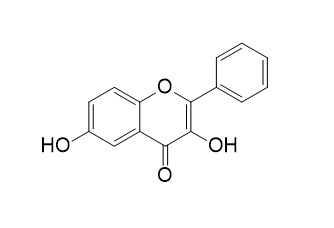
3,6-Dihydroxyflavone
3,6-Dihydroxyflavone is an anti-cancer agent, it induces apoptosis in leukemia HL-60 cell via reactive oxygen species-mediated p38 MAPK/JNK pathway. 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone is a potent agonist of the human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (hPPAR) with cytotoxic effects on human cervical cancer cells. 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone exhibits antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria through inhibition of β-ketoacyl acyl carrier protein synthase III (KAS III).
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Journal of Apiculture2019, 34(2):131-136
J Cell Mol Med.2023, jcmm.18071.
J Cell Mol Med.2020, 24(21):12308-12317.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021, 14(10):986.
Phytomedicine.2021, 83:153483.
BMC Microbiol.2019, 19(1):78
Plant Physiol Biochem.2023, 201:107795.
J Ethnopharmacol.2024, 318(Pt B):116961.
J Mol Med (Berl).2018, 96(7):661-672
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020, 21(4):935-941.
Related and Featured Products
Molecules, 2014, 19(9):13200-13211.
Cytotoxic activity of 3,6-dihydroxyflavone in human cervical cancer cells and its therapeutic effect on c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibition.[Pubmed:
25165860]
Previously we have shown that 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone (3,6-DHF) is a potent agonist of the human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (hPPAR) with cytotoxic effects on human cervical cancer cells. To date, the mechanisms by which 3,6-DHF exerts its antitumor effects on cervical cells have not been clearly defined.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we demonstrated that 3,6-DHF exhibits a novel antitumor activity against HeLa cells with IC50 values of 25 μM and 9.8 μM after 24 h and 48 h, respectively. We also showed that the anticancer effects of 3,6-DHF are mediated via the toll-like receptor (TLR) 4/CD14, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), Jun-N terminal kinase (JNK), extracellular-signaling regulated kinase (ERK), and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 pathways in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. We found that 3,6-DHF showed a similar IC50 (113 nM) value to that of the JNK inhibitor, SP600125 (IC50 = 118 nM) in a JNK1 kinase assay. Binding studies revealed that 3,6-DHF had a strong binding affinity to JNK1 (1.996 × 105 M-1) and that the 6-OH and the carbonyl oxygen of the C ring of 3,6-DHF participated in hydrogen bonding interactions with the carbonyl oxygen and the amide proton of Met111, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, 3,6-DHF may be a candidate inhibitor of JNKs, with potent anticancer effects.
Bulletin- Korean Chemical Society, 2011, 32329(9).
Antimicrobial Flavonoid, 3, 6-Dihydroxyflavone, Have Dual Inhibitory Activity against KAS III and KAS I.[Reference:
WebLink]
Three types of β-ketoacyl acyl carrier protein synthase (KAS) are important for overcoming the bacterial resistance problem. Recently, we reported the discovery of a antimicrobial flavonoid, YKAF01 (3,6-Dihydroxyflavone), which exhibits antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria through inhibition of β-ketoacyl acyl carrier protein synthase III (KAS III).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this report, we suggested that YKAF01 can be an inhibitor β-ketoacyl acyl carrier protein synthase I (KAS I) with dual inhibitory activity for KAS I as well as KAS III. KAS I is related to the elongation of unsaturated fatty acids in bacterial fatty acid synthesis and can be a good therapeutic target of designing novel antibiotics. We performed docking study of Escherichia coli KAS I (ecKAS I) and YKAF01, and determined their binding model. YKAF01 binds to KAS I with high binding affinity (2.12 × 10 6) and exhibited an antimicrobial activity against the multidrug-resistant E. coli with minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 512 μg/mL.
CONCLUSIONS:
Further optimization of this compound will be carried out to improve its antimicrobial activity and membrane permeability against bacterial cell membrane.
European Journal of Pharmacology, 2010, 648(1-3):31-38.
3,6-Dihydroxyflavone induces apoptosis in leukemia HL-60 cell via reactive oxygen species-mediated p38 MAPK/JNK pathway.[Pubmed:
20840847]
We have previously selected a promising anti-cancer agent 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone by pharmacodynamic experiments.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we investigated its pro-apoptosis mechanisms in leukemia HL-60 cell. Our data revealed that 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone dose- and time-dependently decreases cell viability and induces apoptosis by activating caspase cascade, cleaving poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). The anti-cancer effects of 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone are associated with the generation of reactive oxygen species, the altered glutathione-redox balance as significantly decreased glutathione (GSH) and its ratio to gluthatione disulfide (GSSG), and the accumulation of lipid peroxidation indicator malondialdehyde. Addition of antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) prevents the elevation of reactive oxygen species induced by 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone and partially suppresses the cytotoxic effects. Furthermore, 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone reduces cell membrane fluidity and induces the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone was also found to modulate the activities of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family members, which includes increased protein kinase of 38 kDa (p38), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and decreased extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation. The effect of 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone on MAPKs pathway could be abrogated by co-treatment with NAC.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taking together, our data suggested that 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone increases intracellular oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, thereby affecting the physical and functional properties of plasma membrane, as well as MAPKs signal pathway, which are likely to play a role in the 3,6-Dihydroxyflavone-induced HL-60 cell cytotoxicities.