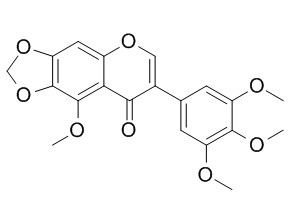
Irisflorentin
Irisflorentin has anti-inflammatory activity, it can markedly reduce the transcriptional and translational levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) as well as the production of NO, it also can significantly inhibit TNF-α, IL-1βand IL-6 at both the transcriptional and translational levels; Irisflorentin has potential to ameliorate Parkinson’s disease in Caenorhabditis elegans models by promoting rpn-3 expression and down-regulating egl-1 expression; Irisflorentin may as an immunotherapeutic adjuvant.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
CZECH MYCOLOGY2021, 73(1):1-19.
Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci.2021, 29(1):45-50.
Korean J. Food Sci. & Technol.2022, 54(2):241-246
J Agric Food Chem.2016, 64(35):6783-90
BMC Complement Altern Med.2019, 19(1):325
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy2018, 49(3):270-277
Journal of Ginseng Research2019, 10.1016
Journal of Molecular Liquids2021, 334:116014.
Foods.2023, 12(6):1227.
J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol.2022, 50(5):338-352.
Related and Featured Products
Biomedicine (Taipei). 2015;5(1):4. Epub 2015 Feb 2.
Irisflorentin improves α-synuclein accumulation and attenuates 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic neuron degeneration, implication for Parkinson's disease therapy.[Pubmed:
25705584]
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that is characterized by progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta as well as motor impairment. Aggregation of α-synuclein in neuronal cells plays a key role in this disease. At present, therapeutics for PD provides moderate symptomatic benefits, but it is not able to delay the development of the disease.
Current efforts toward the treatment of PD are to identify new drugs that slow or arrest the progressive course of PD by interfering with a disease-specific pathogenetic process in PD patients. Irisflorentin derived from the roots of Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC. is an herb which has been used for the treatment of inflammatory disorders in traditional Chinese medicine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The purpose of the present study was to assess the potential for Irisflorentin to ameliorate PD in Caenorhabditis elegans models. Our data reveal that Irisflorentin prevents α-synuclein accumulation in the transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans model and also improves dopaminergic neuron degeneration, food-sensing behavior, and life-span in a 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Caenorhabditis elegans model, thus indicating its potential as a anti-parkinsonian drug candidate. Irisflorentin may exert its effects by promoting rpn-3 expression to enhance the activity of proteasomes and down-regulating egl-1 expression to block apoptosis pathways.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings encourage further investigation on Irisflorentin as a possible potent agent for PD treatment.
Cell Transplant. 2015;24(3):573-88.
Irisflorentin modifies properties of mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells and reduces the allergic contact hypersensitivity responses.[Pubmed:
25654487]
Irisflorentin is an isoflavone component derived from the roots of Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC. In traditional Chinese medicine, this herb has pharmacological properties to treat inflammatory disorders. Dendritic cells (DCs) are crucial modulators for the development of optimal T-cell immunity and maintenance of tolerance. Aberrant activation of DCs can induce harmful immune responses, and so agents that effectively improve DC properties have great clinical value.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We herein investigated the effects of Irisflorentin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated maturation of mouse bone marrow-derived DCs in vitro and in the contact hypersensitivity response (CHSR) in vivo. Our results demonstrated that treatment with up to 40 μM Irisflorentin does not cause cellular toxicity. Irisflorentin significantly lessened the proinflammatory cytokine production (tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-12p70) by LPS-stimulated DCs. Irisflorentin also inhibited the expression of LPS-induced major histocompatibility complex class II and costimulatory molecules (CD40 and CD86) on LPS-stimulated DCs. In addition, Irisflorentin diminished LPS-stimulated DC-elicited allogeneic T-cell proliferation. Furthermore, Irisflorentin significantly interfered with LPS-induced activation of IκB kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38, as well as the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65. Subsequently, treatment with Irisflorentin obviously weakened 2,4-dinitro-1-fluorobenzene-induced delayed-type hypersensitivity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest new insights into the role of Irisflorentin as an immunotherapeutic adjuvant through its capability to modulate the properties of DCs.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014 Apr 16;239(8):1018-1024.
Suppressive effects of irisflorentin on LPS-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages.[Pubmed:
24740875]
Irisflorentin, a naturally occurring isoflavone, is an abundant active constituent in Rhizoma Belamcandae. Although some chemical studies have been reported, pharmacological actions of Irisflorentin are not well studied.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we demonstrate the anti-inflammatory activity of Irisflorentin in lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Irisflorentin markedly reduces the transcriptional and translational levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) as well as the production of NO. Furthermore, it also significantly inhibits TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 at both the transcriptional and translational levels. These effects mainly act via ERK1/2 - and p38-mediated the activator protein-1 (AP-1) rather than the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, our study elucidates the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Irisflorentin in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages.
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011 Dec 1;879(31):3735-41.
Simultaneous determination of tectorigenin, irigenin and irisflorentin in rat plasma and urine by UHPLC-MS/MS: application to pharmacokinetics.[Pubmed:
22071270]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A sensitive and reliable ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS) has been developed and validated for the simultaneous determination of three active components, i.e., tectorigenin, irigenin and Irisflorentin, in rat plasma and urine after oral administration of Rhizoma Belamcandae extract. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a Zorbax SB-C(18) column (50 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.8 μm; Agilent, USA) with gradient elution using a mobile phase that consisted of acetonitrile - 0.1% formic acid in water at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min. Detection was performed by a triple-quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode via polarity switching between the negative (for tectorigenin and irigenin) and positive (for Irisflorentin) ionization modes. The calibration curve was linear over a range of 50-50,000 ng/mL for tectorigenin, 10-5000 ng/mL for irigenin and 0.1-200 ng/mL for Irisflorentin, respectively. The intra- and inter-day precisions (RSD %) were within 11.3% for all analytes, whereas the deviation of assay accuracies ranged from -8.7 to +11.1%.
CONCLUSIONS:
All analytes were proven to be stable during all sample storage and analysis procedures. This method was successfully applied to a pharmacokinetic study of the three isoflavones after oral administration of Rhizoma Belamcandae extract to rats.