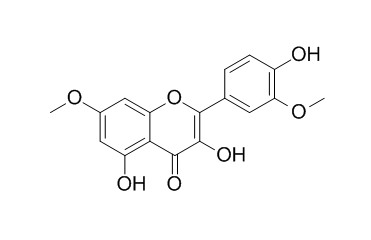
Rhamnazin
Rhamnazin, a novel inhibitor of VEGFR2 signaling with potent antiangiogenic activity and antitumor efficacy, it attenuates inflammation and inhibits alkali burn-induced corneal neovascularization in rats. Rhamnazin has anti-oxidative, and anti-inflammatry activities, it also shows apoptogenic activity via mitochondrial pathway and associated with activation of caspase-9 and -3.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Pak J Pharm Sci.2023, 36(1):51-57.
Phytomedicine2022, 104:154318
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2024, 251:116444.
Mol Med Rep.2015, 12(5):7789-95
J Food Biochem.2019, 43(9):e12970
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2021, 2021:8707280.
The Korea Journal of Herbology2020, 35(3):33-45.
Front Pharmacol.2022, 13:806869.
Biotechnol Bioeng.2020, 117(7):2198-2208.
Biomol Ther (Seoul).2020, 28(6):542-548.
Related and Featured Products
Ukr Biochem J, 2015, 87(6):122-128.
Rhamnazin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human Jurkat leukemia cells in vitro.[Reference:
WebLink]
Antiproliferative and apoptogenic effects of Rhamnazin, a dimethoxylated derivative of quercetin, were studied in human acute lymphoblastic leukemia Jurkat cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The cytotoxicity and apoptogenic activity of Rhamnazin in vitro are inferior to that of quercetin. The apoptogenic activity of Rhamnazin is realized via mitochondrial pathway and associated with activation of caspase-9 and -3. The additive apoptogenic effect of Rhamnazin and suboptimal doses of etoposide, a DNA topoisomerase II inhibitor, is demonstrated.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, methylation of quercetin modifies its biological effects considerably.
Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications, 2015, 458(4):913-919.
Rhamnazin, a novel inhibitor of VEGFR2 signaling with potent antiangiogenic activity and antitumor efficacy.[Reference:
WebLink]
Anti-angiogenesis targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) has emerged as an important tool for cancer therapy. The identification of new drugs from natural products has a long and successful history.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we described a novel VEGFR2 inhibitor, Rhamnazin, which inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth. Rhamnazin significantly inhibited proliferation, migration and tube formation of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro as well as inhibited sprouts formation of rat aorta ring. In addition, it inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR2 and its downstream signaling regulator in HUVECs. Moreover, Rhamnazin could directly inhibit proliferation of breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 in vitro and in vivo. Oral administration of Rhamnazin at a dose of 200 mg/kg/day could markedly inhibited human tumor xenograft growth and decreased microvessel densities (MVD) in tumor sections.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these preclinical evaluations suggest that Rhamnazin inhibits angiogenesis and may be a promising anticancer drug candidate.
Journal of Nutrition & Health, 2016, 49(5):288-294.
Rhamnazin inhibits LPS-induced inflammation and ROS/RNS in raw macrophages.[Reference:
WebLink]
The aim of this work was to investigate the beneficial effects of Rhamnazin against inflammation, reactive oxygen species (ROS)/reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and anti-oxidative activity in murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To examine the beneficial properties of Rhamnazin on inflammation, ROS/ RNS, and anti-oxidative activity in the murine macrophage RAW264.7 cell model, several key markers, including COX and 5-LO activities, NO•, ONOO⁻, total reactive species formation, lipid peroxidation, •O2 levels, and catalase activity were estimated. Results show that Rhamnazin was protective against LPS-induced cytotoxicity in macrophage cells. The underlying action of Rhamnazin might be through modulation of ROS/RNS and anti-oxidative activity through regulation of total reactive species production, lipid peroxidation, catalase activity, and •O2, NO•, and ONOO• levels. In addition, Rhamnazin down-regulated the activities of pro-inflammatory COX and 5-LO.
CONCLUSIONS:
The plausible action by which Rhamnazin renders its protective effects in macrophage cells is likely due to its capability to regulate LPS-induced inflammation, ROS/ RNS, and anti-oxidative activity.
Rsc Advances, 2018, 8(47):26696-26706.
Rhamnazin attenuates inflammation and inhibits alkali burn-induced corneal neovascularization in rats.[Reference:
WebLink]
The purpose of our study was to determine whether Rhamnazin inhibits corneal neovascularization in the rat alkali burn model, and alleviates the inflammatory response of the cornea.
Rhamnazin inhibited the proliferation of HUVEC cells in a dose-dependent manner, and it also inhibited the migration and luminal formation of HUVEC cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
20 μM Rhamnazin eye drops were applied to an animal model of corneal alkali burn neovascularization 4 times a day for 14 days. The corneal neovascularization in the Rhamnazin group was obviously less than that in the PBS control group. In the Rhamnazin group, the inflammatory index of the cornea decreased gradually over time, whereas the inflammatory index of the PBS group decreased only slightly with time. The corneal CNV area in the PBS group was significantly larger than that in the Rhamnazin group. The expression level of VEGF protein of the Rhamnazin group was lower than that in the PBS group, and the expression level of PEDF was significantly higher than that of the PBS group. Rhamnazin downregulated the expression of VEGFR2 protein and decreased the expression levels of p-STAT3, p-MAPK and p-Akt proteins.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study provides a new idea for the study of the molecular mechanism of corneal neovascularization.