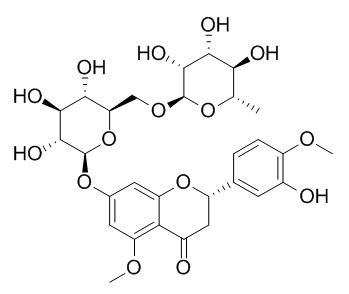
Methyl hesperidin
Methyl hesperidin has potentiating effect on coronary vasodilation induced by adenosine or related compounds, It caused inhibition of nitrendipine transport in the ileum and jejunum, but not in the duodenum. Methyl hesperidin exerts no obvious toxic effects in mice of either sex when administered at a level as high as 5.0% in the diet.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2021, 2021:8850744.
Molecules.2020, 25(7):1625.
J Nat Prod.2019, 82(4):1002-1008
Phytomedicine Plus2022, 2(1):100207.
Rep.Grant.Res.,Asahi Glass Foun.2023, No.119.
Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry2023, 49:1689ĘC1698.
Drug Des Devel Ther.2020, 14:61-71
Food Chem.2019, 278:683-691
Free Radic Biol Med.2017, 112:191-199
China Pharmacy2015, 26(27)
Related and Featured Products
Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 2008;23(3-4):299-310.
Influence of some bioflavonoids on the transport of nitrendipine.[Pubmed:
19326773]
Flavonoids form a large class of phenolic substances widely distributed in nature and exhibit several biological effects. P-glycoprotein is part of a large family of efflux transporters found in the gut, gonads and other organs.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Male albino rats were used for this study. The whole small intestine was flushed with 50 ml of ice-cold saline after sacrificing the animal with an overdose of pentobarbital. The small intestine was isolated and divided into duodenum, jejunum and ileum. Each segment was everted, a 5-cm long sac was prepared, 1 ml of nitrendipine solution was introduced into the everted sac (serosal side), and both ends of the sac were ligated tightly. The sac containing nitrendipine solution was immersed in 30 ml of Dulbecco's phosphate buffer solution (D-PBS) containing 25 mM glucose and the same concentration of different bioflavonoids, viz., diosmin, quercetin, chrysin, Methyl hesperidin and gossypin, was introduced into the mucosal side. Transport of nitrendipine from serosal to mucosal surfaces across the intestine was determined by collecting samples from the mucosal medium periodically at different intervals: 0, 10, 20, 30, 60, 90 and 120 minutes. The samples were analyzed by HPLC. Diosmin and quercetin decreased the transport rate of nitrendipine to nearly the same extent in all regions. Chrysin and gossypin decreased the transport rate of nitrendipine to a greater extent in the ileum than in the duodenum and jejunum. Methyl hesperidin caused inhibition of nitrendipine transport in the ileum and jejunum, but not in the duodenum.
CONCLUSIONS:
All bioflavonoids, i.e., quercetin, diosmin, Methyl hesperidin, gossypin and chrysin, decreased the transport of nitrendipine, a P-gp substrate in the rat intestine. The highest expression of P-gp was found in the ileum followed by the jejunum and duodenum.
Food Chem Toxicol. 1990 Sep;28(9):613-8.
Carcinogenicity study of methyl hesperidin in B6C3F1 mice.[Pubmed:
2272558]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A long-term carcinogenicity study of Methyl hesperidin, a compound of the vitamin P group, was carried out in B6C3F1 mice receiving dietary concentrations of 0, 1.25 or 5%. Administration was continued for 96 wk and then the mice were maintained on basal diet for an additional 8 wk. Growth retardation during the experiment with final changes in organ weights were observed in females given the 1.25% dose of Methyl hesperidin and in both sexes receiving the 5.0% treatment. However, no biologically significant effects were evident with respect to mortality or clinical signs. Furthermore, treatment with Methyl hesperidin did not result in any changes in haematology, clinical chemistry and urinalysis data. On histological examination, no significant alteration of non-neoplastic and neoplastic lesion incidence was observed in treated mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results thus demonstrated that Methyl hesperidin lacked any carcinogenicity for B6C3F1 mice in the 96-wk feeding regimen used in this study.
Arzneimittelforschung. 1967 Aug;17(8):979-80.
The potentiating effect of methyl hesperidin on coronary vasodilation induced by adenosine or related compounds[Pubmed:
5632073]
The potentiating effect of Methyl hesperidin on coronary vasodilation induced by adenosine or related compounds