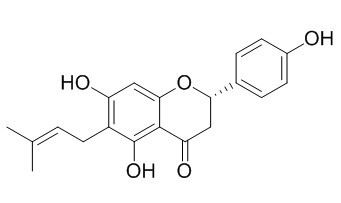
6-Prenylnaringenin
6-Prenylnaringenin is an isomer of the potent phytoestrogen, 8-prenylnaringenin. It exhibits both mixed and non-competitive inhibitory characteristics against tyrosinase, tyrosinase is the rate-limiting enzyme for the production of melanin and other pigments via the oxidation of l-tyrosine. 6-Prenylnaringenin has anti-cancer potential , dose-dependent reduction of cellular proliferation of human PC-3 prostate cancer and UO.31 renal carcinoma cells upon treatment. 6-Prenylnaringenin can inhibit 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA)-induced inflammation (1μg/ear) in mice, it also exhibits inhibitory effects on skin-tumor promotion in anin vivo two-stagemouse-skin carcinogenesis test based on 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]- anthracene (DMBA) as initiator and with TPA as promoter.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Toxicol Mech Methods.2021, 1-12.
ACS Omega.2022, 7(44):40009-40020.
J. of Med. Plant Research.2013, 90-151
Biomolecules.2020, 10(2):E184
Front Plant Sci.2022, 13:982771.
Russian J Bioorganic Chemistry 2021, 47:1411-1417.
Plant Archives2020, 2(1),2929-2934
Journal of Life Science2017, 233-240
Nutrients2023, 15(18), 4016.
Mol Biol Rep.2024, 51(1):117.
Related and Featured Products
Chem. Biodivers., 2012, 9(6):1045-54.
Anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor-promoting effects of 5-deprenyllupulonol C and other compounds from Hop (Humulus lupulus L.).[Pubmed:
22700224 ]
A new phloroglucinol derivative, 5-deprenyllupulonol C (1), along with four other phloroglucinol derivatives, 2-5, five chalcones, 6-10, four flavanones, 11-14, two flavonol glycosides, 15 and 16, and five triterpenoids, 17-21, were isolated from the female inflorescence pellet extracts of hop (Humulus lupulus L.).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Upon evaluation of these compounds against the Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) activation induced by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA) in Raji cells, twelve compounds, i.e., 1-4, 11-14, 17-19, and 21, showed potent inhibitory effects on EBV-EA induction, with IC₅₀ values in the range of 215-393 mol ratio/32 pmol TPA. In addition, eleven compounds, i.e., 1-4, 6, 11, 12, 14, 17, 18, and 20, were found to inhibit TPA-induced inflammation (1 μg/ear) in mice, with ID₅₀ values in the range of 0.13-1.06 μmol per ear. Further, lupulone C (2) and 6-Prenylnaringenin (14) exhibited inhibitory effects on skin-tumor promotion in an in vivo two-stage mouse-skin carcinogenesis test based on 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) as initiator and with TPA as promoter.
J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Ch., 2016, 31(5):1-6.
Phenols displaying tyrosinase inhibition from Humulus lupulus.[Pubmed:
26162028 ]
Tyrosinase is the rate-limiting enzyme for the production of melanin and other pigments via the oxidation of l-tyrosine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The methanol extract from Humulus lupulus showed potent inhibition against mushroom tyrosinase. The bioactivity-guided fractionation of this methanol extract resulted in the isolation of seven flavonoids (1-7), identified as xanthohumol (1), 4'-O-methylxanthohumol (2), xanthohumol C (3), flavokawain C (4), xanthoumol B (5), 6-Prenylnaringenin (6) and isoxanthohumol (7). All isolated flavonoids (1-7) effectively inhibited the monophenolase (IC50s = 15.4-58.4 μM) and diphenolase (IC50s = 27.1-117.4 μM) activities of tyrosinase. Kinetic studies using Lineweaver-Burk and Dixon-plots revealed that chalcones (1-5) were competitive inhibitors, whereas flavanones (6 and 7) exhibited both mixed and non-competitive inhibitory characteristics.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, this study is the first to demonstrate that the phenolic phytochemicals of H. lupulus display potent inhibitory activities against tyrosinase.
Res. Pharm. Sci. 2015 May-Jun; 10(3): 182–191.
Stereospecific quantitation of 6-prenylnaringenin in commercially available H. lupulus-containing natural health products and dietary supplements[Pubmed:
PMC4621624]
6-Prenylnaringenin (6PN) is a chiral prenylflavonoid found most prevalently in hops (Humulus lupulus) and present in hops and hop products. It is an isomer of the potent phytoestrogen, 8-prenylnaringenin. An enantiospecific method for quantitation 6PN by LC-ESI-MS has been developed.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Baseline enantiomeric resolution of 6PN was attained on a Chiralpak® AD-RH column with an isocratic mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and 10 mM ammonium formate (pH 8.5) (39:61, v/v) and a flow rate of 1.25 mL/min. Quantitative MS data were obtained by selected ion monitoring of the [M-H]--ion of both enantiomers of 6PN (m/z 339.10) and the internal standard, 4-acetamidobenzoic acid (m/z 178.05). The method was found to be accurate and precise for enantiospecific quantification of 6PN. The method was successfully applied to the content analysis of 39 commercially available natural health products and dietary supplements reported to contain H. lupulus plant material, extracts and label claims of 6PN. 6PN was present in 25 of 34 products containing plant material or extracts of H. lupulus.
CONCLUSIONS:
Of the five products with claimed amounts of 6PN, all were found to possess <50% of label claims. Results of the content analysis indicated a lack of uniformity in botanical nutraceuticals claiming 6PN content.