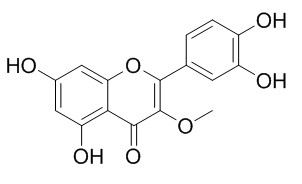
3-O-Methylquercetin
3-O-Methylquercetin is a selective and competitive PDE3/PDE4 inhibitor, and inhibits PDE3 than PDE4 with a low K(m) value; it inhibits total cAMP- and cGMP-phosphodiesterase (PDE) of guinea pig trachealis at low concentrations. 3-O-Methylquercetin has antiviral, anti-inflammatory and bronchodilating effects, and has the potential for use in the treatment of asthma at a dose without affecting blood pressure.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int J Mol Sci.2020, 21(19):7209.
RSC Adv.2023, 13(9):6317-6326.
Aquaculture2017, 481:94-102
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy.2020, 51(2):100-106
Microchemical Journal2018, 137:168-173
Food Bioscience2022, 50:102187.
Int J Oncol.2016, 49(4):1497-504
University of Central Lancashire2017, 20472
Cell Rep.2022, 39(1):110643.
Molecules.2020, 25(18),4089.
Related and Featured Products
4'-hydroxy-6,7,8,3'-tetramethoxyflavonol
Catalog No: CFN91846
CAS No: 1879030-01-9
Price: $318/5mg
5,7,3',4'-Tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN91116
CAS No: 855-97-0
Price: $30/20mg
Retusin
Catalog No: CFN89520
CAS No: 1245-15-4
Price: $158/10mg
Quercetin 3,5,7,3,4-pentamethyl ether
Catalog No: CFN70262
CAS No: 1247-97-8
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Artemetin
Catalog No: CFN98731
CAS No: 479-90-3
Price: $80/20mg
Artemetin acetate
Catalog No: CFN97530
CAS No: 95135-98-1
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Quercetin
Catalog No: CFN99272
CAS No: 117-39-5
Price: $40/20mg
Azaleatin
Catalog No: CFN91007
CAS No: 529-51-1
Price: $268/10mg
3-O-Methylquercetin
Catalog No: CFN99616
CAS No: 1486-70-0
Price: $338/10mg
3-O-Methylquercetin tetraacetate
Catalog No: CFN99615
CAS No: 1486-69-7
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Pharmazie. 2009 Nov;64(11):726-30.
Development of topical nanoemulsions containing quercetin and 3-O-methylquercetin.[Pubmed:
20099516]
This study describes the physico-chemical properties and the skin permeation profile of quercetin (Q) and 3-O-Methylquercetin (MQ) from lipid nanoemulsions.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Formulations composed of octyldodecanol, egg lecithin, water (NE) and cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CNE) were obtained by spontaneous emulsification. This procedure yielded monodisperse nanoemulsions exhibiting a mean droplet size of approximately 200-300 nm. Nanoemulsions were further characterized in terms of zeta-potential, surface tension, and morphology by transmission electron microscopy. The amount of flavonoids incorporated into nanoemulsions reached nearly 100% (at 1 mg/mL). The permeation studies were carried out using ear pig skin mounted in Franz diffusion cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
The overall results have shown a slow permeation profile of both Q and 3-O-Methylquercetin from nanoemulsions. However, a higher permeation flux rate of flavonoids from CNE (approximately 0.2 microg/cm2/h) as compared to NE (approximately 0.08 microg/cm2/h) was observed, showing the effect of the positively charged surface of CNE on this parameter.
Such results open interesting perspectives for the topical administration of the flavonoids Q and 3-O-Methylquercetin.
Planta Med. 2003 Apr;69(4):310-5.
3-O-methylquercetin more selectively inhibits phosphodiesterase subtype 3.[Pubmed:
12709896]
Rhamnus nakaharai Hayata (Rhamnaceae), has been used as a folk medicine in Taiwan for treating constipation, inflammation, tumors and asthma. 3-O-Methylquercetin (3-MQ), a main constituent of the plant, has been reported to inhibit total cAMP- and cGMP-phosphodiesterase (PDE) of guinea pig trachealis. Therefore we were interested in investigating the inhibitory effect of 3-O-Methylquercetin on various PDE isozymes from guinea pig lungs and hearts.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Isolated guinea pig lungs and hearts were homogenized and centrifuged. The supernatant was chromatographed over a column of Q-sepharose, and eluted with various concentrations of NaCl. In the following order, PDE subtypes 1, 5, 2, 4 from lungs, and 3 from hearts were separated. The IC 50 values of 3-O-Methylquercetin on these isozymes were 31.9, 86.9, 18.6, 28.5 and 1.6 microM, respectively. 3-O-Methylquercetin (10-100 microM) non-competitively inhibited PDE2, but competitively inhibited PDE4. 3-O-Methylquercetin (1-10 microM) also competitively inhibited PDE3. However, 3-O-Methylquercetin (10-100 microM) did not competitively inhibit PDE1 and 5, although it had a tendency to competitively inhibit PDE1 at concentrations of 10 - 30 microM. The present results showed that K i value of 3-O-Methylquercetin was similar to that of milrinone in PDE3, and was not significantly different from that of Ro 20 - 1724 in PDE4, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, 3-O-Methylquercetin was revealed to be a selective and competitive PDE3/PDE4 inhibitor, although its inhibitory effect on PDE4 was not potent. Therefore, 3-O-Methylquercetin may have a potential in the treatment of asthma beside its antiviral activity.
Planta Med. 2004 Dec;70(12):1123-7.
Suppressive effects of 3-O-methylquercetin on ovalbumin-induced airway hyperresponsiveness.[Pubmed:
15643544]
Rhamnus nakaharai Hayata (Rhamnaceae) has been used as a folk medicine in Taiwan for treating constipation, inflammation, tumors, and asthma. 3-O-Methylquercetin (3-MQ), a main constituent of the plant, has been reported to inhibit total cAMP- and cGMP-phosphodiesterase (PDE) of guinea pig trachealis at low concentrations. 3-O-Methylquercetin has been also reported to more selectively inhibit PDE3 than PDE4 with a low K(m) value.
Therefore we were interested in investigating its suppressive effects on ovalbumin (OVA)-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in vivo and in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
3-O-Methylquercetin (3-30 micromol/kg, i. p.) significantly suppressed the enhanced pause (Penh) value induced by aerosolized methacholine (50 mg/mL) in sensitized mice after secondary allergen challenge. 3-O-Methylquercetin (3-30 micromol/kg, i. p.) also significantly suppressed total inflammatory cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and eosinophils, but not lymphocytes. In addition, 3-MQ (3 micromol/kg, i. p.) significantly decreased the secretion of TNF-alpha, and at the highest dose (30 micromol/kg, i. p.) even decreased the secretions of IL-4, IL-5, and TNF-alpha. 3-O-Methylquercetin (1-10 microM) as well as Ro 20-1724 (3-30 microM), a selective PDE4 inhibitor, significantly attenuated OVA (100 microg/mL)-induced contractions. 3-O-Methylquercetin (30 microM) as well as milrinone (1-10 microM), a selective PDE3 inhibitor, significantly enhanced baseline contractions in isolated guinea pig left and right atria. However, neither 3-O-Methylquercetin nor milrinone significantly affected baseline beating rate in the right atria. 3-O-Methylquercetin (3-30 micromol/kg, i. p.) did not significantly affect systolic pressure in conscious mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, 3-O-Methylquercetin has both anti-inflammatory and bronchodilating effects, and has the potential for use in the treatment of asthma at a dose without affecting blood pressure.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2006 Jan 16;103(2):281-7.
Mechanisms of suppression of nitric oxide production by 3-O-methylquercetin in RAW 264.7 cells.[Pubmed:
16213685]
Rhamnus nakaharai Hayata (Rhamnaceae) is used as a folk medicine in Taiwan for treating constipation, inflammation, tumors, and asthma. 3-O-Methylquercetin (3-MQ), a main constituent of the plant, has been reported to have potential for use in the treatment of asthma. The mechanisms of anti-inflammation of 3-O-Methylquercetin are still unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Nitric oxide (NO) production induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) through iNOS expression in RAW 264.7 cells, a mouse macrophage cell line, may reflect the degree of inflammation and may provide a measure for assessing the effect of drugs on the inflammatory process. Therefore, we were interested in investigating the mechanisms of suppression of NO production by 3-O-Methylquercetin in RAW 264.7 cells. 3-O-Methylquercetin (1-10 microM) concentration-dependently inhibited LPS (100 ng/mL)-induced NO production in RAW 264.7 cells. The IC(50) value was calculated to be 4.23 microM. 3-O-Methylquercetin(1-10 microM) significantly and concentration-dependently inhibited LPS (100 ng/mL)-induced iNOS protein and mRNA expressions in cells. The IC(50) values were calculated to be 4.36 and 6.53 microM, respectively.
There was no significant difference among these three IC(50) values of 3-O-Methylquercetin.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, 3-O-Methylquercetinmay exert its anti-inflammatory effect through the inhibition of iNOS DNA transcription.