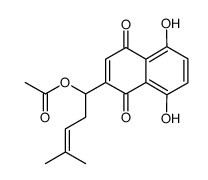
Acetylshikonin
Acetylshikonin has anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activity, it is a novel general P450 inhibitor with IC50 values of 1.4-4.0 μM for all tested P450s. Acetylshikonin exhibits weak cytotoxicity against human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with IC50 of over 20 microM, exhibits the antiangiogenic and antitumorigenic effects by suppressing proliferation and angiogenic factors. Certain shikonin derivatives(such as Acetylshikonin) act as modulators of the Nur77-mediated apoptotic pathway.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
bioRxiv - Biochemistry2023, 548213.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2024, 17(4):462.
Molecules.2022, 27(7):2360.
J.the Korean Socie. Food Sci.&Nut.2023; 52(1):26-39.
Cell Commun Signal.2024, 22(1):597.
Nat Prod Commun.2017, 12(5):771-778
Molecules.2019, 24(4):E709
Onco Targets Ther.2017, 10:3467-3474
Molecules.2019, 24(11):E2102
J Cancer.2019, 10(23):5843-5851
Related and Featured Products
Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008 Nov;128(11):1681-8.
Shikonin, acetylshikonin, and isobutyroylshikonin inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis and suppress tumor growth in lewis lung carcinoma-bearing mice.[Pubmed:
18981704]
Lithospermum erythrorhizon has been used for treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer as a folk remedy. Based on the evidences that anti-inflammatory agents frequently exert antiangiogenic activity, thus we examined comparatively the antiangiogenic activities of three naphthoquinone derivatives (shikonin, Acetylshikonin, and isobutyroylshikonin) isolated from the plant.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three derivatives exhibited weak cytotoxicity against human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with IC50 of over 20 microM. Shikonin had more specific inhibitory effects on proliferation and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production by VEGF compared with different derivatives. All of derivatives significantly suppressed the migration of VEGF treated HUVECs at different optimal concentrations. Also, shikonin and Acetylshikonin significantly disrupted VEGF-induced tube formation. Furthermore, three derivatives effectively downregulated the expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), but not its receptor uPAR. Additionally, shikonin significantly inhibited tumor growth in LLC-bearing mice, whereas its derivatives had relatively mild effects.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our findings suggest that shikonin and its derivatives exhibit the antiangiogenic and antitumorigenic effects by suppressing proliferation and angiogenic factors.
Phytomedicine . 2017 Jan 15;24:134-140.
Identification of acetylshikonin as the novel CYP2J2 inhibitor with anti-cancer activity in HepG2 cells[Pubmed:
28160853]
Abstract
Background: Acetylshikonin is one of the biologically active compounds derived from the root of Lithospermum erythrorhizon, a medicinal plant with anti-cancer and anti-inflammation activity. Although there have been a few previous reports demonstrating that Acetylshikonin exerts anti-cancer activity in vitro and in vivo, it is still not clear what is the exact molecular target protein of Acetylshikonin in cancer cells.
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the inhibitory effect of Acetylshikonin against CYP2J2 enzyme which is predominantly expressed in human tumor tissues and carcinoma cell lines.
Study design: The inhibitory effect of Acetylshikonin on the activities of CYP2J2-mediated metabolism were investigated using human liver microsomes (HLMs), and its cytotoxicity against human hepatoma HepG2 cells was also evaluated.
Method: Astemizole, a representative CYP2J2 probe substrate, was incubated in HLMs in the presence or absence of Acetylshikonin. After incubation, the samples were analyzed by liquid chromatography and triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. The anti-cancer activity of Acetylshikonin was evaluated on human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. WST-1, cell counting, and colony formation assays were further adopted for the estimation of the growth rate of HepG2 cells treated with Acetylshikonin.
Results: Acetylshikonin inhibited CYP2J2-mediated astemizole O-demethylation activity (Ki = 2.1μM) in a noncompetitive manner. The noncompetitive inhibitory effect of Acetylshikonin on CYP2J2 enzyme was also demonstrated using this 3D structure, which showed different binding location of astemizole and Acetylshikonin in CYP2J2 model. It showed cytotoxic effects against human hepatoma HepG2 cells (IC50 = 2μM). In addition, Acetylshikonin treatment inhibited growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells leading to apoptosis accompanied with p53, bax, and caspase3 activation as well as bcl2 down-regulation.
Conclusion: Taken together, our present study elucidates Acetylshikonin displays the inhibitory effects against CYP2J2 in HLMs and anti-cancer activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells.
Keywords: Acetylshikonin; Anti-cancer; CYP2J2; Inhibition.
Biopharm Drug Dispos . 2017 Dec;38(9):553-556.
Acetylshikonin is a novel non-selective cytochrome P450 inhibitor[Pubmed:
28866862]
Abstract
Acetylshikonin is a biologically active compound with anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activity, which is isolated from the roots of Lithospermum erythrorhizoma. An inhibitory effect of Acetylshikonin against CYP2J2 activity was discovered recently. Based on this result, this study was expanded to evaluate the inhibitory effects of Acetylshikonin against nine different cytochrome P450 (P450) isoforms in human liver microsomes (HLMs) using substrate cocktails incubation assay. Acetylshikonin showed a strong inhibitory effect against all P450s tested with IC50 values of 1.4-4.0 μ m. Pre-incubation of Acetylshikonin with HLMs and NADPH did not alter the inhibition potency, indicating that Acetylshikonin is not a mechanism-based inhibitor. SKF-525A, a widely used non-specific P450 inhibitor, had no inhibitory activity against CYP1A2, 2A6, 2E1 and 2J2, while it showed an inhibitory effect against CYP2B6, CYP2C19 and 2D6 with IC50 values of 2.5, 3.6 and 0.5 μ m, respectively. Our findings indicate that Acetylshikonin may be a novel general P450 inhibitor, which could replace SKF-525A.
Keywords: SKF-525A; Acetylshikonin; cytochrome P450; inhibitor.
Phytomedicine. 2003;10(5):375-80.
Anti-inflammatory activity of shikonin derivatives from Arnebia hispidissima.[Pubmed:
12834001]
Arnebia hispidissima ethanolic extract, after chromatography, yielded a number of shikonin derivatives, which were identified as arnebin-5, arnebin-6, teracryl shikonin, arnebinone and Acetylshikonin.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
All these compounds were firstly reported from this plant species and evaluated to the anti-inflammatory activity of ethanolic extract and isolated shikonin derivatives, models with carrageenan-induced paw edema and complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced chronic arthritis in rats were conducted.
CONCLUSIONS:
The observed results indicated that pre-treatment with arnebinone significantly inhibited the carrageenan-induced paw edema and also suppressed the development of chronic arthritis induced by CFA.
Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 1;68(21):8871-80.
Modulation of orphan nuclear receptor Nur77-mediated apoptotic pathway by acetylshikonin and analogues.[Pubmed:
18974131]
Shikonin derivatives, which are the active components of the medicinal plant Lithospermum erythrorhizon, exhibit many biological effects including apoptosis induction through undefined mechanisms. We recently discovered that orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 migrates from the nucleus to the mitochondria, where it binds to Bcl-2 to induce apoptosis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we report that certain shikonin derivatives could modulate the Nur77/Bcl-2 apoptotic pathway by increasing levels of Nur77 protein and promoting its mitochondrial targeting in cancer cells. Structural modification of Acetylshikonin resulted in the identification of a derivative 5,8-diacetoxyl-6-(1'-acetoxyl-4'-methyl-3'-pentenyl)-1,4-naphthaquinones (SK07) that exhibited improved efficacy and specificity in activating the pathway. Unlike other Nur77 modulators, shikonins increased the levels of Nur77 protein through their posttranscriptional regulation. The apoptotic effect of SK07 was impaired in Nur77 knockout cells and suppressed by cotreatment with leptomycin B that inhibited Nur77 cytoplasmic localization. Furthermore, SK07 induced apoptosis in cells expressing the COOH-terminal half of Nur77 protein but not its NH(2)-terminal region. Our data also showed that SK07-induced apoptosis was associated with a Bcl-2 conformational change and Bax activation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Together, our results show that certain shikonin derivatives act as modulators of the Nur77-mediated apoptotic pathway and identify a new shikonin-based lead that targets Nur77 for apoptosis induction.
Biol. Pharmaceut. Bull., 1994, 17(8):1075-7.
Accelerative effect of shikonin, alkannin and acetylshikonin on the proliferation of granulation tissue in rats.[Pubmed:
7820111]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study was carried out to compare the accelerative effect of shikonin (R-type), alkannin (S-type), and Acetylshikonin on the proliferation of granulation tissue in rats, and to elucidate the correlation between the potency of the effect and their optical activity. Koushikon mainly contained the R-type of Acetylshikonin, and Nanshikon mainly contained the S-type of Acetylshikonin. Each compound produced a dose-dependent acceleration of the cotton pellet-induced granuloma formation. In comparing identical doses of shikonin, alkannin and Acetylshikonin, the potency of their accelerative effects on the proliferation of granulation tissue was about the same.
CONCLUSIONS:
This result suggests that their absolute configurations (R-type or S-type) and their acetylation on the hydroxy group of the sidechain of shikonin or alkannin may not be important in producing the effect.