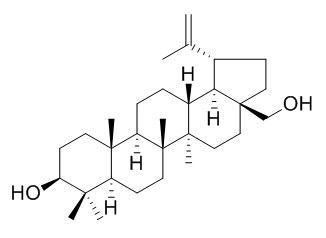
Betulin
Betulin (Trochol), is a sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) inhibitor with an IC50 of 14.5 μM in K562 cell line. Betulin has hypoglycemic, antineoplastic, anti-HIV, antimalarial and anti-inflammatory activities. Betulin can improve hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance and reduce atherosclerotic plaques. Betulin inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines expression and NF-κB signaling activation through STAT3 signaling, it is associated with activation of AMP kinase and inhibition of mTOR/p70S6K/pS6 signaling in these cells.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Nutrients.2020, 12(12):3638.
ACS Omega.2024, 9(41):42227-42244.
Materials Today Communications2023, 37:107216
Int J Mol Med.2015, 35(5):1237-45
J Ethnopharmacol.2023, 317:116789.
Front Microbiol.2023, 14:921653.
Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2021, 20(6):1165-1170.
Toxicol In Vitro.2024, 99:105876.
New Journal of Chemistry2019, 43:12538-12547
Int J Nanomedicine.2022, 17:6513-6525.
Related and Featured Products
Microb Pathog. 2014 Oct;75:21-8.
Betulin protects mice from bacterial pneumonia and acute lung injury.[Pubmed:
25173422]
Betulin, a naturally occurring triterpene, has shown anti-HIV activity, but details on the anti-inflammatory activity are scanty.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we sought to investigate the effect of Betulin on LPS-induced activation of cell lines with relevance for lung inflammation in vitro and on lung inflammation elicited by either LPS or viable Escherichia coli (E. coli) in vivo. In vitro, Betulin inhibited LPS-induced tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and (interleukin) IL-6 levels and up-regulated the level of IL-10. Also Betulin suppressed the phosphorylation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) p65 protein in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. In vivo, Betulin alleviated LPS-induced acute lung injury. Treatment with Betulin diminished pro-inflammatory cytokines, myeloperoxidase activity and bacterial loads in lung tissue during gram-negative pneumonia.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings demonstrated that Betulin inhibits pro-inflammatory responses induced by the gram-negative stimuli LPS and E. coli, suggesting that Betulin may represent a novel strategy for the treatment of lung inflammation.
Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014 Feb 6;68:191-7.
Influence of betulin and 28-O-propynoylbetulin on proliferation and apoptosis of human melanoma cells (G-361).[Pubmed:
24662787]
Pentacyclic triterpenes are a group of compounds known to have anticancer activity. One of the best characterized triterpenes is Betulin, which can be isolated from bark of birch trees and modified into new compounds with various interesting medical properties. Betulin is involved in activation of the caspase cascade and promotes cell death. The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of Betulin and its acetylenic derivative, 28-O-propynoylBetulin, on proliferation and apoptosis in a human melanoma cell line.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The G-361 melanoma cell line was used. To evaluate growth arrest and caspase-3 activity, cells were treated with Betulin and its derivative at a wide range of concentrations from 0.1 to 10 μg/mL.
Betulin and 28-O-propynoylBetulin inhibited cell proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner. The cell cycle analysis revealed an increase of the sub-G1 cell fraction (representing dead cells) after incubation of cells with Betulin and 28-O-propynoylBetulin. The observed cytotoxic effects were more pronounced for 28-O-propynoylBetulin. Activity of caspase-3 in 28-O-propynoylBetulin treated cells was nearly 2-fold greater compared to cells incubated with Betulin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results show that Betulin and 28-O-propynoylBetulin were effective in inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptosis in a human melanoma cell line. The addition of the propynoyl group at the C-28 hydroxyl group of Betulin led to a greater proapoptotic and antiproliferative effect in comparison to unmodified Betulin. These observations suggest that the obtained derivative is a potent anti-melanoma agent.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006 Sep;29(1):1-13.
Pharmacological properties of the ubiquitous natural product betulin.[Pubmed:
16716572]
Betulin (lup-20(29)-ene-3beta,28-diol) is an abundant naturally occurring triterpene and it is found predominantly in bushes and trees forming the principal extractive (up to 30% of dry weight) of the bark of birch trees. Presently, there is no significant use for this easily isolable compound, which makes it a potentially important raw material for polymers and a precursor of biologically active compounds.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Betulin can be easily converted to Betulinic acid, which possesses a wide spectrum of biological and pharmacological activities. Betulinic acid has antimalarial and anti-inflammatory activities. Betulinic acid and its derivatives have especially shown anti-HIV activity and cytotoxicity against a variety of tumor cell lines comparable to some clinically used drugs. A new mechanism of action has been confirmed for some of the most promising anti-HIV derivatives, which makes them potentially useful additives to the current anti-HIV therapy. Betulinic acid is specifically cytotoxic to several tumor cell lines by inducing apoptosis in cells. Moreover, it is non-toxic up to 500 mg/kg body weight in mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
The literature concerning derivatization of Betulin for structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies and its pharmacological properties is reviewed.
Biomed Res Int . 2015;2015:584189.
Comprehensive review on betulin as a potent anticancer agent[Pubmed:
25866796]
Abstract
Numerous plant-derived substances, and their derivatives, are effective antitumour and chemopreventive agents. Yet, there are also a plethora of tumour types that do not respond, or become resistant, to these natural substances. This requires the discovery of new active compounds. Betulin (BE) is a pentacyclic triterpene and secondary metabolite of plants abundantly found in the outer bark of the birch tree Betulaceae sp. BE displays a broad spectrum of biological and pharmacological properties, among which the anticancer and chemopreventive activity attract most of the attention. In this vein, BE and its natural and synthetic derivatives act specifically on cancer cells with low cytotoxicity towards normal cells. Although the antineoplastic mechanism of action of BE is not well understood yet, several interesting aspects of BE's interactions are coming to light. This review will summarize the anticancer and chemopreventive potential of BE in vitro and in vivo by carefully dissecting and comparing the doses and tumour lines used in previous studies, as well as focusing on mechanisms underlying its activity at cellular and molecular level, and discuss future prospects.
Cell Metab. 2011 Jan 5;13(1):44-56.
Inhibition of SREBP by a small molecule, betulin, improves hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance and reduces atherosclerotic plaques.[Pubmed:
21195348 ]
Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) are major transcription factors activating the expression of genes involved in biosynthesis of cholesterol, fatty acid and triglyceride.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we identified a small molecule, Betulin, that specifically inhibited the maturation of SREBP by inducing interaction of SREBP cleavage activating protein (SCAP) and Insig. Inhibition of SREBP by Betulin decreased the biosynthesis of cholesterol and fatty acid. In vivo, Betulin ameliorated diet-induced obesity, decreased the lipid contents in serum and tissues, and increased insulin sensitivity. Furthermore, Betulin reduced the size and improved the stability of atherosclerotic plaques.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our study demonstrates that inhibition SREBP pathway can be employed as a therapeutic strategy to treat metabolic diseases including type II diabetes and atherosclerosis. Betulin, which is abundant in birch bark, could be a leading compound for development of drugs for hyperlipidemia.
Neurotoxicology . 2016 Dec;57:104-111.
Protective effect of betulin on cognitive decline in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats[Pubmed:
27640960]
Abstract
Betulin is extracted from birch tree bark and exerts diverse pharmacological activities. The present study was designed to investigate the protective effect of Betulin (BE) on cognitive decline in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. The diabetic model was built by streptozotocin (STZ) (30mg/kg, ip). After 4 weeks, the diabetic rats were treated with vehicle or BE (20mg/kg, 40mg/kg) for 4 weeks. The oral glucose tolerance (OGTT) and serum insulin were detected. Three days later, Morris water maze (MWM) test was used to evaluate memory function. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) content in hippocampus were examined. Inflammatory cytokines including interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in serum and hippocampus were measured. The protein expressions of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and NF-κB pathways-related molecules in hippocampus were examined. As a results, BE could improve glucose intolerance and modify basal learning performance. Treatment with BE significantly restored SOD activity and decreased MDA content in hippocampus. BE also markedly reduced the contents of inflammatory cytokines in serum and hippocampus. Furthermore, administration of BE effectively upregulated the expressions of Nrf2, HO-1 and blocked the phosphorylations of IκB, NF-κB. In summary, BE might exhibit protective effect on cognitive decline in STZ-induced diabetic rats through HO-1/Nrf-2/NF-κB pathway.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(3):455-60.
Betulin inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines expression through activation STAT3 signaling pathway in human cardiac cells.[Pubmed:
25720718]
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is an important regulator of cardiac survival pathways. Decreased expression or activity of STAT3 in patients with end-stage heart failure demonstrated a clinical relevance of STAT3 in cardiac diseases. Betulin, a pentacyclic triterpene, has drawn extensive attention towards its beneficial effects. However, little is known about its roles in cardiac cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the effects of Betulin on the pro-inflammatory processes in human cardiac AC16 cells. Genes expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and activation of NF-κB signaling were analyzed. Besides, levels of phosphorylated STAT3 and its down-stream target genes were measured to evaluate the activation of STAT3. Finally, STAT3 inhibitor and small interfering RNA (siRNA) oligos were used to determine the roles of STAT3 in AC16 cells treated with Betulin.
Our results revealed that Betulin inhibited pro-inflammatory cytokines expression and NF-κB signaling activation through STAT3 signaling. Besides, Betulin treatment also induced the expression of Bcl-xL, an anti-apoptotic downstream effector of STAT3.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results, for the first time, uncovered the cardioprotective roles of Betulin, which may be useful to reduce the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular events.
Toxicology. 2011 Feb 27;280(3):152-63.
Betulin and betulinic acid attenuate ethanol-induced liver stellate cell activation by inhibiting reactive oxygen species (ROS), cytokine (TNF-α, TGF-β) production and by influencing intracellular signaling.[Pubmed:
21172400]
Liver fibrosis has been reported to be inhibited in vivo by oleanolic and ursolic acids. However, the mechanisms of the action of those triterpenoids are poorly understood. In this study, we aimed to determine the antifibrotic potential of other triterpenes, Betulin and Betulinic acid, and to characterize their influence on the signal transduction pathways involved in ethanol-activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Investigated was the influence of preincubation of rat HSCs with Betulin and Betulinic acid, at non-toxic concentrations, on ethanol-induced toxicity, migration, and several markers of HSC activation such as smooth muscle α-actin (α-SMA) and procollagen I expression, release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cytokines: tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and tumor growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), and production of metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-1 and TIMP-2). To assess the mechanism of the action of those triterpenes, intracellular signals such as nuclear factor-κB (NFκB), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) induced by ethanol were examined.
In vitro, Betulin, but not Betulinic acid, protected HSCs against ethanol toxicity. However, both Betulin and Betulinic acid inhibited the production of ROS by HSCs treated with ethanol and inhibited their migration as well as ethanol-induced TNF-α, and TGF-β1, production. Betulin and Betulinic acid down-regulated ethanol-induced production of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2. Betulin and Betulinic acid, also decreased ethanol-induced activity of MMP-2. In ethanol-induced HSCs, Betulin inhibited the activation of the p38 MAPK and the JNK transduction pathways, while Betulinic acid inhibited the JNK transduction pathway only. They also significantly inhibited phosphorylation of IκB and Smad 3 and attenuated the activation of TGF-β1 and NFκB/IκB transduction signaling.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicated that Betulin and Betulinic acid inhibited ethanol-induced activation of HSCs on different levels, acting as antioxidants, inhibitors of cytokine production, and inhibitors of TGF-β, and NFκB/IκB transduction signaling. Betulin was also inhibitor of both JNK and p38 MAPK signal transduction, while Betulinic acid inhibited only JNK. The remarkable inhibition of several markers of HCS activation makes triterpenes, especially Betulin, promising agents for anti-fibrotic combination therapies.
Drug Deliv. 2014 Sep;21(6):467-79.
Preparation and characterization of betulin nanoparticles for oral hypoglycemic drug by antisolvent precipitation.[Pubmed:
24479653]
Betulin, a kind of small molecular compound, was reported that has hypoglycemic effect. Due to its low aqueous solubility and high permeability, Betulin has low and variable oral bioavailability.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, Betulin nanoparticles were thus prepared by antisolvent precipitation for accelerating dissolution of this kind of poorly water-soluble drugs. Ethanol was used as solvent and deionized water was used as antisolvent. The effects of various experimental parameters on the mean particle size (MPS) of nanocrystallization Betulin were investigated. The MPS of Betulin nanoparticles suspension basically remain unchanged when precipitation time was within 60 min and then increased from 304 nm to 505 nm later. However, the MPS of Betulin nanoparticles suspension decreased with increased Betulin solution concentration. On the contrary, the MPS of Betulin nanoparticles suspension decreased along with the increase of temperature. Stirring intensity and the speed ratio of solvent adding into antisolvent had no significant influences on the MPS of Betulin nanoparticles suspension. Betulin nanoparticles suspension with a MPS of approximately 110 nm was achieved under the optimal precipitation conditions. FTIR, Liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) were used to analyze the characteristic of Betulin nanoparticles powder. These results show that Betulin nanoparticles powder has the same chemical structure as raw drug, but a smaller size and lower crystallinity. The dissolution rate and solubility of Betulin nanoparticles powder were separately 3.12 and 1.54 times of raw drug. The bioavailability of Betulin nanoparticles powder increased 1.21 times compared with raw Betulin.
CONCLUSIONS:
The result of in vivo evaluation on diabetic animals demonstrates that the Betulin nanoparticles powder show an excellent hypoglycemic effect compared with raw Betulin. In addition, the residual ethanol is less than the ICH (International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human) limit for class 3 solvents of 5000 ppm or 0.5% for solvents.