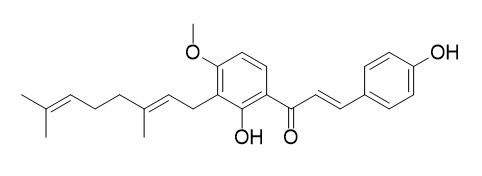
Xanthoangelol F
Xanthoangelol F showed strong PTP1B inhibitory effect with the IC50 values of 1.67 μg/mL. It inhibited phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction through endothelium-dependent production of EDRF/NO and/or through the reduction of the [Ca2+]i elevation induced by phenylephrine.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules. 2013, 18(11):14105-21
Biomed Pharmacother.2022, 156:113929.
Universitat Stuttgart2022, opus-12200.
Mol Med Rep.2015, 12(5):7789-95
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2017, 2017:6360836
Front Neurosci.2019, 13:1091
J Sep Sci.2019, 42(21):3352-3362
Molecules.2016, 21(10)
Agronomy2023, 13(9), 2410.
Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology2023, j.synbio.
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 2015 Oct 23;78(10):2481-7
Chalcones from Angelica keiskei: Evaluation of Their Heat Shock Protein Inducing Activities.[Pubmed:
26431394]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Five new chalcones, 4,2',4'-trihydroxy-3'-[(2E,5E)-7-methoxy-3,7-dimethyl-2,5-octadienyl]chalcone (1), (±)-4,2',4'-trihydroxy-3'-[(2E)-6-hydroxy-7-methoxy-3,7-dimethyl-2-octenyl]chalcone (2), 4,2',4'-trihydroxy-3'-[(2E)-3-methyl-5-(1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)-2-pentenyl]chalcone (3), 2',3'-furano-4-hydroxy-4'-methoxychalcone (4), and (±)-4-hydroxy-2',3'-(2,3-dihydro-2-methoxyfurano)-4'-methoxychalcone (5), were isolated from the aerial parts of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi together with eight known chalcones, 6-13, which were identified as (±)-4,2',4'-trihydroxy-3'-[(6E)-2-hydroxy-7-methyl-3-methylene-6-octenyl]chalcone (6), xanthoangelol (7), Xanthoangelol F (8), xanthoangelol G (9), 4-hydroxyderricin (10), xanthoangelol D (11), xanthoangelol E (12), and xanthoangelol H (13), respectively. Chalcones 1-13 were evaluated for their promoter activity on heat shock protein 25 (hsp25, murine form of human hsp27). Compounds 1 and 6 activated the hsp25 promoter by 21.9- and 29.2-fold of untreated control at 10 μM, respectively. Further protein expression patterns of heat shock factor 1 (HSF1), HSP70, and HSP27 by 1 and 6 were examined. Compound 6 increased the expression of HSF1, HSP70, and HSP27 by 4.3-, 1.5-, and 4.6-fold of untreated control, respectively, without any significant cellular cytotoxicities, whereas 1 did not induce any expression of these proteins.
CONCLUSIONS:
As a result, 6 seems to be a prospective HSP inducer.
Planta Med. 2001 Apr;67(3):230-5.
Artery relaxation by chalcones isolated from the roots of Angelica keiskei.[Pubmed:
11345693 ]
An EtOAc-soluble fraction from a 50% EtOH extract of the roots of Angelica keiskei inhibited phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction in rat aortic rings, while an EtOAc-insoluble fraction had no effect at 100 micrograms/ml.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Five active substances isolated from the EtOAc-soluble fraction of the roots were identified as xanthoangelol (1), 4-hydroxyderricin (2), and xanthoangelols B (3), E (4) and F (5), which inhibited phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction at the concentrations of 10-100 micrograms/ml. It was found that xanthoangelol (1), 4-hydroxyderricin (2), and xanthoangelol E (4) and Xanthoangelol F (5) inhibited the phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction through endothelium-dependent endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) production and/or nitric oxide (NO) production. Among the five chalcones, xanthoangelol B (3) inhibited the phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction most strongly, and it inhibited the phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction in the presence or absence of endothelium and in the presence or absence of NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA) (an NO synthetase inhibitor). Furthermore, 4-hydroxyderricin (2) and xanthoangelol B (3) at concentrations of 10-100 micrograms/ml concentration-dependently inhibited the elevation of intracellular free calcium [Ca2+]i induced by phenylephrine.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrate that compounds 1, 2, 4 and 5 inhibit phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction through endothelium-dependent production of EDRF/NO and/or through the reduction of the [Ca2+]i elevation induced by phenylephrine. On the other hand, the inhibitory mechanism of compound 3 on phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction might involve the direct inhibition of smooth muscle functions through the reduction of [Ca2+]i elevation without affecting EDRF/NO production.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015;25(10):2028-32.
PTP1B inhibitors from stems of Angelica keiskei (Ashitaba).[Pubmed:
25891102 ]
Three new chalcones, xanthoangelols K-M (1-3), together with 19 known compounds were isolated from the stems of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi, a well-known rejuvenated and anti-diabetic plant originated from Japan.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structures of compounds 1-3 were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic data and Mosher's method. All compounds were evaluated for their inhibitory activity against protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B). Among them, six chalcones, xanthoangelol K (1), xanthoangelol (4), Xanthoangelol F (5), 4-hydroxyderricin (6), xanthoangelol D (7), xanthoangelol E (8), and a coumarin, methoxsalen (17), showed strong PTP1B inhibitory effect with IC50 values of 0.82, 1.97, 1.67, 2.47, 3.97, 1.43, and 2.53μg/mL, respectively. A kinetic study revealed that compound 1 inhibited PTP1B with characteristics typical of a competitive inhibitor.
CONCLUSIONS:
Molecular docking simulations elucidated that ring B of 1 may anchor in a pocket of PTP1B and the molecule is stabilized by hydrogen bonds with Arg47, Asp48, and π-π interaction with Phe182 of PTP1B.