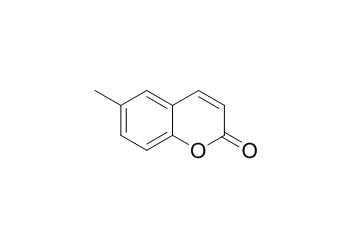
6-Methylcoumarin
6-Methylcoumarin, widely used in cosmetics, is capable of inducing contact photoallergy in human volunteers.It has hepatotoxicity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Res Int.2020, 133:109130.
Antioxidants (Basel).2022, 11(12):2327.
Phytother Res.2022, 10.1002:ptr.7592.
Toxicol Rep.2021, 8:1131-1142.
J Colloid Interface Sci.2022, 622:298-308.
Plants (Basel).2023, 12(5):1120.
BioRxiv-The Preprint server for biology2023, 586957.
South African Journal of Botany2021, 142:114-123.
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 975:176644.
Antioxidants (Basel).2020, 9(11):1121.
Related and Featured Products
Contact Dermatitis, 2010, 4(5):277-282.
Photocontact allergy to 6-methylcoumarin.[Pubmed:
743874]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A proprietary sunscreen-induced photosensitivity reactions in a small number of users. Laboratory study revealed that the reactions were of the photoallergic type and were due to the presence of a synthetic fragrance, 6-Methylcoumarin.
CONCLUSIONS:
By photomaximization testing 6-Methylcoumarin was found to be a potent photocontact allergen.
Food and Chemical Toxicology, 1994, 32(8):743-751.
Comparison of the hepatic effects of coumarin, 3,4-Dimethylcoumarin, dihydrocoumarin and 6-methylcoumarin in the rat.[Reference:
WebLink]
The mechanism of coumarin-induced hepatotoxicity in the rat has been investigated by comparing the effects of coumarin with those of three coumarin derivatives, namely 3,4-dihydrocoumarin (DHC), 3,4-dimethylcoumarin (3,4-DMC) and 6-Methylcoumarin (6-MC).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were fed either control diet or diets containing 0.5 or 0.75% coumarin, 0.76% DHC, 0.6 or 0.9% 3,4-DMC or 0.82% 6-MC for 13 wk. The dietary levels of 0.5% coumarin and 0.6% 3,4-DMC, were equimolar (3.43mmol/100g diet), as were the dietary levels of 0.75% coumarin, 0.76% DHC, 0.9% 3,4-DMC and 0.82% 6-MC (5.14mmol/100g diet). All treatments resulted in an increase in relative liver weight, but only coumarin increased plasma alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase activities. Morphological examination of liver sections from coumarin treated rats revealed vacuolation of centrilobular hepatocytes and bile duct hyperplasia. Cholangiofibrosis was also observed, particularly in rats given 0.75% coumarin. Treatment with DHC produced no abnormalities, whereas a slight hypertrophy of centrilobular hepatocytes was observed in some 3,4-DMC treated animals and a slight vacuolation of individual hepatocytes was noted in some 6-MC treated rats. DHC, 6-MC and particularly 3,4-DMC treatment resulted in an induction of cytochrome P-450 dependent mixed function oxidase enzyme activities. All treatments induced hepatic GSHS-transferase and γ-glutamyltransferase activities, induction being most marked in rats given coumarin and 6-MC.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results provide further evidence that coumarin-induced hepatotoxicity in the rat is due to the formation of a 3,4-epoxide intermediate.