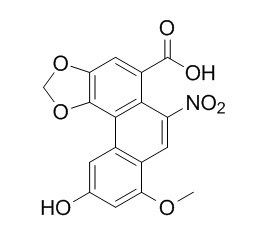
Aristolochic acid D
Chinese-herb nephropathy (CHN) is a rapidly progressive renal fibrosis associated with the intake of a Chinese herb (Aristolochia fangchi) containing nephrotoxic and carcinogenic aristolochic acids.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
LWT2021, 150:112021.
Comparative Clinical Pathology 2021, 30:961-971.
Integrative Medicine Research2024, 13(1):101025.
Molecules.2018, 23(2)
Pharmacia2024, 71:1-9.
Cells.2023, 12(3):395.
Phytomedicine.2019, 58:152893
Int J Mol Sci.2018, 19(2)
Fitoterapia.2024, 175:105958.
Yakugaku Zasshi.2018, 138(4):571-579
Related and Featured Products
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1968, 33(10):3735-3738.
The isolation and structural elucidation of novel derivatives of aristolochic acid from Aristolochia indica.[Reference:
WebLink]
The isolation and structural elucidation are reported of three new companion Aristolochic acid Derivatives, aristolochic acid D (4), aristolochic acid-D methyl ether lactam (6), and aristololactam β-D-glucoside (8).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Aristolochic acid D was assigned the molecular formula C17H11NO8 on the basis of elemental analysis and nmr spectroscopy. Methylation with diazomethane yielded the dimethyl derivative 5, and hydrogenation of 5 yielded aristolochic acid-D methyl ether lactam (6), identical with the material of natural origin. The structure of 5 was initially deduced on the basis of spectral evidence, and confirmed by direct comparison with a sample prepared by total synthesis. Spectral arguments are presented which favor structure 4 for Aristolochic acid D.
CONCLUSIONS:
Aristololactam β-D-glucoside (8) was characterized by elemental and nmr, ir, and uv spectral analysis. Acetylation gave the tetraacetate, 9. Lithium aluminum hydride reduction of 8, followed by mild acid hydrolysis, gave α-D-glucose and the aglycone 11, characterized by comparison with the product obtained by lithium aluminum hydride reduction of aristololactam.