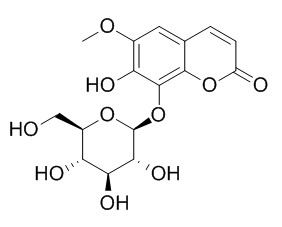
Fraxin
Fraxin possesses a variety of bioactivities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, analgesic, antimicrobial, antiviral, immunomodulatory, anti-hyperuricemia and diuresis. Fraxin enhances urate excretion partly by inhibiting mURAT1 or mGLUT9 in kidney of hyperuricemic mice.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules.2019, 24(10):E1926
Fitoterapia.2015, 100:179-86
J Pharmaceut Biomed2020, 178:112894
Natural Product Communications2020, doi: 10.1177.
LWT2024, v208:116677
Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess.2020, 37(9):1437-1448.
Cells.2021, 10(11):2919.
Biomed Chromatogr.2019, 8:e4774
J Herbmed Pharmacol.2018, 7(4):280-286
PLoS One.2015, 10(5):e0127060
Related and Featured Products
Exp Mol Med. 2005 Oct 31;37(5):436-46.
Natural compounds,fraxin and chemicals structurally related to fraxin protect cells from oxidative stress.[Pubmed:
16264268]
Coumarins comprise a group of natural phenolic compounds found in a variety of plant sources. In view of the established low toxicity, relative cheapness, presence in the diet and occurrence in various herbal remedies of coumarins, it appears prudent to evaluate their properties and applications further.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The purpose of this study is to investigate cellular protective activity of coumarin compound, Fraxin extracted from Weigela florida var. glabbra, under oxidative stress, to identify genes expressed differentially by Fraxin and to compare antioxidative effect of Fraxin with its structurally related chemicals. Of the coumarins, protective effects of Fraxin against cytotoxicity induced by H2O2 were examined in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Fraxin showed free radical scavenging effect at high concentration (0.5 mM) and cell protective effect against H2O2-mediated oxidative stress. Fraxin recovered viability of HUVECs damaged by H2O2-treatment and reduced the lipid peroxidation and the internal reactive oxygen species level elevated by H2O2 treatment. Differential display reverse transcription-PCR revealed that Fraxin upregulated antiapoptotic genes (clusterin and apoptosis inhibitor 5) and tumor suppressor gene (ST13). Based on structural similarity comparing with Fraxin, seven chemicals, fraxidin methyl ether (29.4% enhancement of viability), prenyletin (26.4%), methoxsalen (20.8%), diffratic acid (19.9%), rutoside (19.1%), xanthyletin (18.4%), and kuhlmannin (18.2%), enhanced more potent cell viability in the order in comparison with Fraxin, which showed only 9.3% enhancement of cell viability.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Fraxin and Fraxin-related chemicals protect HUVECs from oxidative stress.
J Nat Prod. 2006 May;69(5):755-7.
Metabolic fate of fraxin administered orally to rats.[Pubmed:
16724835]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Naturally occurring Fraxin (1) was administered orally to rats to investigate its metabolism. Urinary metabolites were analyzed by three-dimensional HPLC, and fraxetin-7-O-sulfate (2), fraxetin-7-O-beta-glucuronide (3), fraxetin (4), 6,7,8-trihydroxycoumarin (5), and fraxidin (6) were isolated. Fraxin (1) was extensively metabolized to 4, which was partly metabolized to 5 in a rat fecal suspension after incubation for 24 h. Urinary excretion of 4 and 5 in rats administered orally with 1 was substantially reduced when the rats were treated with antibiotics to suppress their intestinal flora. Incubation of 1 with a rat liver S-9 mixture yielded 6.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that hydrolysis and demethylation of 1 are performed by intestinal microflora, while methylation occurs in the liver.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;666(1-3):196-204.
Protective effects of cortex fraxini coumarines against oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and renal dysfunction in mice.[Pubmed:
21620826]
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of cortex Fraxini coumarines esculetin, esculin, fraxetin and Fraxin on renal dysfunction and expression abnormality of renal organic ion transporters in hyperuricemic animals.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Mice were orally given 250 mg/kg oxonate for seven consecutive days to induce hyperuricemia and renal dysfunction. After 1h of oxonate induction daily, animals were orally treated with esculetin, esculin, fraxetin and Fraxin at 20 and 40 mg/kg, respectively. Esculetin, esculin, fraxetin and Fraxin significantly decreased serum urate, creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels and increased urine urate and creatinine excretion in hyperuricemic mice. Esculetin and esculin up-regulated expressions of renal organic anion transporter 1 (mOAT1), organic cation and carnitine transporters (mOCT1-2 and mOCTN1-2), but failed to affect renal glucose transporter 9 (mGLUT9) and urate transporter 1 (mURAT1) in this model. Fraxetin specifically inhibited renal mURAT1, while Fraxin extensively interacted with renal mGLUT9, mURAT1, mOAT1 and mOCT1 in hyperuricemic mice. Furthermore, esculetin, fraxetin and Fraxin increased mABCG2 mRNA expression and decreased its protein levels in renal apical membrane in hyperuricemic mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that esculetin and esculin have beneficial effects on hyperuricemia and renal dysfunction, resulting in restoration of mOAT1, mOCT1-2 and mOCTN1-2, and fraxetin and Fraxin enhance urate excretion partly by inhibiting mURAT1 or mGLUT9 in kidney of hyperuricemic mice. Regulation of mABCG2 by cortex Fraxini coumarines may be partly contributed to their beneficial actions. This study provides an evidence to support clinical therapeutic effects of cortex Fraxini coumarines on hyperuricemia with renal dysfunction.
Biomed Chromatogr. 2005 Nov;19(9):696-702.
Non-aqueous capillary electrophoresis for separation and simultaneous determination of fraxin, esculin and esculetin in Cortex fraxini and its medicinal preparations.[Pubmed:
15828063]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A non-aqueous capillary electrophoresis method has been developed for the separation and simultaneous determination of Fraxin, esculin and esculetin in Cortex Fraxini and its preparation for the first time. Optimum separation of the analytes was obtained on a 47 cm x 75 microm i.d. fused-silica capillary using a non-aqueous buffer system of 60 mM sodium cholate, 20 mM ammonium acetate, 20% acetonitrile and 3% acetic acid at 20 kV and 292 K, respectively. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) of the migration times and the peak heights of the three analytes were in the range of 0.23-0.28 and 2.12-2.60%, respectively. Detection limits of Fraxin, esculin and esculetin were 0.1557, 0.4073 and 0.5382 microg/mL, respectively. In the tested concentration range, good linear relationships (correlation coefficients 0.9995 for Fraxin, 0.9999 for esculin and 0.9992 for esculetin) between peak heights and concentrations of the analytes were observed.
CONCLUSIONS:
This method has been successfully applied to simultaneous determination of the three bioactive components with the recoveries from 90.2 to 109.2% in the five samples.