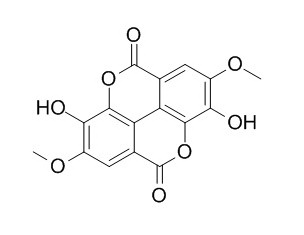
4,4'-Di-O-methylellagic acid
4,4'-di-O-methylellagic acid is the most effective compound in the inhibition of colon cancer cell proliferation.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Phytomedicine.2018, 38:45-56
J Appl Biol Chem2023, 66:455−461
J. Traditional Thai Medical Res. 2022,8(1):1-14.
Int J Med Sci.2020, 17(5):626-631
Neuropharmacology2019, 151437
Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).2023, 69(15):167-173.
Int Immunopharmacol.2024, 141:112906.
Nutr Res Pract2019, 13:e45
J Ethnopharmacol.2022, 289:115018.
Front Microbiol.2022, 12:833233.
Related and Featured Products
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 May;353(2):433-44.
The ellagic acid derivative 4,4'-di-O-methylellagic acid efficiently inhibits colon cancer cell growth through a mechanism involving WNT16.[Pubmed:
25758919]
Ellagic acid (EA) and some derivatives have been reported to inhibit cancer cell proliferation, induce cell cycle arrest, and modulate some important cellular processes related to cancer.
This study aimed to identify possible structure-activity relationships of EA and some in vivo derivatives in their antiproliferative effect on both human colon cancer and normal cells, and to compare this activity with that of other polyphenols.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Our results showed that 4,4'-Di-O-methylellagic acid (4,4'-DiOMEA) was the most effective compound in the inhibition of colon cancer cell proliferation. 4,4'-DiOMEA was 13-fold more effective than other compounds of the same family. In addition, 4,4'-DiOMEA was very active against colon cancer cells resistant to the chemotherapeutic agent 5-fluoracil, whereas no effect was observed in nonmalignant colon cells. Moreover, no correlation between antiproliferative and antioxidant activities was found, further supporting that structure differences might result in dissimilar molecular targets involved in their differential effects. Finally, microarray analysis revealed that 4,4'-DiOMEA modulated Wnt signaling, which might be involved in the potential antitumor action of this compound.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggest that structural-activity differences between EA and 4,4'-DiOMEA might constitute the basis for a new strategy in anticancer drug discovery based on these chemical modifications.