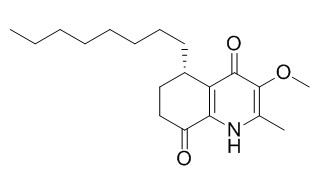
Antidesmone
Antidesmone is a selective post-emergent herbicide probe at 300μM by reducing the biomass production of Physalis ixacarpa plants, it also behaves as pre-emergent herbicide due to inhibit Physalis ixacarpa plant growth about 60%. Antidesmone is a relative toxic anti-inflammatory drug, it can inhibit inflammation on stimulated macrophages and thereby prevents acute lung injury by regulating MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Antidesmone also exhibits potent antitrypanosomal activity against Trypanasoma cruzi, the pathogenic agent of Chagas disease.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules.2019, 24(4):E744
Cancer Sci.2022, 113(4):1406-1416.
J Ethnopharmacol.2020, 249:112396
Universidade Estadual Paulista2017, 42785
Toxins (Basel).2021, 13(12):898.
Nat Prod Sci.2019, 25(3):238
Molecules.2019, 24(6):E1155
Cytotechnology.2017, 69(5):765-773
Korean Herb. Med. Inf.2020, 8(2):243-254.
Planta Med.2018, 84(6-07):465-474
Related and Featured Products
Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Apr;45:34-42.
Antidesmone, a unique tetrahydroquinoline alkaloid, prevents acute lung injury via regulating MAPK and NF-κB activities.[Pubmed:
28157559 ]
Acute lung injury, characterized by inflammation, is a main cause of respiratory failure that affects patients worldwide. Antidesmone is one compound mainly isolated from Ajugade cumbens Thunb (Labiatae), an herb agent of Labiatae family.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this research, we investigated the anti-inflammation effect of Antidesmone in vitro and in vivo. Antidesmone exerted none apparently cytotoxicity in vitro and toxic in vivo. In vitro results demonstrated that Antidesmone suppressed the excess inflammatory cytokines production, including tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6 and interleukin-1β in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-exposed RAW264.7 cells. In vivo results suggested that Antidesmone inhibited inflammatory cytokines in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and lung tissue after LPS stimulation. Moreover, Antidesmone attenuated the nuclear translocation of p65. Mechanism study revealed that mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathways play important roles in Antidesmone's action.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our data uncover a relative toxic anti-inflammatory drug, Antidesmone, can inhibit inflammation on stimulated macrophages and thereby prevents acute lung injury by regulating MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways.
Pharm.Pharmacol.Lett.,2001,2:47-8.
Antidesmone, a novel antitrypanosomal alkaloid.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Antidesmone, a novel acetogenic quinolone alkaloid from the African shrub Antidesma membranaceum, has been found to exhibit potent antitrypanosomal activity against Trypanasoma cruzi, the pathogenic agent of Chagas disease.
CONCLUSIONS:
The activity seems to be highly selective, being much larger than that towards other protozoan parasites causing tropical diseases.
Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2016 Nov;134:55-62.
Evaluation of antidesmone alkaloid as a photosynthesis inhibitor.[Pubmed:
27914540]
Antidesmone, isolated from Waltheria brachypetala Turcz., owns special structural features as two α,β-unsaturated carbonyl groups and a side alkyl chain that can compete with the quinones involved in the pool of plastoquinones at photosystem II (PSII).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, we showed that the alkaloid is an inhibitor of Hill reaction and its target was located at the acceptor side of PSII. Studies of chlorophyll (Chl) a fluorescence showed a J-band that indicates direct action of Antidesmone in accumulation of QA- (reduced plastoquinone A) due to the electron transport blocked at the QB (plastoquinone B) level similar to DCMU. In vivo assays indicated that Antidesmone is a selective post-emergent herbicide probe at 300μM by reducing the biomass production of Physalis ixacarpa plants. Furthermore, Antidesmone also behaves as pre-emergent herbicide due to inhibit Physalis ixacarpa plant growth about 60%.
CONCLUSIONS:
Antidesmone, a natural product containing a 4(1H)-pyridones scaffold, will serve as a valuable tool in further development of a new class of herbicides.
Phytochemistry. 2002 Jul;60(5):489-96.
Chemotaxonomy of the tribe Antidesmeae (Euphorbiaceae): antidesmone and related compounds.[Pubmed:
12052515]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Selected species of the tribe Antidesmeae (Euphorbiaceae, subfamily Phyllanthoideae) have been screened for Antidesmone occurrence and its content by quantitative HPLC (UV) and qualitative LC-MS/MS analysis. The LC-MS analysis allowing the additional detection of 17,18-bis-nor-Antidesmone, 18-nor-Antidesmone, 8-dihydroAntidesmone and 8-deoxoAntidesmone was carried out in the selected reaction monitoring (SRM) mode. Leaf material from herbarium specimens of 13 Antidesma spp., Hyeronima alchorneoides and Thecacoris stenopetala (all subtribe Antidesminae), as well as Maesobotrya barteri, Aporosa octandra (both Scepinae) and Uapaca robynsii (Uapacinae) were analysed. Additionally, freshly collected samples of different plant parts of two Antidesma spp. were investigated to ensure the significance of the results on herbarium specimens and to compare the Antidesmone content in bark, root and leaves.
CONCLUSIONS:
Antidesmone could be unambiguously identified in 12 of 13 Antidesma spp., as well as in the two other investigated genera of subtribe Antidesminae, in levels of up to 65 mg/kg plant dry weight.
Antidesmone was not found in specimens from other subtribes. Antidesmone-derived compounds occur in much lower concentrations than Antidesmone.