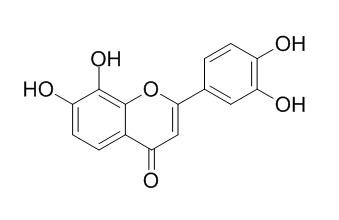
3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone
3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone loss and may therefore be considered a promising drug candidate for treating or preventing bone-lytic diseases. 3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone exhibits antibacterial activity against S. mutans.
It can absorb UV light and form photooxidation derivatives.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025, 417(17):3879-3892.
Expert Opin Ther Targets.2024, :1-11.
Reprod Toxicol.2020, 96:1-10.
Am J Chin Med.2022, 1-20.
Biofactors.2018, 44(2):168-179
Legume Science2021, 3(4): e101.
Aquaculture2019, 510:392-399
Plant J.2021, 107(6):1711-1723.
J Agric Food Chem.2024, 72(15):8784-8797.
J Med Food.2016, 19(12):1155-1165
Related and Featured Products
Die Pharmazie, 01 Mar 2017, 72(3):161-166.
3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption.[Reference:
WebLink]
Osteoclasts, which are specialized bone multinuclear cells, are responsible for bone lytic diseases such as osteoporosis. 3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone is a flavonoid from Acacia confusa.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we found that 3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone markedly inhibited receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclastic differentiation from mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs). 3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone also reduced the mRNA expression levels of osteoclastic marker genes including the calcitonin receptor (CTR) and cathepsin K. In addition, 3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone decreased the bone resorption activity of osteoclasts on dentin slices. We found that 3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone inhibited RANKL-induced expression of c-Fos and nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 (NFATc1), a key transcription factor of osteoclast differentiation. Furthermore, ectopic overexpression of a constitutively active form of NFATc1 completely rescued the anti-osteoclastogenic effect of 3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone, suggesting that the anti-osteoclastogenic effect was mainly attributed to the reduction in NFATc1 expression.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our data suggest that 3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone loss and may therefore be considered a promising drug candidate for treating or preventing bone-lytic diseases.
Archives of Pharmacal Research, 2013, 36(6):723-730.
Antibacterial substances fromAlbizia myriophyllawood against cariogenicStreptococcus mutans.[Reference:
WebLink]
Albizia myriophylla has been used for long by Thai traditional healers as an important ingredient herb in Thai herbal formulas for caries.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, three flavonoids lupinifolin (6), 8-methoxy-7,3',4'-trihydroxyflavone (7), and 7,8,3',4'-tetrahydroxyflavone (3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone,8), a triterpenoid lupeol (3) as well as four sterols β-sitosterone (1), stigmasta-5,22-dien-3-one (2), β-sitosterol (4), and stigmasterol (5) were isolated from A. myriophylla wood. The antibacterial activity of these compounds against Streptococcus mutans ATCC 25175 was performed using broth microdilution method. All compounds exhibited antibacterial activity against S. mutans with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) ranging from 1-256 and 2-256 μg/ml, respectively. Among the isolated compounds, lupinifolin (6) was found to be the most potent with MIC and MBC of 1 and 2 μg/ml, respectively. Lupinifolin (6) also showed a strong activity against ten clinical isolates of S. mutans with MIC and MBC ranging from 0.25-2 and 0.5-8 μg/ml, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results reported the bioactive ingredients of A. myriophylla which support its ethnomedical claims as well. Lupinifolin (6) may have a potential to be a natural anticariogenic agent.
Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2014, 105(JUL.):42-47.
Study on inhibition mechanisms of light-induced wood radicals by Acacia confusa heartwood extracts.[Reference:
WebLink]
The aim of this study was to investigate the inhibition mechanisms of light-induced wood radicals by Acacia confusa heartwood extracts (AcE).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Wood radical scavenging analysis was determined by ESR spectroscopy. The results obtained demonstrated that wood radicals could be inhibited through UV absorption of AcE. According to results of AcE photooxidation derivative analyses detected by HPLC–DAD, HPLC–MS/MS and FTIR spectroscopy, o-quinones, peroxides and other oxidation derivatives were yielded from flavonols (such as melanoxetin and transilitin) in AcE; okanin (chalcone) might be formed from 7,8,3′,4′-tetrahydroxyflavanone (3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone ,flavanone); 7,8,3′,4′-tetrahydroxyflavone and 7,3′,4′-trihydroxyflavone (flavones) would transform to flavanone. On the basis of GPC analysis results, proanthocyanidins and derivatives of higher molecular weight might be polymerized from melacacidin (flavan-3,4-diol).
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results clearly demonstrated that A. confusa heartwood extract can absorb UV light and form photooxidation derivatives. Accordingly, wood radicals induced by UV light were inhibited and consequently wood photodegradation was retarded.