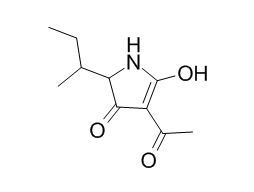
Tenuazonic acid
Tenuazonic acid, an active component in the A. alternata toxin.Tenuazonic acid exhibits a strong inhibition in photosystem II (PSII) activity, it causes cell necrosis of host-plants by oxidative damage from chloroplast-mediated ROS eruption, and enhances the plant's resistances against rose aphids.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Plant Physiol Biochem.2023, 203:108073.
Allergol Immunopathol (Madr).2022, 1;50(4):23-30.
J Food Biochem.2021, 45(7):e13774.
Front Plant Sci.2022, 13:982771.
Journal of Herbal Medicine2024, 48:100950
J Colloid Interface Sci.2024, 662:760-773.
Front Cell Dev Biol.2021, 9:638174.
Sains Malaysiana2022, 51(4):1143-1154
Foods.2021, 10(11):2754.
Foods.2023, 12(19):3647.
Related and Featured Products
J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015 Apr;16(4):264-74.
Alternaria toxin-induced resistance in rose plants against rose aphid (Macrosiphum rosivorum): effect of tenuazonic acid.[Pubmed:
25845360]
Many different types of toxins are produced by the fungus, Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissler. Little is known, however, regarding the influence of these toxins on insects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we investigated the toxin-induced inhibitory effects of the toxin produced by A. alternata on the rose aphid, Macrosiphum rosivorum, when the toxin was applied to leaves of the rose, Rosa chinensis. The results demonstrated that the purified crude toxin was non-harmful to rose plants and rose aphids, but had an intensive inhibitory effect on the multiplication of aphids. The inhibitory index against rose aphids reached 87.99% when rose plants were sprayed with the toxin solution at a low concentration. Further results from bioassays with aphids and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analyses demonstrated that Tenuazonic acid (TeA) was one of the most important resistance-related active components in the crude toxin. The content of TeA was 0.1199% in the crude toxin under the HPLC method. Similar to the crude toxin, the inhibitory index of pure TeA reached 83.60% 15 d after the rose plants were sprayed with pure TeA solution at the lower concentration of 0.060 μg/ml, while the contents of residual TeA on the surface and in the inner portion of the rose plants were only 0.04 and 0.00 ng/g fresh weight of TeA-treated rose twigs, respectively, 7 d after the treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results show that TeA, an active component in the A. alternata toxin, can induce the indirect plant-mediated responses in rose plants to intensively enhance the plant's resistances against rose aphids, and the results are very helpful to understand the plant-mediated interaction between fungi and insects on their shared host plants.
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013 May;405(12):4149-58.
Determination of tenuazonic acid in human urine by means of a stable isotope dilution assay.[Pubmed:
23397093]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The content of Tenuazonic acid in human urine was determined by a stable isotope dilution assay (SIDA) that was recently developed for the analysis of food commodities and extensively re-validated for urine matrix in this study. Linearity of the response curve was proven between molar ratios n(labeled standard)/n(analyte) of 0.02-100. The limits of detection and determination were 0.2 and 0.6 μg/L, respectively. The mean recovery of the stable isotope dilution assay was 102 ± 3 % in the range between 1.0 and 100 μg/L. Interassay precision was 6.7 % (relative standard deviation of three triplicate analyses of a human urine sample during 3 weeks). The method was applied to two studies dealing with urinary excretion of Tenuazonic acid: In the first study, Tenuazonic acid was quantified in the 24-h urine of six volunteers from Germany (three female, three male) in a concentration range of 1.3-17.3 μg/L or 2.3-10.3 ng/mg(-1) creatinine, respectively. In the second study, two volunteers (one female, one male) ingested 30 μg Tenuazonic acid by consumption of naturally contaminated whole meal sorghum infant cereals and tomato juice, respectively. The urinary excretion of the ingested Tenuazonic acid was 54-81 % after 6 h, depending on matrix and volunteer. After 24 h, 87-93 % of the ingested amount of Tenuazonic acid was excreted, but the fate of the remaining about 10 % is open.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, it is not possible to exclude potential health hazards for the consumer, completely.
Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014 Nov;84:10-21.
In vivo assessment of effect of phytotoxin tenuazonic acid on PSII reaction centers.[Pubmed:
25240106]
Tenuazonic acid (TeA), a phytotoxin produced by the fungus Alternaria alternata isolated from diseased croftonweed (Ageratina adenophora), exhibits a strong inhibition in photosystem II (PSII) activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In vivo chlorophyll fluorescence transients of the host plant croftonweed, show that the dominant effect of TeA is not on the primary photochemical reaction but on the biochemical reaction after QA. The most important action site of TeA is the QB site on the PSII electron-acceptor side, blocking electron transport beyond QA(-) by occupying the QB site in the D1 protein. However, TeA does not affect the antenna pigments, the energy transfer from antenna pigment molecules to reaction centers (RCs), and the oxygen-evolving complex (OEC) at the donor side of PSII. TeA severely inactivated PSII RCs. The fraction of non-QA reducing centers and non-QB reducing centers show a time- and concentration-dependent linear increase. Conversely, the amount of active QA or QB reducing centers declined sharply in a linear way.
CONCLUSIONS:
The fraction of non-QB reducing centers calculated from data of fluorescence transients is close to the number of PSII RCs with their QB site filled by TeA. An increase of the step-J level (VJ) in the OJIP fluorescence transients attributed to QA(-) accumulation due to TeA bound to the QB site is a typical characteristic response of the plants leaf with respect to TeA penetration.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Mar;1797(3):391-405.
Chloroplastic oxidative burst induced by tenuazonic acid, a natural photosynthesis inhibitor, triggers cell necrosis in Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng.[Pubmed:
20026008]
Tenuazonic acid (TeA), a nonhost-specific phytotoxin produced by Alternaria alternata, was determined to be a novel natural photosynthesis inhibitor owning several action sites in chloroplasts. To further elucidate the mode of its action, studies were conducted to assess the production and involvement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the toxic activity of Tenuazonic acid.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A series of experiments indicated that Tenuazonic acid treatment can induce chloroplast-derived ROS generation including not only (1)O(2) but also superoxide radical, H(2)O(2) and hydroxyl radicals in Eupatorium adenophorum mesophyll cells, resulting from electron leakage and charge recombination in PSII as well as thylakoid overenergization due to inhibition of the PSII electron transport beyond Q(A) and the reduction of end acceptors on the PSI acceptor side and chloroplast ATPase activity. The initial production of Tenuazonic acid-induced ROS was restricted to chloroplasts and accompanied with a certain degree of chloroplast damage.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results show that Tenuazonic acid causing cell necrosis of host-plants is a result of direct oxidative damage from chloroplast-mediated ROS eruption.