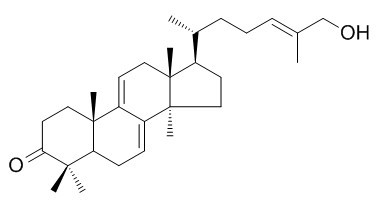
Ganoderol A
Ganoderol A has significant anti-inflammatory activity and protection against UVA damage. it has an inhibitory effect on angiotensin converting enzyme activity and cholesterol biosynthesis.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Phytomedicine.2017, 24:77-86
LWT2024, v208:116677
J Exp Bot.2016, 67(12):3777-88
Food Sci Biotechnol.2021, 30(2):217-226.
Neuropharmacology.2018, 131:68-82
Curr Res Food Sci.2024, 9:100827.
Asian Journal of Chemistry2014, 26(22):7811-7816
Sci Rep.2019, 9(1):4646
Molecules.2021, 26(4):816.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(23):14826.
Related and Featured Products
Trop. J. Pharm. Res., 2015, 14(3):412-21.
In vitro Protective Effect of Ganoderol A Isolated from Ganadermalucidum Against Ultraviolet A Radiation and its Anti-inflammatory Properties[Reference:
WebLink]
Purpose: To evaluate the ultraviolet A (UVA) protection and anti-inflammatory activity of Ganoderol A extracted from Ganodermalucidum.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Methods: The cytotoxicity and in vitro protective effect of Ganoderol A against UVA damage were evaluated by MTT assay. Apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest of NIH/3T3 fibroblast cells were assayed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FCS). Expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) were determined using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Results: The results indicate that the maximal non-toxic concentration of Ganoderol A in NIH/3T3 cells and RAW 264.7 macrophages was 50 and 25 μg/mL respectively. DNA in the tails and tail length decreased by 55 and 70%, respectively, in the group pretreated with Ganoderol A compared with the UVA-treated group. G1 phase cells decreased by 23%, whereas the number of apoptotic cells returned to normal. The expression of MCP-1 and iNOS declined to 60 and 15%, respectively, compared with LPS-stimulated group.
CONCLUSIONS:
Conclusion: Ganoderol A has significant anti-inflammatory activity and protection against UVA damage, thus suggesting that the compound is a candidate for the development of a suitable product to protect skin from UV-induced photoaging.
Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jul;71(7):3653-8.
Effect of 26-oxygenosterols from Ganoderma lucidum and their activity as cholesterol synthesis inhibitors.[Pubmed:
16000773 ]
Ganoderma lucidum is a medicinal fungus belonging to the Polyporaceae family which has long been known in Japan as Reishi and has been used extensively in traditional Chinese medicine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We report the isolation and identification of the 26-oxygenosterols Ganoderol A, ganoderol B, ganoderal A, and ganoderic acid Y and their biological effects on cholesterol synthesis in a human hepatic cell line in vitro. We also investigated the site of inhibition in the cholesterol synthesis pathway. We found that these oxygenated sterols from G. lucidum inhibited cholesterol biosynthesis via conversion of acetate or mevalonate as a precursor of cholesterol. By incorporation of 24,25-dihydro-[24,25-3H2]lanosterol and [3-3H]lathosterol in the presence of Ganoderol A, we determined that the point of inhibition of cholesterol synthesis is between lanosterol and lathosterol.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrate that the lanosterol 14alpha-demethylase, which converts 24,25-dihydrolanosterol to cholesterol, can be inhibited by the 26-oxygenosterols from G. lucidum. These 26-oxygenosterols could lead to novel therapeutic agents that lower blood cholesterol.
Chem. Pharm. Bull., 1986, 34(7):3025-8.
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Triterpenes from Ganoderma lucidim[Reference:
WebLink]
The 70% MeOH extract of Ganoderma lucidum had an inhibitory effect on angiotensin converting enzyme activity, and from this extract, five new triterpenes, named ganoderal A, Ganoderol A and ganoderol B, and ganoderic acids K and S, were isolated. Their structures were determined on the basis of spectral evidence.
J Sep Sci. 2006 Nov;29(17):2609-15.
Quality evaluation of Ganoderma through simultaneous determination of nine triterpenes and sterols using pressurized liquid extraction and high performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed:
17313101]
A method combining HPLC and pressurized liquid extraction was developed for simultaneous quantification of nine components, including eight triterpenes (ganoderic acid A, ganoderic acid Y, ganoderic acid DM, Ganoderol A, ganoderol B, ganoderal A, methyl ganoderate D and ganoderate G) and a sterol (ergosterol), in Ganoderma.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The determination was achieved by using a Zorbax ODS C18 analytical column (4.6 x 250 mm id, 5 microm) and gradient elution with diode-array detection. All calibration curves showed good linearity (r2 > 0.9997) within the test ranges. The developed method showed good repeatability for the quantification of the nine investigated components in Ganoderma with intra- and inter-day variations of less than 2.4% and 4.1%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The validated method was successfully applied to quantify the nine components in two species of Ganoderma, i.e. G. lucidum and G. sinense, used as Lingzhi in China. Furthermore, hierarchical clustering analysis based on the nine components in HPLC profiles from the tested 11 samples showed that chemical characteristics were significantly different between G. lucidum and G. sinense, which suggested that clinical investigation should be performed so as to ensure the safety and efficacy of medication.