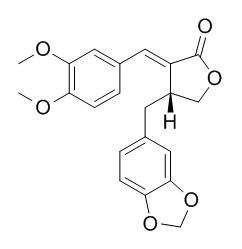
Kaerophyllin
Kaerophyllin has anti-fibrotic effects, it can protect the rat liver from TAA-caused injury and fibrogenesis by suppressing hepatic inflammation and inhibiting HSC activation, possibly through upregulation of PPAR-γ expression. Kaerophyllin inhibits AB-induced LX-2 activation and migration with downregulation of Akt/ERK phosphorylations and NF-κB activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int J Med Sci.2021, 18(10):2155-2161.
Mol Cell.2017, 68(4):673-685
Univerzita Karlova2022, 228192.
J. of Agricultural Science2015, 1916-9760
Antioxidants.2022, 11(3):491.
Nutrients.2020, 12(11):3448.
Industrial Crops and Products2018, 353-362
Toxins (Basel).2021, 13(12):898.
Integr Med Res.2024, 13(1):101025.
Reprod Sci.2022,10.1007/s43032-022-01117-4.
Related and Featured Products
Liver Int. 2011 May;31(5):618-29.
Kaerophyllin inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by apoptotic bodies from hepatocytes.[Pubmed:
21457435]
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the key cell type for hepatic fibrosis, become activated and profibrogenic in the presence of hepatocyte apoptotic bodies (ABs). Bupleurum scorzonerifolium (BS), a widely used traditional Chinese herb for liver diseases, was fractionated, and the inhibitory effects of BS extracts on AB-induced HSC migration were screened. The activity-guided fractionation led to a lignan, Kaerophyllin. In this study, the anti-fibrotic effects of Kaerophyllin were studied in the presence of ABs.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
LX-2 cells phagocytosing ultraviolet (UV)-induced HepG2 ABs were investigated by confocal microscopy and flow cytometry. AB-induced HSC activation was evaluated by immunoblotting and real-time PCR analyses. HSC migration was measured by wound-healing assays. HepG2 ABs induced LX-2 activation, with the production of collagen I and α-smooth muscle actin, upregulated profibrogenic gene transcriptions and increased NF-κB activity, cell migration and phagocytosis. Kaerophyllin from BS antagonized AB-induced HSC migration and activation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Kaerophyllin inhibited AB-induced LX-2 activation and migration with downregulation of Akt/ERK phosphorylations and NF-κB activity. Our study suggests a novel platform for screening anti-fibrotic compounds with ABs.
Planta Med. 2011, 77(12):1410-1410.
Kaerophyllin Suppresses Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation by Apoptotic Bodies and Ameliorates Hepatic Fibrosis in Rats.[Reference:
WebLink]
Hepatocyte apoptosis is a central feature of many liver diseases, leading to liver inflammation and fibrosis. In this study, we screened potential drugs inhibiting hepatic stellate cell (HSC) migration induced by hepatocyte apoptotic bodies (ABs) and evaluated the in vivo therapeutic effects in a rat model of hepatic fibrosis induced by thioacetamide (TAA).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Rat HSCs were exposed to UV-irradiated hepatocyte ABs or TNF-α to investigate the anti-fibrotic effects of Kaerophyllin. Liver fibrosis was induced by TAA injection into rats twice weekly for 6 weeks. Kaerophyllin (10 or 30mg/kg) or curcumin (150mg/kg, as a positive control) was given by gavage twice daily for 4 weeks starting 2 weeks after TAA injection. Kaerophyllin (α-(trans-3,4-dimethoxybenzylidene)-β-(3,4-methylenedioxy-benzyl)-γ-butyrolactone, a lignan isolated from a Chinese herb Bupleurum scorzonerifolium by bioactivity-guided fractionation) attenuated ABs- and TNF-α-induced HSC migration, protein levels of collagen I and α-SMA, and the mRNA levels of ICAM-1, MCP-1 and IL-1β genes, but elevated PPAR-γ luciferase activity. Furthermore, Kaerophyllin reduced TNF-α- and ABs-induced NF-κB luciferase activity with decreased IκB phosphorylation and p65 nuclear translocation. In TAA rats, Kaerophyllin and curcumin treatment significantly protected liver from injury by reducing serum AST and ALT levels, and improved the histological architecture and fibrosis score. In addition, Kaerophyllin treatment suppressed α-SMA protein expression, and mRNA levels of collagen I, TIMP-1, TNF-α, IL-1β and MCP-1 genes in TAA rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results demonstrated that Kaerophyllin protected the rat liver from TAA-caused injury and fibrogenesis by suppressing hepatic inflammation and inhibiting HSC activation.
Eur J Clin Invest. 2012 Jun;42(6):607-16.
Protective effects of kaerophyllin against liver fibrogenesis in rats.[Pubmed:
22103576]
We previously demonstrated that Kaerophyllin, a lignan, isolated from a widely used traditional Chinese herb, Bupleurum scorzonerifolium, leading to the inhibition of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) activation in vitro. This current study evaluated the in vivo role of Kaerophyllin in protecting the liver against injury and fibrogenesis caused by thioacetamide (TAA) in rats and further explored the underlying mechanisms.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Liver fibrosis in Sprague-Dawley rats was induced by intraperitoneal injection of TAA (200 mg/kg) twice per week for 6 weeks. Animals were divided into five groups: vehicle control, TAA control, TAA + low dose Kaerophyllin, TAA + high dose Kaerophyllin and TAA + curcumin groups. Kaerophyllin (10 or 30 mg/kg) or curcumin (150 mg/mL) was given by gavage twice per day consecutively for 4 weeks starting 2 weeks after TAA injection. Rat HSCs were used to investigate the anti-inflammatory role of Kaerophyllin against tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in vitro. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) expression was knocked down in rat HSCs using PPAR-γ small interfering RNAs. Kaerophyllin significantly protected liver from injury by reducing serum aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase levels and by improving the histological architecture and fibrosis score. In addition, Kaerophyllin suppressed inflammation by reducing the mRNA of TNF-α, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) genes. In HSCs, Kaerophyllin elevated PPAR-γ activity and reduced TNF-α-stimulated mRNA levels of intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), MCP-1 and IL-1β genes, which were reversed by small interfering RNA knockdown of PPAR-γ gene.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results demonstrated that Kaerophyllin protected the rat liver from TAA-caused injury and fibrogenesis by suppressing hepatic inflammation and inhibiting HSC activation, possibly through upregulation of PPAR-γ expression.
Planta Med. 1981 Dec;43(4):378-80.
Kaerophyllin, a new lignan from Chaerophyllum maculatum.[Pubmed:
17402063]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
From the methanolic extract of roots of spotted cow parsley (Chaerophyllum maculatum Willd.) a new lignan, named Kaerophyllin, has been isolated and identified as A-(trans-3,4-dimethoxybenzylidene)- beta-(3,4-methylenedioxylbenzyl)-gamma-butyrolactone.
CONCLUSIONS:
Its structure has been established on the basis of the analysis of UV, IR-, (1)H-NMR, (13)C-NMR and mass spectra.