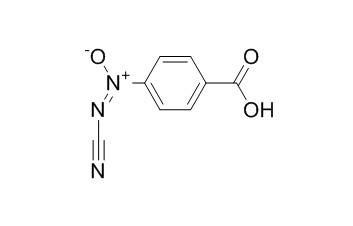
Calvatic acid
Calvatic acid is a new antibiotic with both a carboxylic group and an azoxy function in the benzene ring. It shows antimicrotubular effect.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Microchemical Journal2023. 191:108938
Molecules.2019, 24(4):E744
Pak J Pharm Sci.2019, 32(6):2879-2885
Chemistry of Natural Compounds2019, 55(1):127-130
Nutrients.2022, 14(23):4997.
Sci Rep.2023, 13(1):14594.
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2021, 196:113931.
Eur J Pharmacol.2022, 917:174744.
Molecules.2020, 25(17):3783.
Int J Mol Med.2020, 45(5):1514-1524.
Related and Featured Products
Research communications in chemical pathology and pharmacology, 1987, 56(2):265-272.
Some biological effects of calvatic acid and its analog on isolated hepatocytes.[Reference:
WebLink]
Calvatic acid is a new antibiotic with both a carboxylic group and an azoxy function in the benzene ring.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The relationship between structure and biological activity in this substance and one of its analog, phenylazoxyxyanide, was investigated. Isolated hepatocytes were used as an experimental system: the release of lactate dehydrogenase and the colchicine-binding activity of tubulin were first evaluated; effects were dose and time dependent. micromolar concentrations of these drugs determined a significant decrease of the glucose-6-phosphatase activity and a slight inhibition of aminopyrene demethylation.
CONCLUSIONS:
A toxic effect at the microsomal level and an interaction with the microtubular system are thus possible.
Cell Biochemistry & Function, 1995, 13(4):231-238.
Antimicrotubular effect of calvatic acid and of some related compounds.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A structure–activity relationship has been established between Calvatic acid and some related synthetic compounds, and their ability to inhibit GTP‐induced microtubular protein polymerization in vitro. These compounds were effective in a dose‐ and a time‐dependent manner. The most active drug was the p‐chloro substituted compound, which showed its inhibitory activity without any preincubation period, which the others needed.
CONCLUSIONS:
Since if cysteine was present, polymerization was no longer affected, an involvement of titratable –SH groups of tubulin could be suggested. In contrast, taxol‐induced polymerization was only slightly inhibited by these compounds, and colchicine‐binding activity was not generally impaired.