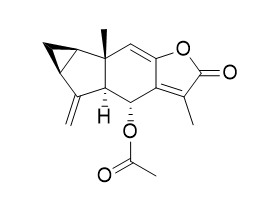
Chlojaponilactone B
Chlojaponilactone B has anti-inflammatory activity, it exhibits pronounced inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Dicle Tip Dergisi2020, 47(2),423-430.
BMC Plant Biol.2018, 18(1):122
Mol Med Rep.2022, 25(1):8.
Phytomedicine.2024, 125:155350.
Hong Kong Baptist University2023, 048330T.
Int Immunopharmacol.2021, 101(Pt A):108181.
LWT-Food Sci Technol2020, 109163
Food Funct.2021, 12(4):1469-1481.
Herbal Formula Science2024, 32(3):203-221
Molecules.2023, 28(4):1526.
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 2016 Sep 23;79(9):2257-63.
Chlojaponilactone B from Chloranthus japonicus: Suppression of Inflammatory Responses via Inhibition of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway.[Pubmed:
27588583 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioassay-guided fractionation of an ethanolic extract of Chloranthus japonicus led to the isolation of the known lindenane-type sesquiterpenoid Chlojaponilactone B (1). This compound exhibited pronounced inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Further anti-inflammatory assays showed that 1 suppressed the levels of some key inflammation mediators, such as iNOS, TNF-α, and IL-6, in a dose-dependent manner, and reduced the ear thickness and neutrophil infiltration in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-stimulated mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
A mechanistic study revealed that compound 1 exerted its anti-inflammatory effects via the suppression of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which inhibited NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity, IκBα phosphorylation, and p65 nuclear translocation. In contrast, Chlojaponilactone B (1) was found to exert little influence on the MAPK signaling pathway.
Helvetica Chimica Acta, 2013, 96(7):1386-1391.
Chlojaponilactones B – E, Four New Lindenane Sesquiterpenoid Lactones from Chloranthus japonicus[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Reinvestigation of the AcOEt-soluble part of the EtOH extract of whole plants of Chloranthus japonicus afforded four new lindenane-type sesquiterpenoid lactones, Chlojaponilactone B,chlojaponilactone C, chlojaponilactone D, chlojaponilactone E (1–4, resp.), together with nine known sesquiterpenoids.
CONCLUSIONS:
Their structures and relative configurations were established on the basis of extensive spectroscopic data and by comparison with the relevant literature.