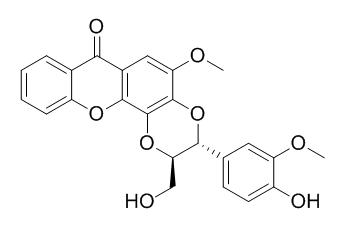
Kielcorin
Kielcorin shows antibacterial activity against strain EMRSA-16. It also shows in vitro anti-inflammatory (respiratory burst) inhibiting activities using isolated human neutrophils (IC (50) = 965.21 ± 65.80 uM). trans-Kielcorin has hepatoprotective activity, it can prevent tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced lipid peroxidation and cell death in freshly isolated rat hepatocytes.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(8),3437.
Industrial Crops and Products2022, 188:115596.
Life (Basel).2021, 11(7):616.
Front Immunol. 2020, 11:62.
J Agric Food Chem.2018, 66(1):351-358
Am J Chin Med.2016, 44(6):1255-1271
Oncotarget.2017, 8(64):108006-108019
Food Bioscience2023, 52:102412
J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol.2022, 50(5):338-352.
Food Res Int.2018, 106:909-919
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 2016 Mar 25;79(3):470-6.
Antistaphylococcal Prenylated Acylphoroglucinol and Xanthones from Kielmeyera variabilis.[Pubmed:
26900954 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioactivity-guided fractionation of the EtOH extract of the branches of Kielmeyera variabilis led to the isolation of a new acylphoroglucinol (1), which was active against all the MRSA strains tested herein, with pronounced activity against strain EMRSA-16. Compound 1 displayed an MIC of 0.5 mg/L as compared with an MIC of 128 mg/L for the control antibiotic norfloxacin. The structure of the new compound was elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic analysis and mass spectrometry, and experimental and calculated ECD were used to determine the absolute configurations. The compounds β-sitosterol (2), stigmasterol (3), ergost-5-en-3-ol (4), and osajaxanthone (5) also occurred in the n-hexane fraction.
CONCLUSIONS:
The EtOAc fraction contained nine known xanthones: 3,6-dihydroxy-1,4,8-trimethoxyxanthone (6), 3,5-dihydroxy-4-methoxyxanthone (7), 3,4-dihydroxy-6,8-dimethoxyxanthone (8), 3,4-dihydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone (9), 5-hydroxy-1,3-dimethoxyxanthone (10), 4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone (11), Kielcorin (12), 3-hydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone (13), and 2-hydroxy-1-methoxyxanthone (14), which showed moderate to low activity against the tested MRSA strains.
Planta Med. 2011 Dec;77(18):2013-8.
Anti-inflammatory xanthones from the twigs of Hypericum oblongifolium wall.[Pubmed:
21870324 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two new xanthonolignoids, hypericorin A (1) and hypericorin B (2), along with five known new source compounds, a xanthonolignoid, Kielcorin (3), 4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone (4), 3,4,5-trihydroxyxanthone (5), 1,3-dihydroxy-5-methoxyxanthone ( 6) and 1,3,7-trihydroxyxanthone (7), were isolated from the stems (twigs) of Hypericum oblongifolium Wall. The structures of the new compounds were deduced on the basis of spectroscopic techniques (EI-MS, HREI-MS, (1)H NMR, (13)C NMR, HMQC, HMBC, and NOESY). We also report herein for the first time the single crystal X-ray structure of compound 6.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1- 7 were screened for their IN VITRO anti-inflammatory (respiratory burst) inhibiting activities using isolated human neutrophils; compounds 1, 2, 3, 5, and 7 showed significant activities (IC (50) = 816.23 ± 73.30, 985.20 ± 55.80, 965.21 ± 65.80, 907.20 ± 50.80, 975.20 ± 81.10 μM, respectively), compound 6 showed moderate activity (IC (50) = 2500.85 ± 50.50 μM), while compound 4 was totally inactive at 1000 μg/mL as compared to the positive control used, indomethacin (IC (50) = 757.99 ± 5.90 μM), and aspirin (IC (50) = 279.44 ± 4.40 μM). Compound 4 was also inactive in comparison with other tested Hypericum compounds.
Pharm Res. 1995 Nov;12(11):1756-60.
Hepatoprotective activity of xanthones and xanthonolignoids against tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced toxicity in isolated rat hepatocytes--comparison with silybin.[Pubmed:
8592682]
Synthesize and evaluate the protective activity against tertbutylhydroperoxide-induced toxicity in freshly isolated rat hepatocytes of trans-Kielcorin, trans-isoKielcorin B, as well as their respective building blocks 3,4-dihydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone and 2,3-dihydroxy-4-methoxyxanthone.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Wistar rats, weighing 200-250g were used. Hepatocyte isolation was performed by collagenase perfusion. Incubations were performed at 37 degrees C, using 1 million cells per milliliter in modified Krebs--Henseleit buffer. The protective activity was evaluated by measuring reduced and oxidized glutathione, lipid peroxidation and cell viability after inducing toxicity with tert-butylhydroperoxide (1.0 mM, 30 min), with or without the studied compounds in the concentrations of 0.025, 0.050, 0.100 and 0.200 mM. Silybin was tested in the same experimental conditions to serve as a positive control. Using these concentrations, the tested compounds prevented tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced lipid peroxidation and cell death in freshly isolated rat hepatocytes. All compounds were also effective in preventing perturbation of cell glutathione homeostasis in some extent. 3,4-Dihydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone and 2,3-dihydroxy-4-methoxyxanthone were more effective than trans-Kielcorin and trans-isoKielcorin B respectively. Silybin was less effective in protecting cells against lipid peroxidation and loss of cell viability than the four xanthonic derivatives.
CONCLUSIONS:
The tested compounds protected the freshly isolated rat hepatocytes against tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced toxicity.