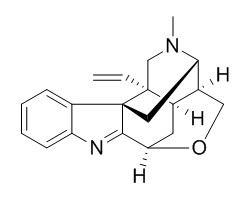
Koumine
Koumine shows potent anti-tumor, anxiolytic, antistress, antipsoriatic, and analgesic activities, it also protects against the development of arthritis in Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) animal models.Koumine can induce apoptosis of LoVo cells in a time-dependent manner and inhibit the DNA synthesis in LoVo cells, thereby blocking the cell cycle from G1 to S phase.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Ethnopharmacol.2022, 289:115018.
Pharmaceutics.2023, 15(9):2355.
Int J Cosmet Sci.2023, 45(2):155-165.
Konkuk University2023, 29:4634721
J Herbmed Pharmacol.2018, 7(4):280-286
J Biol Chem.2021, 297(6):101362.
Molecules.2020, 25(7):1625.
Planta Med.2016, 82(13):1208-16
Antioxidants2022, 11(2),234.
Molecules.2021, 26(4):1084.
Related and Featured Products
Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Jan 6.
Apoptotic Effect of Koumine on Human Breast Cancer Cells and the Mechanism Involved.[Pubmed:
25561287]
Koumine is an alkaloid separated from traditional Chinese herb Gelsemium elegans.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, anticancer activity and underlying mechanisms were investigated with an extract using human breast cancer cells. The survival rate was reduced in a concentration- and time-dependent manner as assessed by MTT assay. After incubation for 48 h, typical apoptotic morphological changes were observed by Hoechst 33258 dye assay. Flow cytometry result revealed that the treatment obviously induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. Furthermore, Western blotting demonstrated the down-regulation of protein expression of Bcl-2, whereas Bax and caspase-3 expressions were up-regulated.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, we propose that Koumine has the potential to be a future breast cancer chemotherapeutic agent.
Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao. 2005 May;25(5):562-4.
Effect of koumine on proliferation of murine CD4+ T cells purified by magnetic-activated cell sorting in vitro.[Pubmed:
15897137]
To assess the separation efficiency of magnetic-activated cell sorting in the purification of CD4+ T cells from murine spleen, and observe the effects of Koumine on the proliferation of the separated cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
CD4+ T cells were isolated from murine spleen by magnetic-activated cell sorting (MiniMACS). Fluorescence-activated cell sortering was employed to determine the purity of CD4+ T cells before and after the separation procedure followed by evaluation of the cell viability using trypan blue staining. Concanavalin A- (ConA, 5 microg/ml) or phytahematoagglutinin (PHA,1 mg/ml)-induced murine T cells were treated with different concentrations of Koumine (10-320 microg/ml), and their proliferation was determined by MTT colorimetry, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to measure IL-2 level in the cell culture supernatant.
The purity of CD4+ T cells reached (90.3+/-5.8)% after the purification with a cell viability of (94.9+/-3.6)%. Koumine (20-320 microg/ml) dose-dependently inhibited ConA- or PHA-induced proliferation of murine lymphocytes as compared with the controls (P<0.05). Koumine (20, 100, and 200 microg/ml) significantly decreased the level of IL-2 in comparison with the control group (P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:
CD4+ T cells of high purity can be obtained from murine spleen using MiniMACS without impairing the viability of the cells. Koumine significantly inhibits the proliferation of murine CD4+ T cells due to its immunosuppressive effect and inhibition of IL-2 secretion.
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 May;101(3):504-14.
Effects of koumine, an alkaloid of Gelsemium elegans Benth., on inflammatory and neuropathic pain models and possible mechanism with allopregnanolone.[Pubmed:
22366214 ]
Crude alkaloidal extraction from Gelsemium elegans Benth. produces analgesic property. However, its clinical utility has been obstructed by its narrow therapeutic index.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we investigated the potential of Koumine, a monomer of Gelsemium alkaloids, to reduce both inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Interestingly, allopregnanolone, a neurosteroid, appeared to mediate the reduction of neuropathic pain. The potential anti-inflammatory pain effects of Koumine were evaluated by acetic acid-, formalin- and complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) -induced nociceptive behaviors in mice. Chronic constriction injury (CCI) and L5 spinal nerve ligation (L5 SNL), inducing thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in rats, were used to test whether repeated treatment of Koumine ameliorated neuropathic pain. Finally, we explored if Koumine altered the level of neurosteroids in rat spinal cord of CCI neuropathy using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Koumine dose-dependently reduced the acetic acid-induced writhes and formalin-induced licking/biting time of Phase II in mice. Repeated administrations of Koumine also dose-dependently reversed the CFA-, CCI- and L5 SNL-induced thermal hyperalgesia, as well as, CCI- and L5 SNL-induced mechanical allodynia in rats. The level of allopregnanolone, but not pregnenolone, in the L5-6 spinal cord was elevated by repeated treatment of Koumine in CCI-induced neuropathic rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrate that Koumine has a significant analgesic effect in rodent behavioral models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain, and that the reduction in neuropathic pain may be associated with the upregulation of allopregnanolone in the spinal cord.
Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao. 2003 Sep;23(9):911-3.
Study of koumine-induced apoptosis of human colon adenocarcinoma LoVo cells in vitro.[Pubmed:
13129717]
To study the apoptosis-inducing effect of Koumine on human colon adenocarcinoma LoVo cells in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After Koumine (50 mmol/L) treatment in vitro, the LoVo cells were examined under light microscope, transmission electron microscope and fluoroscope respectively for apoptosis, and the cell cycle distribution was analyzed using flow cytometry.
The percentage of apoptotic cells increased in a time-dependent manner after the cells were treated with Koumine, whose action exhibited remarkable cell cycle specificity. The percentage of LoVo cells in G(0)/G(1) phase rose from 31.3% to 42.3% and the percentage of cells in S phase fells from 62.0% to 38.7%.
CONCLUSIONS:
Koumine can induce apoptosis of LoVo cells in a time-dependent manner and inhibit the DNA synthesis in LoVo cells, thereby blocking the cell cycle from G1 to S phase.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37(5):858-64.
Anti-allodynic and neuroprotective effects of koumine, a Benth alkaloid, in a rat model of diabetic neuropathy.[Pubmed:
24790009 ]
Diabetic neuropathy is characterized by progressive degeneration of nerve fibers associated with diabetes mellitus. Antidepressants and anticonvulsants are the mainstay of pharmacological treatment, but are often limited in effectiveness against the core clinical feature of pain. In the current study, we examined the potential effects of Koumine, a Gelsemium elegans Benth alkaloid, using a rat model of diabetic neuropathy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Rats were administered intraperitoneally a single dose of streptozocin (60 mg/kg) to induce type 1 diabetes. Koumine was given at a dose range of 0.056-7 mg/kg subcutaneously for one week starting 3 weeks after streptozocin adminstration. Behavioral responses to mechanical stimuli were evaluated every day after streptozocin injection. At 4 weeks after streptozocin injection, sensory nerve conduction velocity (SNCV) and morphological alternation of sciatic nerves were assessed by electron microscopy. Diabetic rats developed mechanical hyperalgesia within 3 weeks after streptozocin injection and exhibited reduced SNCV and impaired myelin/axonal structure. Koumine treatment of diabetic rats decreased neuropathic pain behavior as early as after the first administration. At a dose of 7 mg/kg, Koumine was more effective than gabapentin (100 mg/kg), and decreased mechanical sensitivity threshold to a level comparable to healthy control.
CONCLUSIONS:
Repeated treatment of Koumine significantly reduced the damage to axon and myelin sheath of the sciatic nerve and increased SNCV, without affecting body weight and blood glucose. These findings encourage the use of Koumine in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy.
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2013;15(1):46-52.
Four new koumine metabolites in rat liver microsomes.[Pubmed:
23323600]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Four new metabolites M-1 [1,2,18,19-tetradehydro-4-demethyl-3,17-epoxy-7,20(2H,19H)-cyclovobasan], M-2 [1,2,4,21,18,19-hexadehydro-4-demethyl-3,17-epoxy-7,20(2H,19H)-cyclovobasan], M-3 [1,2,18,19-tetradehydro-4-demethyl-4-formaldehyde-3,17-epoxy-7,20(2H,19H)-cyclovobasan], and M-4 [1,2,4,21,18,19-hexadehydro-4-demethyl-4-oxy-3,17-epoxy-7,20(2H,19H)-cyclovobasan] were isolated from the chloroform extract of Koumine incubated with phenobarbital-treated rat liver microsomes. The structures of M-1, M-2, M-3, and M-4 were elucidated by spectroscopic methods including ESI-TOF-MS, 1D, and 2D NMR experiments.
CONCLUSIONS:
The metabolic pathway of Koumine was proposed. The cytotoxic activities between Koumine and its metabolites were also compared in the A549 cell line.