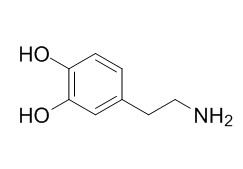
Dopamine hydrochloride
Dopamine hydrochloride is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals,And a dopamine D1-5 receptors agonist.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Journal of Third Military Medical University2018, 40(12):1073-1078
Journal of Cluster Science2024, 35:635-656.
Ind Crops Prod.2014, 62:173-178
J Cosmet Dermatol.2022, 21(1):396-402.
Curr Issues Mol Biol.2022, 44(5):2300-2308.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2024, 17(4):442.
International Food Research Journal2018, 25(6):2560-2571
Nat Plants.2016, 3:16205
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(18):10219.
Plant Cell,Tissue & Organ Culture2016, 127(1):115-121
Related and Featured Products
Am J Vet Res. 2015 Feb;76(2):116-21.
Cardiovascular effects of dopamine hydrochloride and phenylephrine hydrochloride in healthy isoflurane-anesthetized New Zealand White rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus).[Pubmed:
25629908]
To determine the cardiopulmonary effects of progressively increasing infusion rates of Dopamine hydrochloride and phenylephrine hydrochloride in healthy adult New Zealand White rabbits anesthetized with isoflurane.
ANIMALS:
6 New Zealand White rabbits. (Oryctolagus cuniculus).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Each rabbit was anesthetized on 2 occasions (≥ 2 weeks apart) with isoflurane in oxygen at 1.5 times the published isoflurane minimum alveolar concentration of 2.07%. Carotid artery and pulmonary artery catheters were placed. During each anesthetic episode, each rabbit received 5 progressively increasing doses of either dopamine (5, 10, 15, 20, or 30 μg/kg/min) or phenylephrine (0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 μg/kg/min). Blood gas and cardiopulmonary measurements were obtained after a 20-minute equilibration period prior to administration of the first drug dose (baseline) and after each subsequent dose administration.
Dopamine increased stroke index at the highest infusion rate of 30 μg/kg/min; however, cardiac output and mean arterial blood pressure remained unchanged from baseline values. Administration of phenylephrine at a rate of 2 μg/kg/min increased mean arterial blood pressure to 62 mm Hg from the baseline value of 45 mm Hg. This was a result of an increase in systemic vascular resistance with a concomitant decrease in heart rate and no change in cardiac output. Blood lactate concentration increased with time when rabbits received either treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
Within the dose range of 5 to 30 μg/kg/min, dopamine was not an effective treatment for isoflurane-induced hypotension in rabbits and phenylephrine was only minimally effective at a dose of 2 μg/kg/min.
J Chem Phys. 2015 Jan 7;142(1):014502.
Conformation and interactions of dopamine hydrochloride in solution.[Pubmed:
25573567]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The aqueous solution of Dopamine hydrochloride has been investigated using neutron and X-ray total scattering data together with Monte-Carlo based modelling using Empirical Potential Structure Refinement. The conformation of the protonated dopamine molecule is presented and the results compared to the conformations found in crystal structures, dopamine-complexed protein crystal structures and predicted from theoretical calculations and pharmacophoric models. It is found that protonated dopamine adopts a range of conformations in solution, highlighting the low rotational energy barrier between different conformations, with the preferred conformation being trans-perpendicular.
CONCLUSIONS:
The interactions between each of the species present (protonated dopamine molecules, water molecules, and chloride anions) have been determined and are discussed with reference to interactions observed in similar systems both in the liquid and crystalline state, and predicted from theoretical calculations.
The expected strong hydrogen bonds between the strong hydrogen bond donors and acceptors are observed, together with evidence of weaker CH hydrogen bonds and π interactions also playing a significant role in determining the arrangement of adjacent molecules.