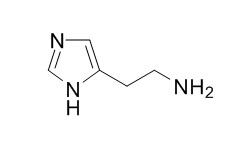
Histamine
Histamine, an organic nitrogenous compound, is involved in local immune responses regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. It is a potent H1 and H2 receptor agonist. Histamine increases Nav1.8 expression in primary afferent neurons via H2 receptor-mediated pathway and thereby contributes to neuropathic pain, H2 receptor antagonists may potentially be used as analgesics for patients with neuropathic pain.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules.2019, 24(9):E1719
Int J Mol Sci.2018, 19(2)
TCI CO.2019, US20190151257A1
Food Chemistry: X2023, 101032.
Front Pharmacol.2022, 13:919230.
Front Microbiol.2022, 13:835463.
Food Research International2016, 106-113
FARMACIA2023, Vol.71,3.
Appl Biochem Biotechnol.2020, 190(2):732-744
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy2019, 50(4):285-290
Related and Featured Products
Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2015 Mar;62(1):87-91.
Modulation of ConA-induced inflammatory ascites by histamine - short communication.[Pubmed:
25823456]
The early phase of the ConA-induced inflammatory ascites was studied, with special reference to Histamine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Concanavalin A (ConA), a cell-surface binding lectin was injected i.p. (25 mg/kg bw) to mice. After 1 h the animals were killed, the ascitic fluid collected and measured. Other agents were injected s.c., 10 min before the ConA-challenge. Exogenous Histamine markedly inhibited the ConA-induced ascites. Release of endogenous vasoactive agents from the mast cells by Compound 48/80 had a similar, but slight effect. Cromolyn, a mast cell stabilizing agent, and chloropyramine, a Histamine H1 receptor antagonist was ineffective. Although Histamine increases endothelial permeability, it did not enhance the formation of ascitic fluid, on the contrary, it inhibited the ConA-induced ascites, presumably due to its known hypotonic effect.
CONCLUSIONS:
It is concluded that ConA-induced ascites is not mediated by mast cell Histamine.
Eur J Immunol. 2015 Apr;45(4):1129-40.
The histamine H4 -receptor (H4 R) regulates eosinophilic inflammation in ovalbumin-induced experimental allergic asthma in mice.[Pubmed:
25501767]
Via the Histamine H4 -receptor (H4 R), Histamine promotes the pathogenesis of experimental allergic asthma in mice. Application of H4 R antagonists during sensitization as well as during provocation reduces the severity of the disease. However, the specific cell types functionally expressing H4 R in experimental allergic asthma have not been well characterized in vivo.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we identified the cell type(s) responsible for H4 R activity in experimental asthma and related physiological mechanisms. Using H4 R-deficient mice, we studied the role of H4 R in the sensitization and effector phase. DCs lacking H4 R expression during the in vitro sensitization reaction resulted in effector T cells unable to induce an entire eosinophilic inflammation in the lung upon adoptive transfer in vivo. Recipient mice lacking H4 R expression, which were adoptively transferred with H4 R(+/+) T cells polarized in the presence of H4 R(+/+) DCs, showed reduced signs of inflammation and ameliorated lung function. Here, we provide in vivo evidence that in experimental asthma in mice the H4 R specifically regulates activation of DCs during sensitization, while in the effector phase the H4 R is active in cells involved in the activation of eosinophils, and possibly other cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
A putative therapy targeting the H4 R may be an option for asthma patients developing IL-5-dependent eosinophilia.
CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014 Oct;20(10):883-92.
Histamine upregulates Nav1.8 expression in primary afferent neurons via H2 receptors: involvement in neuropathic pain.[Pubmed:
24990156]
The upregulation of Nav1.8 in primary afferents plays a critical role in the development and persistence of neuropathic pain. The mechanisms underlying the upregulation are not fully understood.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study aims to investigate the regulatory effect of Histamine on the expression of Nav1.8 in primary afferent neurons and its involvement in neuropathic pain. Histamine at 10(-8) M increased the expression of Nav1.8 in cultured DRG neurons. This effect could be blocked by H2 receptor antagonist cimetidine or famotidine, but not by H1 receptor antagonist pyrilamine or dual H3 /H4 antagonist thioperamide. Peri-sciatic administration of Histamine increased Nav1.8 expression in the sciatic nerve and L4/L5 DRG neurons in a dose-dependent manner, accompanied with remarkable mechanical allodynia and heat hyperalgesia in the ipsilateral hindpaw. Famotidine but not pyrilamine or thioperamide inhibited Nav1.8 upregulation and pain hypersensitivity. In addition, famotidine (40 mg/kg, i.p.) not only suppressed autotomy behavior in the rat neuroma model of neuropathic pain but also attenuated mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia following partial sciatic nerve ligation. Moreover, famotidine inhibited Nav1.8 upregulation in the neuroma and ligated sciatic nerve.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings indicate that Histamine increases Nav1.8 expression in primary afferent neurons via H2 receptor-mediated pathway and thereby contributes to neuropathic pain. H2 receptor antagonists may potentially be used as analgesics for patients with neuropathic pain.