enzyme Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH).[Reference:
WebLink]
In the search for bioactive constituents from Vietnam medicinal plants, the leaves and stems of Murraya paniculata collected in HoaBinh Province, Vietnam were selected for chemical investigation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
From the n-hexane fraction, two sterols, including β-sitosterol (6) and stigmasterol (7), and from the chloroform fraction, five coumarins, including mexoticin (1), omphalocarpin (2), Murrangatin (3), kimcuongin (4), and murracarpin (5), were obtained. The structures of the isolated compounds were determined from ESI-MS, HR-ESI-MS, and NMR (1D and 2D) spectroscopic data. Coumarins (1–5) were elucidated for inhibitory effects against soluble epoxide hydrolase. Among them, coumarins (2–4) showed soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity with IC50 values 2.265±654.7, 13.965±656.5, and 3.265±654.56508M, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
A kinetic study of the five coumarins revealed the noncompetitive enzymatic mode for 3 and 4, and a mixture of competitive/noncompetitive enzymatic modes for coumarin 2. Using molecular modelling, the coumarin kimcuongin (4) showed the best binding outline into active sites of human soluble epoxide hydrolase.for 3 and 4, and a mixture of competitive/noncompetitive enzymatic modes for coumarin 2. Using molecular modelling, the coumarin kimcuongin (4) showed the best binding outline into active sites of human soluble epoxide hydrolase.
Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Apr;34(4):527-31.
C-7 oxygenated coumarins from the fruits of Micromelum minutum.[Pubmed:
21544717 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new 7-oxygenated coumarin, 7-demethylmurralonginol isovalerate (1), and a new natural product, murralonginol (2), together with seven known 7-oxygenated coumarins, murralonginol isovalerate (3), murralongin (4), micromelin (5), scopoletin (6), microminutin (7), Murrangatin (8), and minumicrolin (9), were isolated from the fruits of Micromelum minutum. The structures of these compounds were established on the basis of their 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic data.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among these isolates, compounds 2 and 4 - 9 exhibited cytotoxicity against cholangiocarcinoma cell line, KKU-100.