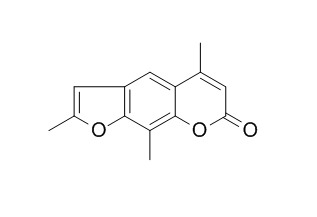
Trioxsalen
Trioxsalen, a toxic component, has tumorigenic property. Trioxsalen derivative 3 can significantly inhibit LOX, with IC(50) 9.4 muM, it has analgesic and anti‐inflammatory effects.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(8):1300.
J Am Soc Mass Spectrom.2021, 32(5):1205-1214.
Nutrients.2023, 15(4):954.
ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci.2022, 5,7,479-490
Biosci Rep.2020, 40(8):BSR20201219.
Processes2021, 9(5),831.
Russian J. Bioorganic Chemistry2024, 50:2897-2903.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2022, 2022:3483511
Pharmaceutics2022, 14(2),376.
Food Res Int.2019, 123:125-134
Related and Featured Products
Journal of Enzyme Inhibition & Medicinal Chemistry, 2009, 24(6):1351-1356.
Trioxsalen derivatives with lipoxygenase inhibitory activity.[Reference:
WebLink]
Trioxsalen (TRX) is a 4,5',8-trimethylated psoralen analog presenting interesting biological activities when irradiated with UVA light.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A series of TRX derivatives, which where obtained by its chemical modification and incorporation of a variety of unsaturated functions at position 4' of the psoralen ring-system, were evaluated for their antioxidant activity and their inhibitory activity on soybean lipoxygenase (LOX) and lipid peroxidation. The reducing properties of the compounds were evaluated using the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging assay and found to be very low, in the range 0-14%, with the exception of the hydroxamic acid 6 which showed almost identical activity to BHT. TRX derivative 3 significantly inhibited LOX, with IC(50) 9.4 muM. With the exception of TRX, all tested analogs inhibited lipid peroxidation in the range of 35-91%.
CONCLUSIONS:
The most potent compound, namely TRX derivative 3, was studied for its anti-inflammatory activity in vivo on rat paw edema induced by carrageenan, and was found to be of almost identical activity to indomethacin. The results of the biological tests are discussed in terms of structural characteristics.
Archives of Dermatology, 1973, 107(3):413-414.
Ineffectiveness of Trioxsalen as an Oral Photosensitizer.[Reference:
WebLink]
The phototoxicity of methoxsalen (8-methoxypsoralen [8-MOP]) and Trioxsalen (trimethylpsoralen) has been compared in humans.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Topically, both drugs evoked equivalently intense reactions at low concentrations after exposure to long ultra-violet rays from the filtered xenon lamp. Whereas 60 mg of orally administered methoxsalen produced sharp reactions with occasional blistering, 200 mg of Trioxsalen had no effect with long ultraviolet rays. Mild phototoxic responses were occasionally obtained with one-hour sunlight exposures after administration of 200 mg, but not less, of Trioxsalen.
CONCLUSIONS:
Since the dose of Trioxsalen is usually not more than 20 mg, the claims of therapeutic value in vitiligo probably reflect observer error.
Archives for Dermatological Research, 1986, 278(5):347-351.
The carcinogenic properties of topical PUVA. A lifelong study in mice.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The tumorigenic properties of topical methoxsalen (8-MOP) and Trioxsalen (TMP) plus ultraviolet light A (UVA) were studied in NMRI female mice. The animals were treated three times weekly for 9 months, and followed up for 18 months. Acetonic solutions of TMP (0.1 mg in 0.2 ml) and 8-MOP (0.6 mg in 0.2 ml) were applied to the shaved back skin of the mice and irradiated with UVA. The doses needed to elicit equivalent phototoxic effects were 0.29 J/cm 2 in the TMP group and 1.09 J/cm 2 in the 8-MOP group. Papillomas, keratoacanthomas, and squamous cell carcinomas developed in the 8-MOP group only, and the first tumor was seen at 10 months after the beginning of the study.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggest that the carcinogenicity of these two modes of photochemotherapy may differ.
Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture, 2007, 87(11):2152-2163.
Analysis of furanocoumarins in vegetables (Apiaceae) and citrus fruits (Rutaceae).[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Several alternative approaches applicable for the analysis of furanocoumarins, toxic components occurring in some fruits and vegetables representing both Apiaceae and Rutaceae families, were tested in our study. Limits of detection (LODs) for angelicin, psoralen, bergapten, xanthotoxin, Trioxsalen, isopimpinellin, sphondin, pimpinellin and isobergapten obtained by GC/MS (SIM) were in the range 0.01-0.08 µg g-1. Slightly higher LODs (0.02-0.20 µg g-1) were achieved by LC/MS-MS. The latter is the only alternative for analysis of bergamottin (LOD = 0.01 µg g-1) in citrus fruits because this furanocoumarin is unstable under GC conditions. Regardless of the determination step used, the repeatability of the measurements (expressed as RSD) did not exceed 10%.
CONCLUSIONS:
As shown in our study the levels of furanocoumarins in celery, celeriac, parsnip, carrot, lemon and other foods obtained at a retail market varied over a wide range; the highest contents were determined in parsnip, while the levels of these toxins in carrots and citrus pulps were relatively low.