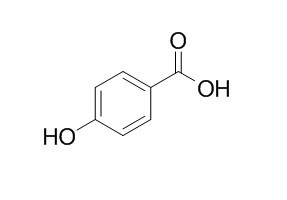
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), is a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid and widely used in organic synthesis. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives has potential to as pan-HDAC inhibitors with anticancer properties. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid positively regulates the expression of gum cluster to promote EPS production in PXO99A; it can inhibit most gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria, with an IC50 of 160 μg/mL.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 25(1):162.
The Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences2023, 47(3):3.
Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed.2024, 40(1):e12950.
Korean J of Pharmacognosy2020, 51,49-54.
The Korea Journal of Herbology2016, 29-35
Plants (Basel).2021, 10(6):1119.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2020, 530(1):4-9.
Virus Res.2023, 335:199199.
Molecules.2023, 28(19):6767.
Phytochem Anal.2016, 27(5):296-303
Related and Featured Products
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998 Nov;62(11):2273-6.
Antimicrobial activity of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and trans 4-hydroxycinnamic acid isolated and identified from rice hull.[Pubmed:
9972252 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two antimicrobial substances in rice hull were isolated and identified as 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid and trans 4-hydroxycinnamic acid by LC-MS, and 1H- and 13C-NMR. An evaluation of 50% inhibition of growth (IC50) revealed that the two substances had different inhibition profiles against various microorganisms.
CONCLUSIONS:
Most of the gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria were sensitive to trans 4-hydroxycinnamic acid and 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid at IC50 concentrations of 100-170 and 160 micrograms/ml, respectively.
Int. J.Pharmaceut. Sci. Rev. Res., 2013, 22(2): 109-15.
A Comprehensive Review on Biological activities of p-hydroxy benzoic acid and its derivatives.[Reference:
WebLink]
p-hydroxy benzoic acid (PHBA) is an organic chemical which can be obtained naturally as well as synthetically. The literature survey reveals its various biological properties viz. antimicrobial, antialgal, antimutagenic, antiestrogenic, hypoglycemic, anti-inflammatory, anti-platelet aggregating, nematicidal, antiviral, antioxidant etc. It is also reported to be used as preservative in many drugs, cosmetic products, pharmaceuticals, food and beverages. Some derivatives of 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid are found to possess direct action on Hbs molecules, inhibit acetic acid induced oedema and used in management of sickle cell disease.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present study will give comprehensive information of the biological activities of this p-hydroxy benzoic acid and its derivatives.
Cancer Lett. 2014 Feb 1;343(1):134-46.
Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid-based inhibitors of histone deacetylases.[Pubmed:
24080339]
Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs) regulate cellular processes by modifying the acetylation status of many proteins. Pathologically altered HDAC activity contributes to cancer development and thus characterization of novel acetylation modulators is important for future anti-cancer therapies.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we identified three novel 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives as pan-HDAC inhibitors that increased protein acetylation levels, arrested cell cycle progression and triggered apoptotic cell death, without affecting viability of normal cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our data support the potential of 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives as pan-HDAC inhibitors with anticancer properties.
Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013 Oct;26(10):1239-48.
The rice bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae produces 3-hydroxybenzoic acid and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid via XanB2 for use in xanthomonadin, ubiquinone, and exopolysaccharide biosynthesis.[Pubmed:
23718125]
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, the causal agent of rice bacterial blight, produces membrane-bound yellow pigments, referred to as xanthomonadins. Xanthomonadins protect the pathogen from photodamage and host-induced perioxidation damage. They are also required for epiphytic survival and successful host plant infection.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we show that XanB2 encoded by PXO_3739 plays a key role in xanthomonadin and coenzyme Q8 biosynthesis in X. oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A. A xanB2 deletion mutant exhibits a pleiotropic phenotype, including xanthomonadin deficiency, producing less exopolysaccharide (EPS), lower viability and H2O2 resistance, and lower virulence. We further demonstrate that X. oryzae pv. oryzae produces 3-hydroxybenzoic acid (3-HBA) and 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid (4-HBA) via XanB2. 3-HBA is associated with xanthomonadin biosynthesis while 4-HBA is mainly used as a precursor for coenzyme Q (CoQ)8 biosynthesis. XanB2 is the alternative source of 4-HBA for CoQ8 biosynthesis in PXO99A. These findings suggest that the roles of XanB2 in PXO99A are generally consistent with those in X. campestris pv. campestris. The present study also demonstrated that X. oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A has evolved several specific features in 3-HBA and 4-HBA signaling. First, our results showed that PXO99A produces less 3-HBA and 4-HBA than X. campestris pv. campestris and this is partially due to a degenerated 4-HBA efflux pump. Second, PXO99A has evolved unique xanthomonadin induction patterns via 3-HBA and 4-HBA. Third, our results showed that 3-HBA or 4-HBA positively regulates the expression of gum cluster to promote EPS production in PXO99A.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the results of this study indicate that XanB2 is a key metabolic enzyme linking xanthomonadin, CoQ, and EPS biosynthesis, which are collectively essential for X. oryzae pv. oryzae pathogenesis.